dom与bom
文档对象模型 DOM
1 DOM概述
1.1 什么是DOM
-
-
文档对象模型 是表示和操作 HTML和XML文档内容的基础API
-
文档对象模型,是W3C组织推荐的处理可扩展标志语言的标准编程接口
1.2 DOM分类
-
核心 DOM - 针对任何结构化文档的标准模型
-
XML DOM - 针对 XML 文档的标准模型
-
HTML DOM - 针对 HTML 文档的标准模型
1.3 DOM树
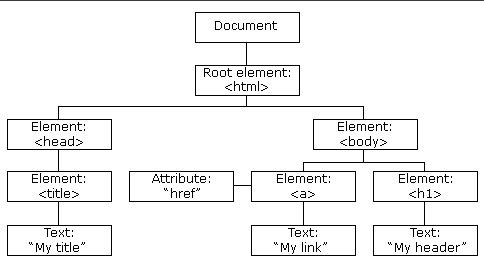
2 节点
2.1 什么是节点
// 节点分类: 6个
// document | doctype | element | text | attr | comment
2.3 节点属性
-
nodeName 节点名字
-
nodeValue 节点值
-
nodeType 节点类型
2.4 节点常规操作

var info_node = document.createAttribute("info"); // 创建 console.log(info_node.nodeName); console.log(info_node.nodeType); info_node.value = '123'; // 设置 console.log(info_node.nodeValue); sup1.setAttributeNode(info_node); // 添加

// 父级 console.log(sup.parentElement) // 子级们 console.log(sup.children); // 第一个子级 console.log(sup.firstElementChild); // 最后一个子级 console.log(sup.lastElementChild); // 上兄弟 console.log(sup.previousElementSibling); // 下兄弟 console.log(sup.nextElementSibling); // 注: 文档结构操作是可以采用连.语法 // sup.children[0].parentElement // 自己

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.show{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border: 3px solid black;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.sup{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: orange;
float: left;
}
.sub{
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: deeppink;
position: relative;
top: 40px;
left: 40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="show">
<!--<div class="sup">-->
<!--<div class="sub"></div>-->
<!--</div>-->
<!--<div class="sup2">-->
<!--<div class="sub2"></div>-->
<!--</div>-->
</div>
</body>
<script>
function randomNum(m,n) {
return parseInt(Math.random()*(n-m+1))+m;
}
function randomColor() {
var color="";
var r=randomNum(0,255);
var g=randomNum(0,255);
var b=randomNum(0,255);
color="rgb("+ r +","+ g +","+ b +")";
return color;
}
var show=document.querySelector('.show');
</script>
<script>
setInterval(function () {
let sup=document.createElement('div');
sup.className='sup';
sup.style.backgroundColor=randomColor();
let sub=document.createElement('div');
sub.className='sub';
sub.style.backgroundColor=randomColor();
sup.appendChild(sub);
if (show.children.length==0){
show.appendChild(sup);
} else {
show.insertBefore(sup,show.firstElementChild);
}
if (show.children.length>25){
show.removeChild(show.lastElementChild);
}
},1000)
</script>
</html>

// 操作步骤 // 1. 创建div(元素节点) // 2. 设置div属性(单一css | css类名 | 文本 | 子标签 | 事件 | ...) // 3. 添加到(文档结构中)指定位置 // 创建:只能由document调用 var box = document.createElement('div'); // 在body元素的最后追加一个子元素 body.appendChild(box); // 在body元素oldEle之前插入一个子元素 body.insertBefore(box, oldEle); // 从body中删除box元素,可以接受返回值,就是删除的元素 var res = body.removeChild(div); // 将body中oldEle元素替换为box,可以接受返回值,就是被替换的元素 res = bodyreplaceChild(box, oldEle); // true深拷贝,拷贝自身与内容, false浅拷贝,只拷贝自身标签 box.cloneNode()

x// ev.target通过父级的事件对象,获取具体相应区域位置的子级元素// 应用场景// 1. 父级的子元素类型不同一,采用循环绑定不方便// 2. 父级子元素较多或不确定

// BOM: Browser Object Model, 提供用户与浏览器交互的标准接口 // BOM的顶级对象为window对象, 页面中出现的其实所有对象都是window的子对象 // 重要的子对象 // document | history | location | navigator | screen // location => url信息 console.log(location); // 域名:端口号 console.log(location.host); // 域名 console.log(location.hostname); // 端口号 console.log(location.port); // 查询信息 console.log(location.search); // history history.back() | history.forward() | history.go(-num | num) // navigator console.log(navigator.userAgent) // Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/70.0.3538.77 Safari/537.36






