Trie树主要应用在信息检索领域,非常高效。今天我们讲Double Array Trie,请先把Trie树忘掉,把信息检索忘掉,我们来讲一个确定有限自动机(deterministic finite automaton ,DFA)的故事。所谓“确定有限自动机”是指给定一个状态和一个变量时,它能跳转到的下一个状态也就确定下来了,同时状态是有限的。请注意这里出现两个名词,一个是“状态”,一个是“变量”,下文会举例说明这两个名词的含义。
举个例子,假设我们一共有10个汉字,每个汉字就是一个“变量”。我们为每个汉字编个序号。
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
啊 |
阿 |
埃 |
根 |
胶 |
拉 |
及 |
廷 |
伯 |
人 |
表1. “变量”的编号
这10个汉字一共可以构成6个词语:啊,埃及,阿胶,阿根廷,阿拉伯,阿拉伯人。
这里的每个词以及它的任意前缀都是一个“状态”,“状态”一共有10个:啊,阿,埃,阿根,阿根廷,阿胶,阿拉,阿拉伯,阿拉伯人,埃及
我们把DFA图画出来:
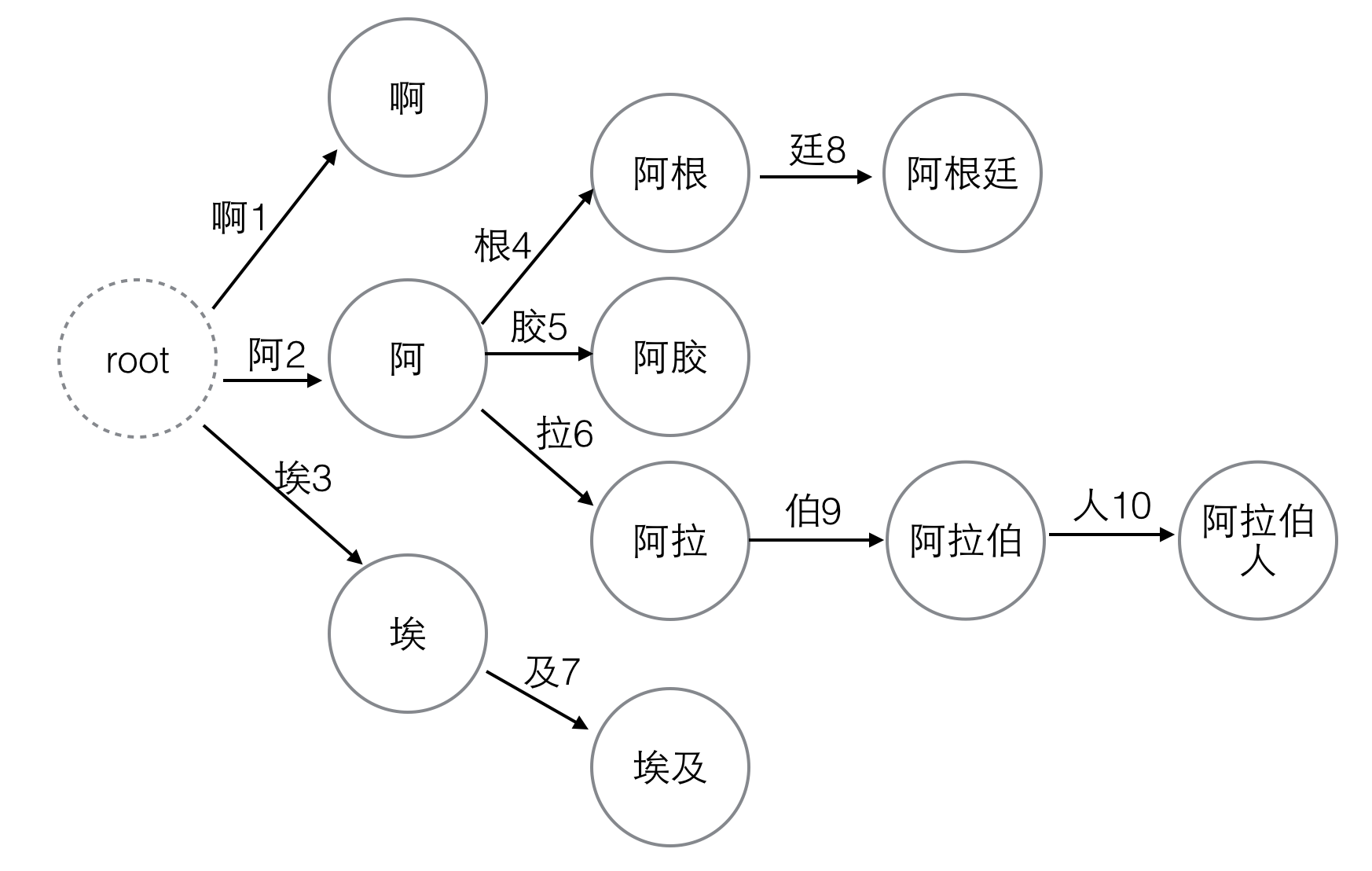
图1. DFA,同时也是Trie树
在图中每个节点代表一个“状态”,每条边代表一个“变量”,并且我们把变量的编号也标在了图中。
下面我们构造两个int数组:base和check,它们的长度始终是一样的。数组的长度定多少并没有严格的规定,反正随着词语的插入,数组肯定是要扩容的。说到数组扩容,大家可以看一下java中HashMap的扩容策略,每次扩容数组的长度都会变为2的整次幂。HashMap中有这么一个精妙的函数:
//给定一个整数,返回大于等于这个数的2的整次幂
static int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : n + 1;
}
回到今天的正题,我们不妨把double array的初始长度就定得大一些。两数组元素初始值均为0。
double array的初始状态:
|
下标 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
|
base |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
check |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
state |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
把词添加到词典的过程就给base和check数组中各元素赋值的过程。下面我们层次遍历图1所示的Trie树。
step1.
第一层上取到3个“状态”:啊,阿,埃。把这3个状态按照其对应的变量的编号(查表1)放到state数组中。
|
下标 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
|
base |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
check |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
state |
啊 |
阿 |
埃 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
step2.
当存在状态转移![]() 时,有
时,有
check[t]=s base[s]+c=t
其中s和t代表某个状态在数组中的下标,c代表变量的编号。
此时层次遍历来到了图1所示DFA的第二层,我们看到“阿”的子节点有“阿根”、“阿胶”、“阿拉”,已知状态“阿”的下标是2,变量“根”、“胶”、“拉”的编号依次是4、5、6,下面我们要给base[2]赋值:从小到大遍历所有的正整数,直到发现某个数正整k满足base[k+4]=base[k+5]=base[k+6]=check[k+4]=check[k+5]=check[k+6]=0。得到k=1,那么就把1赋给base[2],同时也确定了状态“阿根”、“阿胶”、“阿拉”的下标依次是k+4、k+5、k+6,即5、6、7,而且check[5]=check[6]=check[7]=2。
同理,“埃”的子节点是“埃及”,状态“埃”的下标是3,变量“及”的编号是7,此时有check[1+7]=base[1+7]=0,所以base[3]=1,状态“埃及”的下标是8,check[8]=3。
遍历完DFA的第二层后得到下表:
|
下标 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
|
base |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
check |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
state |
啊 |
阿 |
埃 |
|
阿根 |
阿胶 |
阿拉 |
埃及 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
step3.
重复step2,层次遍历完整查询树之后,得到:
|
下标 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
|
base |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
check |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
7 |
10 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
state |
啊 |
阿 |
埃 |
|
阿根 |
阿胶 |
阿拉 |
埃及 |
阿根廷 |
阿拉伯 |
阿拉伯人 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
step4.
最后遍历一次DFA,当某个节点已经是一个词的结尾时,按下列方法修改其base值。
if(base[i]==0)
base[i]=-i
else
base[i]=-base[i]
得到:
|
下标 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
|
base |
-1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
-6 |
1 |
-8 |
-9 |
-1 |
-11 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
check |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
7 |
10 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
state |
啊 |
阿 |
埃 |
|
阿根 |
阿胶 |
阿拉 |
埃及 |
阿根廷 |
阿拉伯 |
阿拉伯人 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
double array建好之后,如果词典中又动态地添加了一个新词,比如“阿拉根”,那么“阿拉”的所有子孙节点在double array中的位置要重新分配。

图2. 动态添加一个词
首先,把“阿拉伯”和“阿拉伯人”对应的base、check值清0,把“阿拉伯”和“阿拉伯人”从state数组中删除掉,把“阿拉”的base值清0。
|
下标 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
|
base |
-1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
-6 |
0 |
-8 |
-9 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
check |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
state |
啊 |
阿 |
埃 |
|
阿根 |
阿胶 |
阿拉 |
埃及 |
阿根廷 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
然后,按照上面step2所述的方法把“阿拉伯”、“阿拉根”插入到double array中。变量“根”、“伯”的编号是4和9,满足base[k+4]=base[k+9]=check[k+4]=check[k+9]=0的最小的k是6,所以base[7]=6,“阿拉伯”和“阿拉根”对应的下标是10和15。同理把“阿拉伯人”插入到double array中。
|
下标 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
|
base |
-1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
-6 |
6 |
-8 |
-9 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
check |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
7 |
15 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
state |
啊 |
阿 |
埃 |
|
阿根 |
阿胶 |
阿拉 |
埃及 |
阿根廷 |
阿拉根 |
阿拉伯人 |
|
|
|
阿拉伯 |
|
|
|
|
最后,遍历图2所示的DFA,当某个节点已经是一个词的结尾时按照step4中的方法修改其base值。
|
下标 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
|
base |
-1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
-6 |
6 |
-8 |
-9 |
-10 |
-11 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
-1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
check |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
7 |
15 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
state |
啊 |
阿 |
埃 |
|
阿根 |
阿胶 |
阿拉 |
埃及 |
阿根廷 |
阿拉根 |
阿拉伯人 |
|
|
|
阿拉伯 |
|
|
|
|
double array建好之后,如何查询一个词是否在词典中呢?
比如要查“阿胶及”,每个字的编号是已知的,我们画出状态转移图。

变量“阿”的编号是2,base[2]=1,变量“胶”的编号是5,base[2]+5=6,我们检查一下check[6]是否等于2。check[6]确实等于2,则继续看下一个状态转移。同时我们发现base[6]是负数,这说明“阿胶”已经是一个完整的词了。
继续看下一个状态转移,base[6]=-6,负数取其相反数,base[6]=6,变量“及”的编号是7,base[6]+7=13,我们检查一下check[13]是否等于6,发现不满足,则“阿胶及”不是一个词,甚至都是不是任意一个词的前缀。
github上一个日本人贡献了他的java版的Darts(Darts本来是一种Double Array Trie的C++实现),代码如下:
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
/**
* DoubleArrayTrie在构建双数组的过程中也借助于一棵传统的Trie树,但这棵Trie树并没有被保存下来,
* 如果要查找以prefix为前缀的所有词不适合用DoubleArrayTrie,应该用传统的Trie树。
*
* @author zhangchaoyang
*
*/
public class DoubleArrayTrie {
private final static int BUF_SIZE = 16384;// 2^14,java采用unicode编码表示所有字符,每个字符固定用两个字节表示。考虑到每个字节的符号位都是0,所以又可以节省两个bit
private final static int UNIT_SIZE = 8; // size of int + int
private static class Node {
int code;// 字符的unicode编码
int depth;// 在Trie树中的深度
int left;//
int right;//
};
private int check[];
private int base[];
private boolean used[];
private int size;
private int allocSize;// base数组当前的长度
private List<String> key;// 所有的词
private int keySize;
private int length[];
private int value[];
private int progress;
private int nextCheckPos;
int error_;
// 扩充base和check数组
private int resize(int newSize) {
int[] base2 = new int[newSize];
int[] check2 = new int[newSize];
boolean used2[] = new boolean[newSize];
if (allocSize > 0) {
System.arraycopy(base, 0, base2, 0, allocSize);// 如果allocSize超过了base2的长度,会抛出异常
System.arraycopy(check, 0, check2, 0, allocSize);
System.arraycopy(used, 0, used2, 0, allocSize);
}
base = base2;
check = check2;
used = used2;
return allocSize = newSize;
}
private int fetch(Node parent, List<Node> siblings) {
if (error_ < 0)
return 0;
int prev = 0;
for (int i = parent.left; i < parent.right; i++) {
if ((length != null ? length[i] : key.get(i).length()) < parent.depth)
continue;
String tmp = key.get(i);
int cur = 0;
if ((length != null ? length[i] : tmp.length()) != parent.depth)
cur = (int) tmp.charAt(parent.depth) + 1;
if (prev > cur) {
error_ = -3;
return 0;
}
if (cur != prev || siblings.size() == 0) {
Node tmp_node = new Node();
tmp_node.depth = parent.depth + 1;
tmp_node.code = cur;
tmp_node.left = i;
if (siblings.size() != 0)
siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).right = i;
siblings.add(tmp_node);
}
prev = cur;
}
if (siblings.size() != 0)
siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).right = parent.right;
return siblings.size();
}
private int insert(List<Node> siblings) {
if (error_ < 0)
return 0;
int begin = 0;
int pos = ((siblings.get(0).code + 1 > nextCheckPos) ? siblings.get(0).code + 1
: nextCheckPos) - 1;
int nonzero_num = 0;
int first = 0;
if (allocSize <= pos)
resize(pos + 1);
outer: while (true) {
pos++;
if (allocSize <= pos)
resize(pos + 1);
if (check[pos] != 0) {
nonzero_num++;
continue;
} else if (first == 0) {
nextCheckPos = pos;
first = 1;
}
begin = pos - siblings.get(0).code;
if (allocSize <= (begin + siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).code)) {
// progress can be zero
double l = (1.05 > 1.0 * keySize / (progress + 1)) ? 1.05 : 1.0
* keySize / (progress + 1);
resize((int) (allocSize * l));
}
if (used[begin])
continue;
for (int i = 1; i < siblings.size(); i++)
if (check[begin + siblings.get(i).code] != 0)
continue outer;
break;
}
// -- Simple heuristics --
// if the percentage of non-empty contents in check between the
// index
// 'next_check_pos' and 'check' is greater than some constant value
// (e.g. 0.9),
// new 'next_check_pos' index is written by 'check'.
if (1.0 * nonzero_num / (pos - nextCheckPos + 1) >= 0.95)
nextCheckPos = pos;
used[begin] = true;
size = (size > begin + siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).code + 1) ? size
: begin + siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).code + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < siblings.size(); i++)
check[begin + siblings.get(i).code] = begin;
for (int i = 0; i < siblings.size(); i++) {
List<Node> new_siblings = new ArrayList<Node>();
if (fetch(siblings.get(i), new_siblings) == 0) {
base[begin + siblings.get(i).code] = (value != null) ? (-value[siblings
.get(i).left] - 1) : (-siblings.get(i).left - 1);
if (value != null && (-value[siblings.get(i).left] - 1) >= 0) {
error_ = -2;
return 0;
}
progress++;
// if (progress_func_) (*progress_func_) (progress,
// keySize);
} else {
int h = insert(new_siblings);
base[begin + siblings.get(i).code] = h;
}
}
return begin;
}
public DoubleArrayTrie() {
check = null;
base = null;
used = null;
size = 0;
allocSize = 0;
// no_delete_ = false;
error_ = 0;
}
// no deconstructor
// set_result omitted
// the search methods returns (the list of) the value(s) instead
// of (the list of) the pair(s) of value(s) and length(s)
// set_array omitted
// array omitted
void clear() {
// if (! no_delete_)
check = null;
base = null;
used = null;
allocSize = 0;
size = 0;
// no_delete_ = false;
}
public int getUnitSize() {
return UNIT_SIZE;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public int getTotalSize() {
return size * UNIT_SIZE;
}
public int getNonzeroSize() {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (check[i] != 0)
result++;
return result;
}
public int build(List<String> key) {
return build(key, null, null, key.size());
}
public int build(List<String> _key, int _length[], int _value[],
int _keySize) {
if (_keySize > _key.size() || _key == null)
return 0;
// progress_func_ = progress_func;
key = _key;
length = _length;
keySize = _keySize;
value = _value;
progress = 0;
resize(65536 * 32);
base[0] = 1;
nextCheckPos = 0;
Node root_node = new Node();
root_node.left = 0;
root_node.right = keySize;
root_node.depth = 0;
List<Node> siblings = new ArrayList<Node>();
fetch(root_node, siblings);
insert(siblings);
// size += (1 << 8 * 2) + 1; // ???
// if (size >= allocSize) resize (size);
used = null;
key = null;
return error_;
}
public void open(String fileName) throws IOException {
File file = new File(fileName);
size = (int) file.length() / UNIT_SIZE;
check = new int[size];
base = new int[size];
DataInputStream is = null;
try {
is = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(file), BUF_SIZE));
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
base[i] = is.readInt();
check[i] = is.readInt();
}
} finally {
if (is != null)
is.close();
}
}
public void save(String fileName) throws IOException {
DataOutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(fileName)));
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
out.writeInt(base[i]);
out.writeInt(check[i]);
}
out.close();
} finally {
if (out != null)
out.close();
}
}
public int exactMatchSearch(String key) {
return exactMatchSearch(key, 0, 0, 0);
}
public int exactMatchSearch(String key, int pos, int len, int nodePos) {
if (len <= 0)
len = key.length();
if (nodePos <= 0)
nodePos = 0;
int result = -1;
char[] keyChars = key.toCharArray();
int b = base[nodePos];
int p;
for (int i = pos; i < len; i++) {
p = b + (int) (keyChars[i]) + 1;
if (b == check[p])
b = base[p];
else
return result;
}
p = b;
int n = base[p];
if (b == check[p] && n < 0) {
result = -n - 1;
}
return result;
}
public List<Integer> commonPrefixSearch(String key) {
return commonPrefixSearch(key, 0, 0, 0);
}
public List<Integer> commonPrefixSearch(String key, int pos, int len,
int nodePos) {
if (len <= 0)
len = key.length();
if (nodePos <= 0)
nodePos = 0;
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
char[] keyChars = key.toCharArray();
int b = base[nodePos];
int n;
int p;
for (int i = pos; i < len; i++) {
p = b;
n = base[p];
if (b == check[p] && n < 0) {
result.add(-n - 1);
}
p = b + (int) (keyChars[i]) + 1;
if (b == check[p])
b = base[p];
else
return result;
}
p = b;
n = base[p];
if (b == check[p] && n < 0) {
result.add(-n - 1);
}
return result;
}
// debug
public void dump() {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.err.println("i: " + i + " [" + base[i] + ", " + check[i]
+ "]");
}
}
}
public class TestDoubleArrayTrie {
/**
* 检索key的前缀命中了词典中的哪些词<br>
* key的前缀有多个,所以有可能命中词典中的多个词
*/
@Test
public void testPrefixMatch() {
DoubleArrayTrie adt = new DoubleArrayTrie();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("阿胶");
list.add("阿拉伯");
list.add("阿拉伯人");
list.add("埃及");
// 所有词必须先排序
Collections.sort(list);
// 构建DoubleArrayTrie
adt.build(list);
String key = "阿拉伯人";
// 检索key的前缀命中了词典中的哪些词
List<Integer> rect = adt.commonPrefixSearch(key);
for (int index : rect) {
System.out.println("前缀 " + list.get(index) + " matched");
}
System.out.println("=================");
}
/**
* 检索key是否完全命中了词典中的某个词
*/
@Test
public void testFullMatch() {
DoubleArrayTrie adt = new DoubleArrayTrie();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("阿胶");
list.add("阿拉伯");
list.add("阿拉伯人");
list.add("埃及");
// 所有词必须先排序
Collections.sort(list);
// 构建DoubleArrayTrie
adt.build(list);
String key = "阿拉";
// 检索key是否完全命中了词典中的某个词
int index = adt.exactMatchSearch(key);
if (index >= 0) {
System.out.println(key + " match " + list.get(index));
} else {
System.out.println(key + " not match any term");
}
key = "阿拉伯";
index = adt.exactMatchSearch(key);
if (index >= 0) {
System.out.println(key + " match " + list.get(index));
} else {
System.out.println(key + " not match any term");
}
key = "阿拉伯人";
index = adt.exactMatchSearch(key);
if (index >= 0) {
System.out.println(key + " match " + list.get(index));
} else {
System.out.println(key + " not match any term");
}
System.out.println("=================");
}
}
本文来自博客园,作者:高性能golang,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangchaoyang/articles/4508266.html



