开发脚本自动部署及监控
1.编写脚本自动部署反向代理、web、nfs;
要求:
I、部署nginx反向代理三个web服务,调度算法使用加权轮询;
II、所有web服务使用共享存储nfs,保证所有web都对其有读写权限,保证数据一致性;
(注:由于受限于机器内存,这里将将共享存储设备与反向代理合成一台机器)
步骤一:编写安装nginx的shell文件。
vim nginx.sh
#!/bin/sh systemctl stop firewalld setenforce 0 iptables -L yum install epel* -y if [ $? -ne 0 ] then echo "epel installing wrong" exit fi yum install nginx -y if [ $? -ne 0 ] then echo "nginx installing wrong" exit fi ip_addr=`ifconfig | awk 'NR==2{print $2}'` if [ "$ip_addr" = "192.168.0.113" ] then msg='upstream web_test{server 192.168.0.108 weight=3;server 192.168.0.106;server 192.168.0.107;}' sed -ri "/^http/a $msg" /etc/nginx/nginx.conf sed -ri '/^ *location \/ \{$/a proxy_pass http://web_test\;' /etc/nginx/nginx.conf else mkdir /web_nfs sed -ri '/^ *location \/ \{$/a root \/web_nfs\;' /etc/nginx/nginx.conf fi systemctl start nginx
步骤二:编写安装nfs的shell文件
vim nfs.sh
#!/bin/bash systemctl stop firewalld setenforce 0 iptables -L yum install rpcbind nfs-utils -y if [ $? -ne 0 ] then echo "installing not sucess" exit fi ip_addr=`ifconfig | awk 'NR==2{print $2}'` if [ "$ip_addr" = "192.168.0.113" ] then mkdir /gongxiang touch /gongxiang/a.txt echo "/gongxiang 192.168.0.0/24(rw,sync,fsid=0)" > /etc/exports systemctl start rpcbind.service systemctl start nfs-server.service chmod -R 777 /gongxiang else systemctl start rpcbind.service systemctl start nfs-server.service mount -t nfs 192.16.0.113:/gongxiang /web_nfs fi
步骤三:将这两个shell安装在这四台机器上(注意安装之前添加可执行权限,可通过scp 目录 ip:/目录 的方法传输shell脚本)。
chmod +x nginx.sh chmod +x nfs.sh
步骤四:可在任意一台web机上进行“增删改查”共享目录下的任何文件,并通过代理机的ip加上共享存储端的共享文件在浏览器上进行访问。
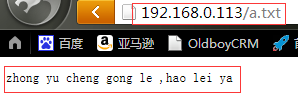
我们在web3上修改共享目录下a.txt
cd /web_nfs echo " zhong yu cheng gong le , hao lei ya " > a.txt
步骤五:在浏览器中通过代理机的ip进行访问。
2.编写监控脚本,监控集群内所有服务存活状态,内存、磁盘剩余率检测,异常则发送报警邮件
步骤一:准备发送邮件的工具(参考http://www.cnblogs.com/linhaifeng/p/6602149.html,利用Python语言编写第三方客户端的登陆程序。)
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import sys import smtplib import email.mime.multipart import email.mime.text server = 'smtp.163.com' port = '25' def sendmail(server,port,user,pwd,msg): smtp = smtplib.SMTP() smtp.connect(server,port) smtp.login(user, pwd) smtp.sendmail(msg['from'], msg['to'], msg.as_string()) smtp.quit() print('邮件发送成功email has send out !') if __name__ == '__main__': msg = email.mime.multipart.MIMEMultipart() msg['Subject'] = 'xx大傻逼' msg['From'] = 'yangming608@163.com' msg['To'] = '18211073657@163.com' user = 'yangming608' pwd = 'yangming123' content='%s\n%s' %('\n'.join(sys.argv[1:4]),' '.join(sys.argv[4:])) #格式处>理,专门针对我们的邮件格式 txt = email.mime.text.MIMEText(content, _charset='utf-8') msg.attach(txt) sendmail(server,port,user,pwd,msg)
步骤二:将上述文件内容拷贝到/usr/bin/mail1并添加可执行权限
vim /usr/bin/mail1 chmod +x /usr/bin/mail1
步骤三:编写监控脚本文件
vim monitor.sh
#!/bin/bash function monitor_nginx(){ ps aux | grep nginx | egrep -v grep &> /dev/null if [ $? -ne 0 ] then systemctl start nginx msg="TIME:$(date +%F_%T) HOSTNAME:$(hostname) IPADDR:$(/usr/sbin/ifconfig |awk 'NR==2{print $2}') #这里ifconfig用绝对路径,否者邮件中无法获取ip地址,可在/tmp/monitor.log查看。 MSG:nginx something wrong , we have restarted it." /usr/bin/mail1 $msg fi } function monitor_nfs(){ ps aux | grep nfs | egrep -v grep &> /dev/null if [ $? -ne 0 ] then systemctl start nfs msg="TIME:$(date +%F_%T) HOSTNAME:$(hostname) IPADDR:$(/usr/sbin/ifconfig |awk 'NR==2{print $2}') MSG:nfs something wrong , we have restarted it." /usr/bin/mail1 $msg fi } mem_limit=50 disk='/dev/sda1' #需要监控的磁盘名 disk_inode_limit=50 #磁盘inode使用超过50%则报警 disk_space_limit=50 #磁盘空间使用超过50%则报警 function monitor_mem(){ mem_total=`free |awk 'NR==2{print $2}'` mem_use=`free |awk 'NR==2{print $3}'` mem_per=`echo "scale=2;$mem_use/$mem_total" |bc -l|cut -d. -f2` if [ $mem_per -gt $mem_limit ] then msg="TIME:$(date +%F_%T) HOSTNAME:$(hostname) IPADDR:$(/usr/sbin/ifconfig |awk 'NR==2{print $2}') MSG:Memory usage exceeds the limit,current value is ${mem_per}%" echo $msg /usr/bin/mail1 $msg fi } function monitor_disk_inode(){ inode_use=`df -i $disk |awk 'NR==2{print $5}' |cut -d% -f1` if [ $inode_use -gt $disk_inode_limit ] then msg="TIME:$(date +%F_%T) HOSTNAME:$(hostname) IPADDR:$(/usr/sbin/ifconfig |awk 'NR==2{print $2}') MSG:Disk inode usage exceeds the limit,current value is ${inode_use}%" echo $msg /usr/bin/mail1 $msg fi } function monitor_disk_space(){ space_use=`df $disk |awk 'NR==2{print $5}'|cut -d% -f1` if [ $space_use -gt $disk_space_limit ] then msg="TIME:$(date +%F_%T) HOSTNAME:$(hostname) IPADDR:$(/usr/sbin/ifconfig |awk 'NR==2{print $2}') MSG:Disk space usage exceeds the limit,current value is ${space_use}%" echo $msg /usr/bin/mail1 $msg fi } monitor_nginx &>> /tmp/monitor.log monitor_nfs &>> /tmp/monitor.log monitor_mem &>> /tmp/monitor.log monitor_disk_inode &>> /tmp/monitor.log monitor_disk_space &>> /tmp/monitor.log
步骤四:关闭nfs服务,运行脚本文件,可在邮箱中查看监控文件的结果。
systemctl stop nfs chmod +x monitor.sh #添加可执行权限 /monitor.sh #此脚本文件我们是在根下创建的
3.编写计划任务,定时运行监控脚本,完成监控操作
步骤一:确定计划任务(制定半小时对集群内的服务以及内存和磁盘使用率进行检测一次的计划)
crontab -e -u root
* * * * * /monitor.sh #这里为了增强演示效果,设置层一分钟,正确为*/30 * * * * /monitor.sh
步骤二:查看计划任务是否生效
tail -f /var/log/cron
步骤三:去邮箱查看是否存在报警邮件