C++学习笔记(1)
C++学习笔记(1)
泛型模板排序
template<typename T> //定义一个泛型类型T /// <summary> /// 定义一个模板方法 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> /// <param name="a"></param> /// <param name="b"></param> void mySwap(T& a, T& b) { T temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } template<class T> void mySort(T arry[], int len) { for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { int max = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < len; j++) { if (arry[max] < arry[j]) { max = j; } } if (max != i)mySwap(arry[max], arry[i]); } } template<class T> void mySort2(T arry[], int len) { for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { int min = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < len; j++) { if (arry[min] > arry[j]) { min = j; } } if (min != i)mySwap(arry[min], arry[i]); } } #include<iomanip> void test5() { char ca[] = "adkblnvg"; int len = sizeof(ca) / sizeof(ca[0]) - 1; cout << setw(20) << "排序前 " << ca << endl; mySort(ca,len); cout << setw(20) <<"从大到小排序后 " << ca << endl; mySort2(ca, len); cout << setw(20) << "从小到大排序后 " << ca << endl; cout << "----------------------------------------\n"; int ai[] = {1,5,9,6,3,4,7,2,8,0}; len = sizeof(ai) / sizeof(ai[0]) - 1; cout << setw(20) << "排序前 " ; for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) { cout << ai[i] << ","; } cout << endl; mySort(ai, len); cout << setw(20) << "从大到小排序后 " ; for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) { cout << ai[i] << ","; } cout << endl; mySort2(ai, len); cout << setw(20) << "从小到大排序后 " ; for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) { cout << ai[i] << ","; } cout << endl; }
运行结果
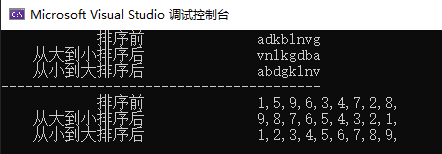
模板和泛型template
template<typename T> //定义一个泛型类型T /// <summary> /// 定义一个模板方法 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> /// <param name="a"></param> /// <param name="b"></param> void mySwap(T &a,T &b) { T temp=a; a = b; b = temp; } //模板测试 void test4() { char a = 'A',b='B'; mySwap(a, b);//隐式类型推导 cout << "a=" << a << " b=" << b << endl; string s1 = "黑马程序员"; string s2 = "C++教程从0到1入门编程"; mySwap(s1,s2);//隐式类型推导 cout << "s1=" << s1 << " s2=" << s2 << endl; double b1 = 3.14, b2 = 5.678; mySwap<double>(b1, b2);//显式指定类型<T> cout << "b1=" << b1 << " b2=" << b2 << endl; }
运行结果
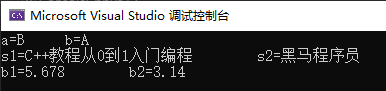
模板定义:将类型参数化,提高代码复用性;模板关键字template,
模板使用方法:1自动类型推导2显式指定类型
模板注意事项:
- 自动类型推导,必须推导出一致的数据类型T,才可以使用模板;
- 模板必须确定出T的类型,才可以使用;
-------------------------------------------------------------
参数传递的三种方式
- 值传递
- 引用传递
- 指针传递
void test14() { int a = 666, b = 888; cout << "数值交换前" << " a=" << a << " b=" << b << endl; swapv(a, b); cout<<"数值交换后" << " a=" << a << " b=" << b << endl; cout << "-----------------------------" << endl; int* pa = &a; int* pb = &b; cout << "指针交换前" << " a=" << a << " b=" << b << endl; swapp(pa,pb); cout << "指针交换后" << " a=" << a << " b=" << b << endl; cout << "-----------------------------" << endl; int& ra = a; int& rb = b; cout << "引用交换前" << " a=" << a << " b=" << b << endl; swapr(ra,rb); cout << "引用交换后" << " a=" << a << " b=" << b << endl; }
运行结果
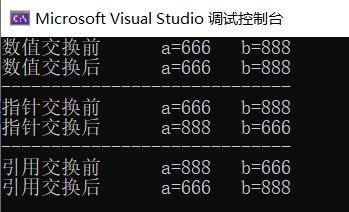
引用&测试
void test13() { int a = 100; int& b = a; cout << "b=" << b << " a=" << a << endl; cout << "(int)&b=" << (int)&b << " (int)&a=" << (int)&a << endl; //b = 100 a = 100 //(int)&b = 13629100 (int)&a = 13629100 a++; cout << "b=" << b << " a=" << a << endl; cout << "(int)&b=" << (int)&b << " (int)&a=" << (int)&a << endl; b++; cout << "b=" << b << " a=" << a << endl; cout << "(int)&b=" << (int)&b << " (int)&a=" << (int)&a << endl; int* p = &a; (*p)++; cout << "b=" << b << " a=" << a << endl; cout << "(int)&b=" << (int)&b << " (int)&a=" << (int)&a << endl; //int& c;//错误,引用不可以先声明,再赋值 //int* p1;//正确,指针可以先声明,再赋值 int c = 66; b = c; cout << "b=" << b << " a=" << a << " c=" << c << endl; cout << "(int)&b=" << (int)&b << " (int)&a=" << (int)&a << " (int)&c=" << (int)&c << endl; }
运行结果
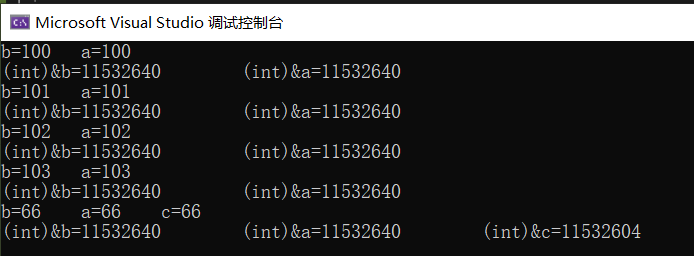
b虽然被赋值成了c,但是b的地址依然指向第一次赋值的a,只是把c的值复制过来了;
可见引用的地址不可改变,相当于指针常量int * const p;
指针常量可以更改指针所指向的值,而不可以更改指针的指向(地址);
编译器自动类型转换int--double--int
void cheers(uint n) { for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { cout << "Cheers!" << endl; } } double cube(double side) { return side * side * side; } void test12() { //编译器:首先将int类型2转换为double类型2.0,以匹配cube函数的类型要求 //编译器:将cube(2)的double类型返回值8.0转换为usigned int类型8,以匹配cheers函数的类型要求; cheers(cube(2)); }
运行结果
数组的替代选项---模板类vector、array
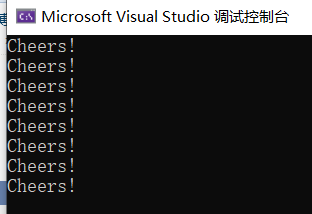
void test11() { unsigned short n = 10; const unsigned short m =10; vector<int> vi; vector<double>vd(n); array<int, 5> ai; //m必须是常量,而不能是变量,可以是一个数值10,或者const unsigned int类型的变量 array<double, m> ad = { 1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0 }; //------------------------------------- double a1[4] = { 1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4 };//静态数组,必须在定义时指定长度 //a1[-1] = -1.0;//错误,索引值超出索引范围0-3 //double a2[];//错误,静态数组必须在定义时指定长度 //double a2[4]=a1;//错误,应该使用{}初始化聚合对象 //a2 = a1;//错误,应该使用{}初始化聚合对象 vector<double> vd1={ 2.22,3.25,5.65,6.74 }; vector<double>vd2{ 2.22,3.25,5.65,6.74 };//可以省略等号进行便捷初始化 vector<double> vd3(4);//不能直接初始化 vd3= { 2.22,3.25,5.65,6.74 }; vector<double>vd4(3); vd4[0] = 1.23; vd4[1] = 3.22; cout << "vd4[0] " << vd4[0] << endl; cout << "vd4[1] " << vd4[1] << endl; cout << "vd4[2] " << vd4[2] << endl; cout << "-------------------------" << endl; vector<double> vd5 = vd4; cout << "&vd4[i] " << "&vd5[i]" << endl; cout << &vd4[0] <<" " << &vd5[0] << endl; cout << &vd4[1] << " " << &vd5[1] << endl; cout << &vd4[2] << " " << &vd5[2] << endl; array<double, 4> arr1{ 5.0,6.0,7.0,8.0 }; //array<double, 5> arr2=arr1;//错误,必须长度相等才可以赋值 //array<long double, 4>arr3 = arr1;//错误,必须类型相同才可以赋值 array<double, 4>arr4 = arr1; cout << "-------------------------" << endl; cout << "&arr4[i] " << "&arr1[i]" << endl; cout << &arr4[0] << " " << &arr1[0] << endl; cout << &arr4[1] << " " << &arr1[1] << endl; cout << &arr4[2] << " " << &arr1[2] << endl; }
运行结果
vector之间可以直接=赋值,赋值后的vector是原vector的一个拷贝;
array之间可以直接=赋值,必须满足两个条件
1、array长度必须相等;
2、元素类型必须完全相同;
赋值后的array是原array的一个拷贝;
指向指针的指针
struct years { int year; bool isLeepYear; }; void test10() { years y1, y2, y3; y1.year = 1998; //成员运算符,用变量名访问成员 years* py = &y2; py->year = 1999; //间接成员运算符,用指针访问成员 years arry[3]; //结构体数组 arry[0].year = 2003; arry[1].year = 2004; arry[2].year = 2005; cout<<"arry->year " << arry->year << endl; cout << "arry[1].year " << arry[1].year << endl; cout << "arry->year " << arry->year << endl; cout << "-------------------------"<<endl; years* arryp[3] = { &y1,&y2,&y3 };//结构体指针数组 cout << "arryp[1]->year " << arryp[1]->year << endl; //数组元素本身是指针(指向结构体), //而数组名也是指针(指向数组的第一个元素), //所以这里的数组名是指向指针的指针years** years** ppa = arryp; auto ppb = arryp; cout << "-------------------------" << endl; cout << "(*ppa)->year " << (*ppa)->year << endl; cout << "(*(ppb + 1))->year " << (*(ppb + 1))->year << endl; }
运行结果

字符串测试
typedef unsigned int uint; char* getname() { char temp[80]; cout << "Enter name (less than 80 characters)" << endl; cin >> temp; uint len = strlen(temp); cout << "len=" << len << endl; //通过一个小的内存空间来存放输入,以节省内存 char* pc = new char[len + 1]; //len表示字符串中字符的个数,而没有包含字符串结束标识"\0" //字符串所占字节数应当包含结束标识"\0",所以为len+1 //strcpy已过时弃用,这里使用更加安全的strcpy_s //第一个参数表示拷贝的目标指针,char*类型 //第二个参数表示需要拷贝的字节数,包含结束标识"\0",所以为len+1, // rsize_t类型,rsize_t类型属于size_t类型,而size_t类型属于unsigned int类型 // rsize_t类型实际就是unsigned int类型,二者等效 //第三个参数表示需要拷贝的数据源const char*类型 strcpy_s(pc, len+1, temp); return pc; } void test9() { char* name; name = getname(); cout << "name=" << name << " name at=" << (int*)name << endl; //只能释放new的资源 delete name; name = getname(); cout << "name=" << name << " name at=" << (int*)name << endl; //只能释放new的资源 delete name; }
运行结果

打开文件是否成功的测试
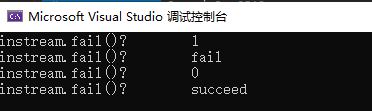
void test2() { ifstream instream; instream.open("in.dat"); string s = instream.fail() ? "fail" : "succeed"; cout <<"instream.fail()? " << instream.fail() << endl; cout << "instream.fail()? " << s << endl; if (!instream.fail())instream.close(); instream.open("inFile.dat"); s = instream.fail() ? "fail" : "succeed"; cout << "instream.fail()? " << instream.fail() << endl; cout << "instream.fail()? " << s << endl; if (!instream.fail())instream.close(); }
运行结果
文件流测试
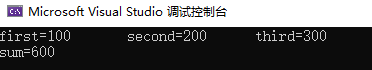
#include<iostream> #include <fstream> using namespace std; void test1() { ifstream inStream; ofstream outStream; inStream.open("inFile.dat"); outStream.open("outFile.dat"); int first, second, third; inStream >> first >> second >> third; cout << "first=" << first << " second=" << second << " third=" << third << endl; cout << "sum=" << first + second + third << endl; outStream << "first=" << first << " second=" << second << " third=" << third << endl; outStream << "sum=" << first + second + third << endl; inStream.close(); outStream.close(); }

运行结果





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律