一笔画连线问题, 代码完美解决.
抖音上有大量这种游戏的主播, 我干脆直接写出代码的求解.
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1gp42127MZ/
https://github.com/zhangbo2008/draw_by_one_line
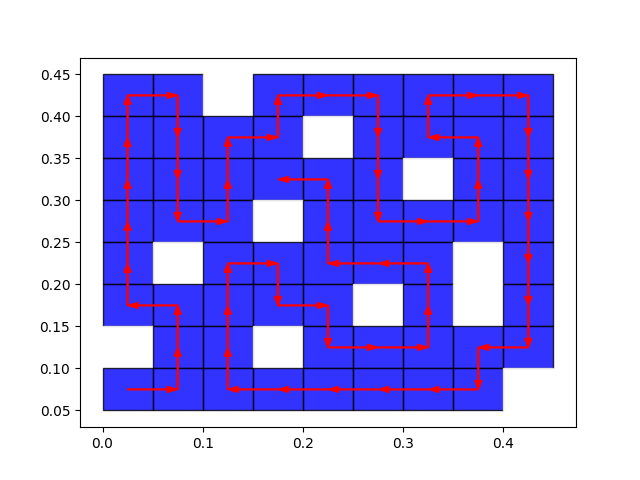
# 2024-04-14,0点26 可能是空间复杂度太高, 改成用树来存储路径.
#=============一笔画问题.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1表示可以走的路, 0表示墙
# 配置地图!!!!!!!!!!!
ditu=[
[1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1],
[1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1],
[1,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,1],
[1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1],
[0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0],
]
#==========cn2选起始点和终点. 排列组合.
all_point=[]
for i in range(len(ditu)):
for j in range(len(ditu[0])):
if ditu[i][j]==1:
all_point.append([i,j])
print(1)
point_num=len(all_point)
#==========任意取2个点的所有组合:
kaishi_jieshu_zuhe=[]
for i in range(len(all_point)-1):
for j in range(i+1,len(all_point)):
kaishi_jieshu_zuhe.append([all_point[i],all_point[j]]) # 406个点.
print(1)
#=============
# 其实我们只需要确定起点就够了. 然后算他的最长路径即可.
# 每一个路径我们都要保存, 所以用多叉树结构来存所有路径
class node:
def __init__(self,val):
self.val=val #自己的值=值是一个point
self.children=[] # childre是node组成的数组.
self.par=None #指向父节点, 用于删除时候用.
self.visited=0
dx=[-1,1,0,0]
dy=[0,0,-1,1] #只能上下左右走.
# #==========输入第n步的全部路线, 输出第n+1步的全部路线.
# def one_step(start_luxian):#========把树高提高一层.
# next_luxian=[]
# tmplujing=[] #用来保存一条完整路径.
# #进行dfs返回一条完整路径.# 因为之前的bfs, 内存不够导致算不出来.
# def dfs1(aaa,history_lujing): #传入要遍历的节点aaa,和这个节点父节点经过的路径
# if aaa.children==[]:
# #如果aaa是一个叶子.那么就尝试添加叶子.
# pass
# for i in start_luxian: #=========进行dfs遍历.
# tmp_luxina=i
# tmp_luxian_zuihouyigedian=i[-1]
# #===最后一个点开始尝试找到下一个点
# candidate=[]
# for j in range(len(dx)):
# nx=[tmp_luxian_zuihouyigedian[0]+dx[j],tmp_luxian_zuihouyigedian[1]+dy[j]]
# if 0<=nx[0]<len(ditu) and 0<=nx[1]<len(ditu[0]) and nx not in tmp_luxina and ditu[nx[0]][nx[1]]==1 :
# # candidate.append([tuple(nx)])
# # # print(1)
# # #========路线合并
# # for j in candidate:
# next_luxian.append(tmp_luxina+[tuple(nx)]) #======这个地方的二维数组确实很饶腾, 以后可以nmpy重写.
# # print(1)
# return next_luxian
#==========根据我们地图我们知道,度为1的点一定是起点!!!!!
#============我们的起点是一个根.
root=node((7,0))
#=====为了测试我们加一层.
# root.children=[node((7,1)),node((6,0))]
start_luxian=root #使用tuple可以进行哈希.
# start_luxian=all_point #如果我们没有度为1的点, 那么我们就只能设置为所有点都可能是起点了.
maxlen=0
early_quit=0
save_history=[]
#========2024-04-14,8点12 改成直接用dfs建立树
def dfs(aaa,history):
global maxlen
global early_quit
global save_history
if early_quit:
return
if aaa.children==[]:#如果是叶子,那么就尝试添加叶子.
tmp_luxian_zuihouyigedian=aaa.val
#=========无效的减掉.
hasnewchild=0
for j in range(len(dx)):
nx=[tmp_luxian_zuihouyigedian[0]+dx[j],tmp_luxian_zuihouyigedian[1]+dy[j]]
if 0<=nx[0]<len(ditu) and 0<=nx[1]<len(ditu[0]) and nx not in history and ditu[nx[0]][nx[1]]==1 :
#添加叶子
ffff=node(nx)
aaa.children.append(ffff)
#'跟踪最长路径'
if len(history)+1>maxlen:
maxlen=len(history)+1
print('当前最长路径长度',len(history)+1)
#=====提前终止:
if maxlen==len(all_point):
early_quit=1#==让其他的dfs函数提前quit
save_history=history+[ffff.val]
return history
break
dfs(ffff,history+[ffff.val])
hasnewchild=1
if not hasnewchild:
pass #是否不用管呢?
else:
#=====遍历叶子.
for i in aaa.children:
dfs(i,history+[aaa.val])
a=dfs(root,[root.val])
print(1)
# for i in range(len(all_point)):#一共可以走这么多步:
# print('当前推理:',i,'步',)
# next_luxian=one_step(start_luxian)
# if next_luxian==[]:
# print('找到最长的路线了',start_luxian[0],'长度',len(start_luxian[0]),'走法一共有',len(start_luxian))
# break
# start_luxian=next_luxian
# print(1)
#===========gui画图
import numpy as np
#======输入左上角
kuan=0.05
print(ditu)
for i in range(len(ditu)):
for j in range(len(ditu[0])):
zuoxiajiaoy=0.05*(len(ditu[0])-i-1)#======这地方衡中坐标也非常复杂.
zuoxiajiaox=0.05*(j)
if ditu[i][j]==1:
square = plt.Rectangle(xy=(zuoxiajiaox, zuoxiajiaoy), width=kuan, height=kuan, alpha=0.8, angle=0.0,facecolor='blue',fill=True,edgecolor ='black')
else:
square = plt.Rectangle(xy=(zuoxiajiaox, zuoxiajiaoy), width=kuan, height=kuan, alpha=0.8, angle=0.0,facecolor='blue',color='white')
plt.gca().add_patch(square)
# square = plt.Rectangle(xy=(100, 100), width=0.2, height=0.2, alpha=0.8, angle=0.0,color='blue')
# plt.gca().add_patch(square)
#========画上解的路线即可.
jie=save_history
x=1
y=1
font={'family':'serif',
'style':'italic',
'weight':'normal',
'color':'red',
'size':6
}
# plt.text((y+0.5)*kuan,(len(ditu[0])-x-0.5)*kuan,color='red',s='1',fontdict=font)
print('jie',jie)
for i in range(len(jie)-1):
aaaa=jie[i]
bbbb=jie[i+1]
dx=bbbb[1]-aaaa[1]
dy=bbbb[0]-aaaa[0]
dy=-dy
plt.arrow((aaaa[1]+0.5)*kuan,(len(ditu[0])-aaaa[0]-0.5)*kuan,kuan*dx,kuan*dy,color='red',head_width=0.007,length_includes_head=True)
plt.savefig('yibihua答案.png')




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!