AQS
1、Lock规范用法
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//加锁
lock.lock();
try{
doSomething();
}finally {
//解锁
lock.unlock();
}
2、AQS
AQS:Abstract Queued Sychronized
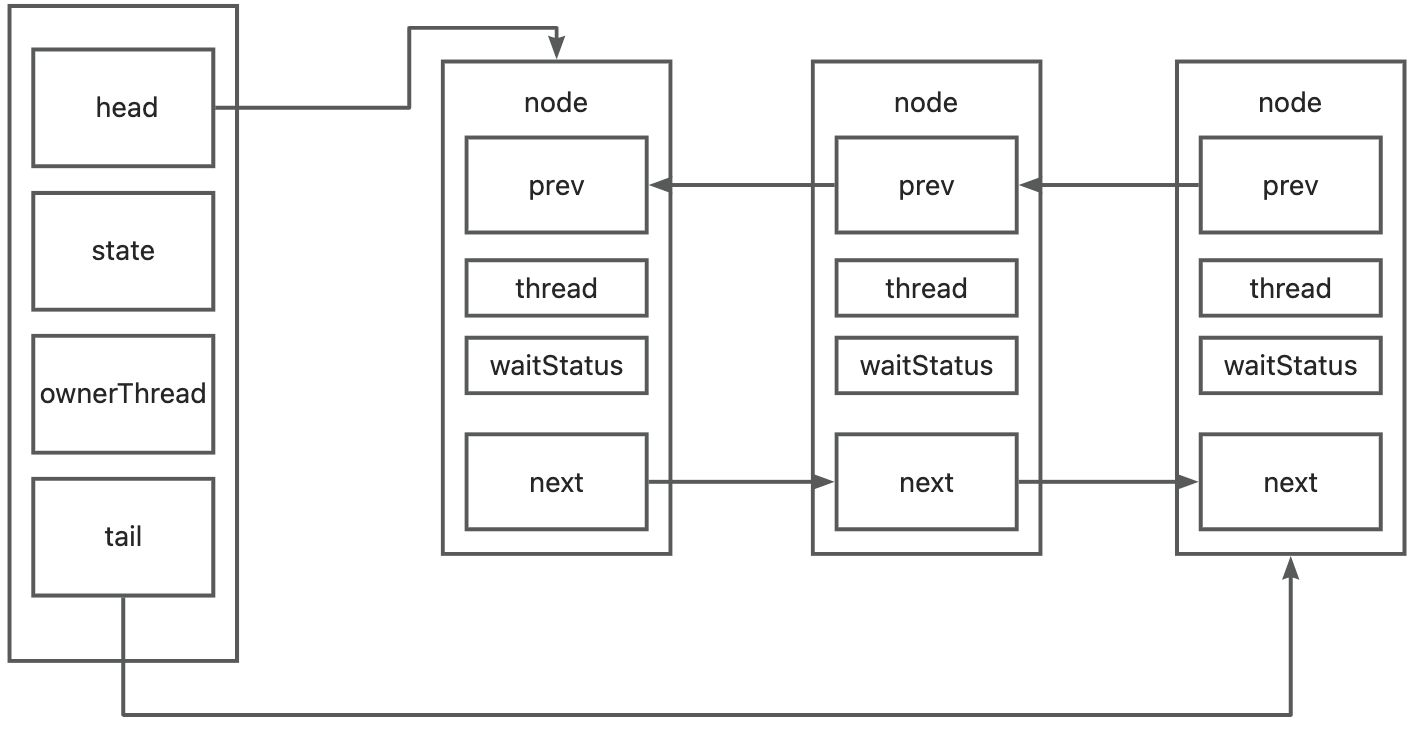
可以看到整个结构的关键就是node
//此处是 Node 的部分属性
static final class Node {
//排他锁标识
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
//如果带有这个标识,证明是失效了
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
//具有这个标识,说明后继节点需要被唤醒
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
//Node对象存储标识的地方
volatile int waitStatus;
//指向上一个节点
volatile Node prev;
//指向下一个节点
volatile Node next;
//当前Node绑定的线程
volatile Thread thread;
//返回前驱节点即上一个节点,如果前驱节点为空,抛出异常
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
Node p = prev;
if (p == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
else
return p;
}
}
node的状态,node的状态来控制线程队列的唤醒逻辑
| 状态值 | |
|---|---|
| 1(CANCELLED) | 当前节点取消获取锁。等待超时或者被中断,会变更为该状态,进入该状态节点状态不再进行变化 |
| -1(SIGNAL) | 后面节点等待当前节点唤醒 |
| -2(CONDITION) | 当前线程阻塞在Condition,如果其他线程调用了Condition的signal方法,这个节点将从等待队列转移到同步队列队尾,等待获取同步锁 |
| -3(PROPAGATE) | 共享模式,前置节点唤醒后面节点后,唤醒操作无条件传播下去 |
| 0(中间状态) | 当前节点后面的节点已经唤醒,但是当前节点线程还是没有执行下去 |
3、加锁
前提:现在有2个线程,线程1,线程2进入加锁逻辑。
加锁代码:
//公平锁
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
//非公平锁
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
非公平锁:CAS设置AQS的state属性,如果设置成功,设置AQS的ownerThread为当前线程,否则进入acquire方法进行尝试。线程1 cas 设置state = 1,设置成功,设置ownerThread为线程1,返回。线程2进入lock,cas设置state = 1,设置失败,失败后进入acquire。
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
可以被描述为:
- tryAcquire:当前线程尝试获取,尝试成功,返回,否则进入下一步
- addWaiter:将当前线程包装为AQS的node
- acquireQueued:将当前节点加入争抢线程的逻辑中
- selfInterrupt:线程自我中断
3.1、tryAcquire
查看非公平锁的tryAcquire实现
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
//获取AQS的状态
int c = getState();
//当前锁可以重新获取
if (c == 0) {
//cas设置state
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
//case设置state成功,设置ownerThread为当前线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
//获取成功
return true;
}
}
//如果当前线程是onwerThread
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
//设置state,重入锁的实现
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
//设置state的新值
setState(nextc);
//获取成功
return true;
}
//获取锁失败
return false;
}
3.2、addWaiter
如果队列中没有元素
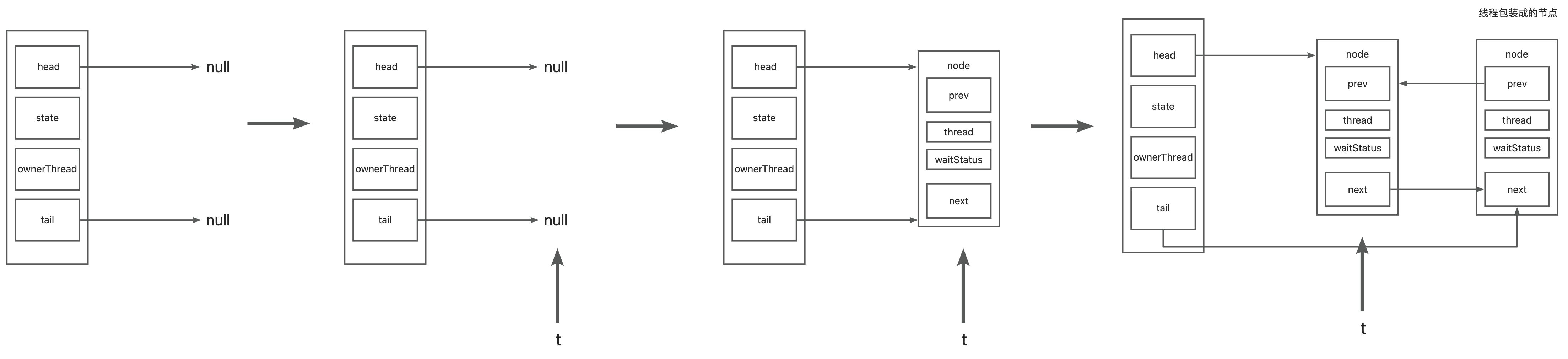
如果队列中有元素,aqs设置节点为队尾成功:

aqs设置队尾失败
死循环将节点追加到队尾
3.3、acquireQueued
队列中的线程不断尝试获取锁
- 如果节点的前置节点是头节点,使用tryAcquire尝试获取
- 获取成功,设置当前节点为头节点
- 获取失败,调用shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire实现流程图,这个方法是用来排出队列中一些不正常状态的节点的。
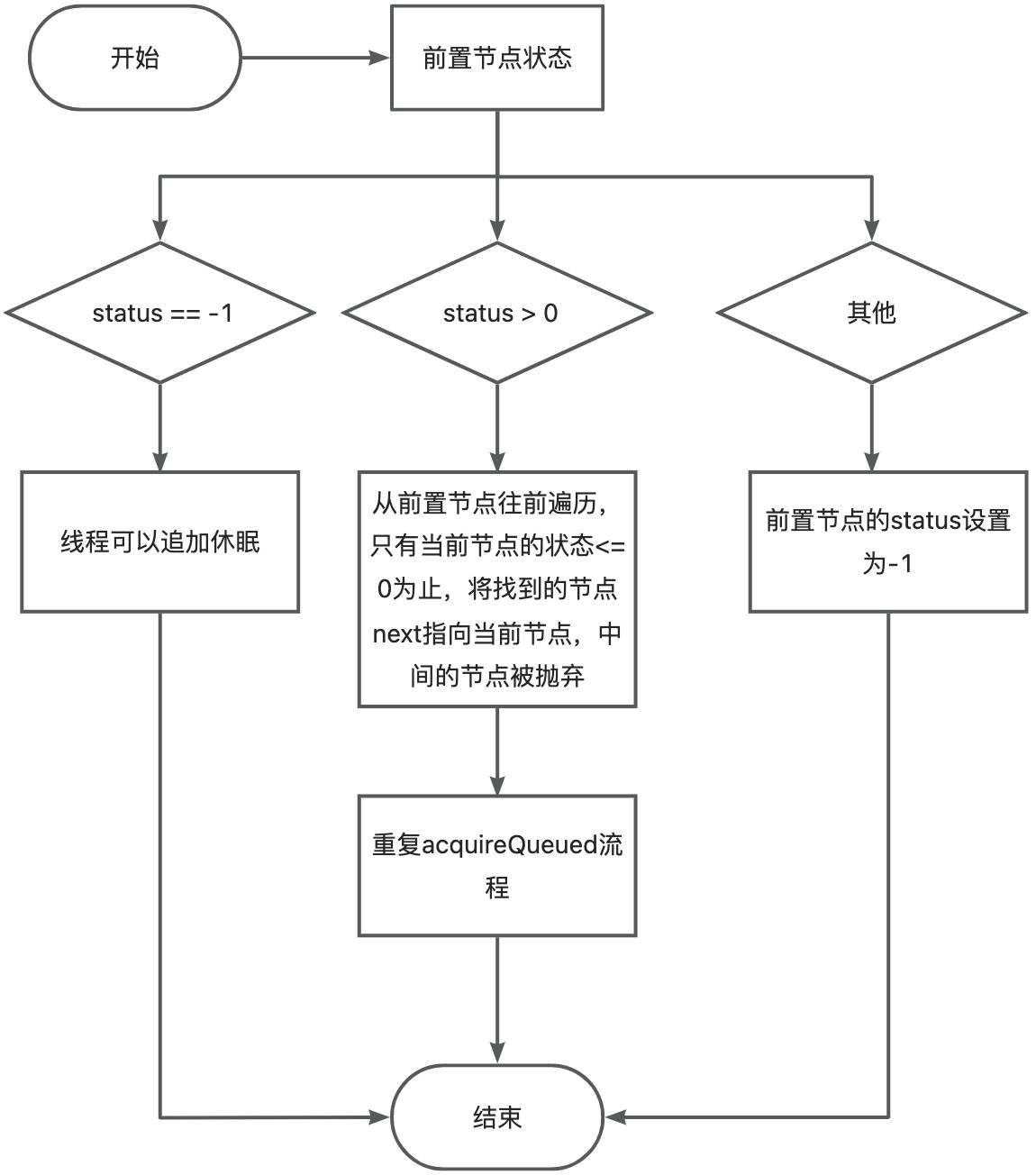
parkAndCheckInterrupt,将本线程暂停。等待unpark方法执行的时候,如果该节点是头节点的下一个节点,那么线程继续执行,继续acquireQueued的无限循环,尝试获取锁。
4、解锁
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
tryRelease
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
//state减1
int c = getState() - releases;
//当前线程!=ownerThread,抛出异常
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
//如果c==0代表可以解锁,清理ownerThrad
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
//设置state的值的新的值
setState(c);
return free;
}
如果state设置完成,开始unpark队列中的节点
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
5、总结
state来标记是否可以加锁,用队列中节点封装争抢执行权的线程,用节点的waitStatus来处理节点的生命周期。
加锁有几个关键步骤:tryAcquire方法,用来判断锁是被获取,获取的线程是自己,如果不是失败。
addWaiter将节点封装为队列中的node,追加队列的队尾,如果队列中没有元素,创建一个虚拟节点作为头节点。
acquireQueued:新加入队列的节点去竞争锁,如果节点的前置节点是头节点,使用tryAcquire去竞争,如果失败,将队列中的节点重新组织,清楚失效节点,然后将当前线程阻塞住。
解锁:修改state状态以及ownerThread,寻找第一个可以被释放的节点,释放节点,acquireQueued方法无限循环继续,继续上述流程。



