codeforces 690C3 C3. Brain Network (hard)(lca)
题目链接:
Breaking news from zombie neurology! It turns out that – contrary to previous beliefs – every zombie is born with a single brain, and only later it evolves into a complicated brain structure. In fact, whenever a zombie consumes a brain, a new brain appears in its nervous system and gets immediately connected to one of the already existing brains using a single brain connector. Researchers are now interested in monitoring the brain latency of a zombie. Your task is to write a program which, given a history of evolution of a zombie's nervous system, computes its brain latency at every stage.
The first line of the input contains one number n – the number of brains in the final nervous system (2 ≤ n ≤ 200000). In the second line a history of zombie's nervous system evolution is given. For convenience, we number all the brains by 1, 2, ..., n in the same order as they appear in the nervous system (the zombie is born with a single brain, number 1, and subsequently brains 2, 3, ..., n are added). The second line contains n - 1 space-separated numbers p2, p3, ..., pn, meaning that after a new brain k is added to the system, it gets connected to a parent-brain 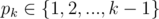 .
.
Output n - 1 space-separated numbers – the brain latencies after the brain number k is added, for k = 2, 3, ..., n.
6
1
2
2
1
5
1 2 2 3 4
题意:
给一棵树的生成过程,问在每次添加一个节点后这棵树的直径是多少;
思路:
在新加的一个节点w前的直径是(u,v),加入w后,直径就变成了max{(u,v)(u,w)(v,w)};
然后就是把lca约束成RMQ问题来了;
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> /* #include <vector> #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <cmath> #include <map> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdio> */ using namespace std; #define For(i,j,n) for(int i=j;i<=n;i++) #define mst(ss,b) memset(ss,b,sizeof(ss)); typedef long long LL; template<class T> void read(T&num) { char CH; bool F=false; for(CH=getchar();CH<'0'||CH>'9';F= CH=='-',CH=getchar()); for(num=0;CH>='0'&&CH<='9';num=num*10+CH-'0',CH=getchar()); F && (num=-num); } int stk[70], tp; template<class T> inline void print(T p) { if(!p) { puts("0"); return; } while(p) stk[++ tp] = p%10, p/=10; while(tp) putchar(stk[tp--] + '0'); putchar('\n'); } const LL mod=1e9+7; const double PI=acos(-1.0); const LL inf=1e18; const int N=2e5+10; const int maxn=1005; const double eps=1e-10; int n,in[N],a[2*N],dep[N],cnt=0,dp[2*N][21],dis[N]; vector<int>ve[N]; void dfs(int x,int deep) { //cout<<x<<" "<<deep<<endl; in[x]=cnt; a[cnt++]=x; dep[x]=deep; int len=ve[x].size(); For(i,0,len-1) { int y=ve[x][i]; dis[y]=dis[x]+1; dfs(y,deep+1); a[cnt++]=x; } } int RMQ() { for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) dp[i][0]=a[i]; for(int j=1;(1<<j)<=cnt;j++) { for(int i=0;i+(1<<j)-1<cnt;i++) { if(dep[dp[i][j-1]]<dep[dp[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]])dp[i][j]=dp[i][j-1]; else dp[i][j]=dp[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]; } } } int query(int l ,int r) { if(l>r)swap(l,r); int temp=(int)(log((r-l+1)*1.0)/log(2.0)); if(dep[dp[l][temp]]<dep[dp[r-(1<<temp)+1][temp]])return dp[l][temp]; return dp[r-(1<<temp)+1][temp]; } int s=1,e=1,pre=0; int check(int x,int y) { //cout<<x<<" "<<y<<" "<<pre<<" @@@@"<<endl; int temp=query(in[x],in[y]); if(dis[x]+dis[y]-2*dis[temp]>pre) { s=x; e=y; pre=dis[x]+dis[y]-2*dis[temp]; } } int main() { read(n); int u; For(i,2,n) { read(u); ve[u].push_back(i); } dis[1]=0; dfs(1,0); RMQ(); For(i,2,n) { int fs=s,fe=e; check(fs,fe); check(fs,i); check(fe,i); cout<<pre<<" "; } return 0; }




