02 - Python之路,Day2 - Python基础2 (三元运算,列表,元组,字符串,字典,集合,文件,字符编码与转码)
本节内容
- 三元运算
- 列表、元组操作
- 字符串操作
- 字典操作
- 集合操作
- 文件操作
- 字符编码与转码
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/alex3714/articles/5717620.html
一、三元运算
result = 值1 if 条件 else 值2
如果条件为真:result = 值1
如果条件为假:result = 值2
三元运算下面举例:
#如果4等于3 那我就执行3-5,否则执行3+4,把运算的得出的结果赋值给a
1 a = 3-5 if 4==3 else 3+4 2 print(a)
二、列表、元组操作
列表是我们最以后最常用的数据类型之一,通过列表可以对数据实现最方便的存储、修改等操作
定义列表
1 names = ['Alex',"Tenglan",'Eric']
通过下标访问列表中的元素,下标从0开始计数
1 >>> names[0] 2 'Alex' 3 >>> names[2] 4 'Eric' 5 >>> names[-1] 6 'Eric' 7 >>> names[-2] #还可以倒着取 8 'Tenglan'
切片:取多个元素

1 >>> names = ["Alex","Tenglan","Eric","Rain","Tom","Amy"] 2 >>> names[1:4] #取下标1至下标4之间的数字,包括1,不包括4 3 ['Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain'] 4 >>> names[1:-1] #取下标1至-1的值,不包括-1 5 ['Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain', 'Tom'] 6 >>> names[0:3] 7 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric'] 8 >>> names[:3] #如果是从头开始取,0可以忽略,跟上句效果一样 9 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric'] 10 >>> names[3:] #如果想取最后一个,必须不能写-1,只能这么写 11 ['Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy'] 12 >>> names[3:-1] #这样-1就不会被包含了 13 ['Rain', 'Tom'] 14 >>> names[0::2] #后面的2是代表,每隔一个元素,就取一个 15 ['Alex', 'Eric', 'Tom'] 16 >>> names[::2] #和上句效果一样 17 ['Alex', 'Eric', 'Tom']
追加

1 >>> names 2 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy'] 3 >>> names.append("我是新来的") 4 >>> names 5 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的']
插入

1 >>> names 2 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的'] 3 >>> names.insert(2,"强行从Eric前面插入") 4 >>> names 5 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', '强行从Eric前面插入', 'Eric', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的'] 6 7 >>> names.insert(5,"从eric后面插入试试新姿势") 8 >>> names 9 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', '强行从Eric前面插入', 'Eric', 'Rain', '从eric后面插入试试新姿势', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的']
修改

1 >>> names 2 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', '强行从Eric前面插入', 'Eric', 'Rain', '从eric后面插入试试新姿势', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的'] 3 >>> names[2] = "该换人了" 4 >>> names 5 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', '该换人了', 'Eric', 'Rain', '从eric后面插入试试新姿势', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的']
删除

1 >>> del names[2] 2 >>> names 3 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain', '从eric后面插入试试新姿势', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的'] 4 >>> del names[4] 5 >>> names 6 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Eric', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的'] 7 >>> 8 >>> names.remove("Eric") #删除指定元素 9 >>> names 10 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', '我是新来的'] 11 >>> names.pop() #删除列表最后一个值 12 '我是新来的' 13 >>> names 14 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy']
扩展

1 >>> names 2 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy'] 3 >>> b = [1,2,3] 4 >>> names.extend(b) 5 >>> names 6 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', 1, 2, 3]
拷贝

1 >>> names 2 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', 1, 2, 3] 3 4 >>> name_copy = names.copy() 5 >>> name_copy 6 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Rain', 'Tom', 'Amy', 1, 2, 3]
统计

1 >>> names 2 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Amy', 'Tom', 'Amy', 1, 2, 3] 3 >>> names.count("Amy") 4 2
排序&翻转

1 >>> names 2 ['Alex', 'Tenglan', 'Amy', 'Tom', 'Amy', 1, 2, 3] 3 >>> names.sort() #排序 4 Traceback (most recent call last): 5 File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> 6 TypeError: unorderable types: int() < str() #3.0里不同数据类型不能放在一起排序了,擦 7 >>> names[-3] = '1' 8 >>> names[-2] = '2' 9 >>> names[-1] = '3' 10 >>> names 11 ['Alex', 'Amy', 'Amy', 'Tenglan', 'Tom', '1', '2', '3'] 12 >>> names.sort() 13 >>> names 14 ['1', '2', '3', 'Alex', 'Amy', 'Amy', 'Tenglan', 'Tom'] 15 16 >>> names.reverse() #反转 17 >>> names 18 ['Tom', 'Tenglan', 'Amy', 'Amy', 'Alex', '3', '2', '1']
获取下标

1 >>> names 2 ['Tom', 'Tenglan', 'Amy', 'Amy', 'Alex', '3', '2', '1'] 3 >>> names.index("Amy") 4 2 #只返回找到的第一个下标
元组
元组其实跟列表差不多,也是存一组数,只不是它一旦创建,便不能再修改,所以又叫只读列表
语法
1 names = ("alex","jack","eric")
它只有2个方法,一个是count,一个是index,完毕。
二、字符串操作
特性:不可修改
1 name.capitalize() 首字母大写 2 name.casefold() 大写全部变小写 3 name.center(50,"-") 输出 '---------------------Alex Li----------------------' 4 name.count('lex') 统计 lex出现次数 5 name.encode() 将字符串编码成bytes格式 6 name.endswith("Li") 判断字符串是否以 Li结尾 7 "Alex\tLi".expandtabs(10) 输出'Alex Li', 将\t转换成多长的空格 8 name.find('A') 查找A,找到返回其索引, 找不到返回-1 9 10 format : 11 >>> msg = "my name is {}, and age is {}" 12 >>> msg.format("alex",22) 13 'my name is alex, and age is 22' 14 >>> msg = "my name is {1}, and age is {0}" 15 >>> msg.format("alex",22) 16 'my name is 22, and age is alex' 17 >>> msg = "my name is {name}, and age is {age}" 18 >>> msg.format(age=22,name="ale") 19 'my name is ale, and age is 22' 20 format_map 21 >>> msg.format_map({'name':'alex','age':22}) 22 'my name is alex, and age is 22' 23 24 25 msg.index('a') 返回a所在字符串的索引 26 '9aA'.isalnum() True 27 28 '9'.isdigit() 是否整数 29 name.isnumeric 30 name.isprintable 31 name.isspace 32 name.istitle 33 name.isupper 34 "|".join(['alex','jack','rain']) 35 'alex|jack|rain' 36 37 38 maketrans 39 >>> intab = "aeiou" #This is the string having actual characters. 40 >>> outtab = "12345" #This is the string having corresponding mapping character 41 >>> trantab = str.maketrans(intab, outtab) 42 >>> 43 >>> str = "this is string example....wow!!!" 44 >>> str.translate(trantab) 45 'th3s 3s str3ng 2x1mpl2....w4w!!!' 46 47 msg.partition('is') 输出 ('my name ', 'is', ' {name}, and age is {age}') 48 49 >>> "alex li, chinese name is lijie".replace("li","LI",1) 50 'alex LI, chinese name is lijie' 51 52 msg.swapcase 大小写互换 53 54 55 >>> msg.zfill(40) 56 '00000my name is {name}, and age is {age}' 57 58 59 60 >>> n4.ljust(40,"-") 61 'Hello 2orld-----------------------------' 62 >>> n4.rjust(40,"-") 63 '-----------------------------Hello 2orld' 64 65 66 >>> b="ddefdsdff_哈哈" 67 >>> b.isidentifier() #检测一段字符串可否被当作标志符,即是否符合变量命名规则 68 True
三、字典操作
字典一种key - value 的数据类型,使用就像我们上学用的字典,通过笔划、字母来查对应页的详细内容。
语法:
1 info = { 2 'stu1101': "TengLan Wu", 3 'stu1102': "LongZe Luola", 4 'stu1103': "XiaoZe Maliya", 5 }
字典的特性:
- dict是无序的
- key必须是唯一的,so 天生去重
增加
1 >>> info["stu1104"] = "苍井空" 2 >>> info 3 {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1104': '苍井空', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1101': 'TengLan Wu'}
修改value
1 >>> info['stu1101'] = "武藤兰" 2 >>> info 3 {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1101': '武藤兰'}
修改key
字典的key默认是不可修改的,我们只能通过方法来修改它:
比如:先取到你要修改key的values,然后把values重新赋值给新的key,再然后把旧的key给删除即可
案列:
1 #把name key改成names 2 dict_data = {"name":"abu","age":22} 3 print(dict_data) 4 names = dict_data["name"] 5 dict_data.pop('name') #删除name key 6 dict_data["names"] = names #重新赋值 7 print(dict_data)
8 输出结果: 9 {'name': 'abu', 'age': 22} 10 {'age': 22, 'names': 'abu'}
删除

1 >>> info 2 {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1101': '武藤兰'} 3 >>> info.pop("stu1101") #标准删除姿势 4 '武藤兰' 5 >>> info 6 {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya'} 7 >>> del info['stu1103'] #换个姿势删除 8 >>> info 9 {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola'} 10 >>> 11 >>> 12 >>> 13 >>> info = {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya'} 14 >>> info 15 {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya'} #随机删除 16 >>> info.popitem() 17 ('stu1102', 'LongZe Luola') 18 >>> info 19 {'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya'}
查找

1 >>> info = {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya'} 2 >>> 3 >>> "stu1102" in info #标准用法 4 True 5 >>> info.get("stu1102") #获取 6 'LongZe Luola' 7 >>> info["stu1102"] #同上,但是看下面 8 'LongZe Luola' 9 >>> info["stu1105"] #如果一个key不存在,就报错,get不会,不存在只返回None 10 Traceback (most recent call last): 11 File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> 12 KeyError: 'stu1105'
多级字典嵌套及操作

1 av_catalog = { 2 "欧美":{ 3 "www.youporn.com": ["很多免费的,世界最大的","质量一般"], 4 "www.pornhub.com": ["很多免费的,也很大","质量比yourporn高点"], 5 "letmedothistoyou.com": ["多是自拍,高质量图片很多","资源不多,更新慢"], 6 "x-art.com":["质量很高,真的很高","全部收费,屌比请绕过"] 7 }, 8 "日韩":{ 9 "tokyo-hot":["质量怎样不清楚,个人已经不喜欢日韩范了","听说是收费的"] 10 }, 11 "大陆":{ 12 "1024":["全部免费,真好,好人一生平安","服务器在国外,慢"] 13 } 14 } 15 16 av_catalog["大陆"]["1024"][1] += ",可以用爬虫爬下来" 17 print(av_catalog["大陆"]["1024"]) 18 #ouput 19 ['全部免费,真好,好人一生平安', '服务器在国外,慢,可以用爬虫爬下来']
其它姿势

1 #values 2 >>> info.values() 3 dict_values(['LongZe Luola', 'XiaoZe Maliya']) 4 5 #keys 6 >>> info.keys() 7 dict_keys(['stu1102', 'stu1103']) 8 9 10 #setdefault 11 >>> info.setdefault("stu1106","Alex") 12 'Alex' 13 >>> info 14 {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1106': 'Alex'} 15 >>> info.setdefault("stu1102","龙泽萝拉") 16 'LongZe Luola' 17 >>> info 18 {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1106': 'Alex'} 19 20 21 #update 22 >>> info 23 {'stu1102': 'LongZe Luola', 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1106': 'Alex'} 24 >>> b = {1:2,3:4, "stu1102":"龙泽萝拉"} 25 >>> info.update(b) 26 >>> info 27 {'stu1102': '龙泽萝拉', 1: 2, 3: 4, 'stu1103': 'XiaoZe Maliya', 'stu1106': 'Alex'} 28 29 #items 30 info.items() 31 dict_items([('stu1102', '龙泽萝拉'), (1, 2), (3, 4), ('stu1103', 'XiaoZe Maliya'), ('stu1106', 'Alex')]) 32 33 34 #通过一个列表生成默认dict,有个没办法解释的坑,少用吧这个 35 >>> dict.fromkeys([1,2,3],'testd') 36 {1: 'testd', 2: 'testd', 3: 'testd'}
循环dict
1 #方法1 2 for key in info: 3 print(key,info[key]) 4 5 #方法2 6 for k,v in info.items(): #会先把dict转成list,数据里大时莫用 7 print(k,v)
五、文件操作
对文件操作流程
- 打开文件,得到文件句柄并赋值给一个变量
- 通过句柄对文件进行操作
- 关闭文件
句柄即是:生成一个实例,把这实例赋值给一个变量,这变量称之为句柄
现有文件如下

1 Somehow, it seems the love I knew was always the most destructive kind 2 不知为何,我经历的爱情总是最具毁灭性的的那种 3 Yesterday when I was young 4 昨日当我年少轻狂 5 The taste of life was sweet 6 生命的滋味是甜的 7 As rain upon my tongue 8 就如舌尖上的雨露 9 I teased at life as if it were a foolish game 10 我戏弄生命 视其为愚蠢的游戏 11 The way the evening breeze 12 就如夜晚的微风 13 May tease the candle flame 14 逗弄蜡烛的火苗 15 The thousand dreams I dreamed 16 我曾千万次梦见 17 The splendid things I planned 18 那些我计划的绚丽蓝图 19 I always built to last on weak and shifting sand 20 但我总是将之建筑在易逝的流沙上 21 I lived by night and shunned the naked light of day 22 我夜夜笙歌 逃避白昼赤裸的阳光 23 And only now I see how the time ran away 24 事到如今我才看清岁月是如何匆匆流逝 25 Yesterday when I was young 26 昨日当我年少轻狂 27 So many lovely songs were waiting to be sung 28 有那么多甜美的曲儿等我歌唱 29 So many wild pleasures lay in store for me 30 有那么多肆意的快乐等我享受 31 And so much pain my eyes refused to see 32 还有那么多痛苦 我的双眼却视而不见 33 I ran so fast that time and youth at last ran out 34 我飞快地奔走 最终时光与青春消逝殆尽 35 I never stopped to think what life was all about 36 我从未停下脚步去思考生命的意义 37 And every conversation that I can now recall 38 如今回想起的所有对话 39 Concerned itself with me and nothing else at all 40 除了和我相关的 什么都记不得了 41 The game of love I played with arrogance and pride 42 我用自负和傲慢玩着爱情的游戏 43 And every flame I lit too quickly, quickly died 44 所有我点燃的火焰都熄灭得太快 45 The friends I made all somehow seemed to slip away 46 所有我交的朋友似乎都不知不觉地离开了 47 And only now I'm left alone to end the play, yeah 48 只剩我一个人在台上来结束这场闹剧 49 Oh, yesterday when I was young 50 噢 昨日当我年少轻狂 51 So many, many songs were waiting to be sung 52 有那么那么多甜美的曲儿等我歌唱 53 So many wild pleasures lay in store for me 54 有那么多肆意的快乐等我享受 55 And so much pain my eyes refused to see 56 还有那么多痛苦 我的双眼却视而不见 57 There are so many songs in me that won't be sung 58 我有太多歌曲永远不会被唱起 59 I feel the bitter taste of tears upon my tongue 60 我尝到了舌尖泪水的苦涩滋味 61 The time has come for me to pay for yesterday 62 终于到了付出代价的时间 为了昨日 63 When I was young 64 当我年少轻狂
基本操作
1 f = open('lyrics') #打开文件 2 first_line = f.readline() 3 print('first line:',first_line) #读一行 4 print('我是分隔线'.center(50,'-')) 5 data = f.read()# 读取剩下的所有内容,文件大时不要用 6 print(data) #打印文件 7 8 f.close() #关闭文件
打开文件的模式有:
- r,只读模式(默认)。
- w,只写模式。【不可读;不存在则创建;存在则删除内容;】
- a,追加模式。【可读; 不存在则创建;存在则只追加内容;】
"+" 表示可以同时读写某个文件
- r+,可读写文件。【可读;可写;可追加】
- w+,写读
- a+,同a
"U"表示在读取时,可以将 \r \n \r\n自动转换成 \n (与 r 或 r+ 模式同使用)
- rU
- r+U
"b"表示处理二进制文件(如:FTP发送上传ISO镜像文件,linux可忽略,windows处理二进制文件时需标注)
- rb
- wb
- ab
其它语法

1 def close(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 2 """ 3 Close the file. 4 5 A closed file cannot be used for further I/O operations. close() may be 6 called more than once without error. 7 """ 8 pass 9 10 def fileno(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 11 """ Return the underlying file descriptor (an integer). """ 12 pass 13 14 def isatty(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 15 """ True if the file is connected to a TTY device. """ 16 pass 17 18 def read(self, size=-1): # known case of _io.FileIO.read 19 """ 20 注意,不一定能全读回来 21 Read at most size bytes, returned as bytes. 22 23 Only makes one system call, so less data may be returned than requested. 24 In non-blocking mode, returns None if no data is available. 25 Return an empty bytes object at EOF. 26 """ 27 return "" 28 29 def readable(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 30 """ True if file was opened in a read mode. """ 31 pass 32 33 def readall(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 34 """ 35 Read all data from the file, returned as bytes. 36 37 In non-blocking mode, returns as much as is immediately available, 38 or None if no data is available. Return an empty bytes object at EOF. 39 """ 40 pass 41 42 def readinto(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 43 """ Same as RawIOBase.readinto(). """ 44 pass #不要用,没人知道它是干嘛用的 45 46 def seek(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 47 """ 48 Move to new file position and return the file position. 49 50 Argument offset is a byte count. Optional argument whence defaults to 51 SEEK_SET or 0 (offset from start of file, offset should be >= 0); other values 52 are SEEK_CUR or 1 (move relative to current position, positive or negative), 53 and SEEK_END or 2 (move relative to end of file, usually negative, although 54 many platforms allow seeking beyond the end of a file). 55 56 Note that not all file objects are seekable. 57 """ 58 pass 59 60 def seekable(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 61 """ True if file supports random-access. """ 62 pass 63 64 def tell(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 65 """ 66 Current file position. 67 68 Can raise OSError for non seekable files. 69 """ 70 pass 71 72 def truncate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 73 """ 74 Truncate the file to at most size bytes and return the truncated size. 75 76 Size defaults to the current file position, as returned by tell(). 77 The current file position is changed to the value of size. 78 """ 79 pass 80 81 def writable(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 82 """ True if file was opened in a write mode. """ 83 pass 84 85 def write(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 86 """ 87 Write bytes b to file, return number written. 88 89 Only makes one system call, so not all of the data may be written. 90 The number of bytes actually written is returned. In non-blocking mode, 91 returns None if the write would block. 92 """ 93 pass
with语句
为了避免打开文件后忘记关闭,可以通过管理上下文,即:
1 with open('log','r') as f: 2 3 ...
如此方式,当with代码块执行完毕时,内部会自动关闭并释放文件资源。
在Python 2.7 后,with又支持同时对多个文件的上下文进行管理,即:
1 with open('log1') as obj1, open('log2') as obj2: 2 pass
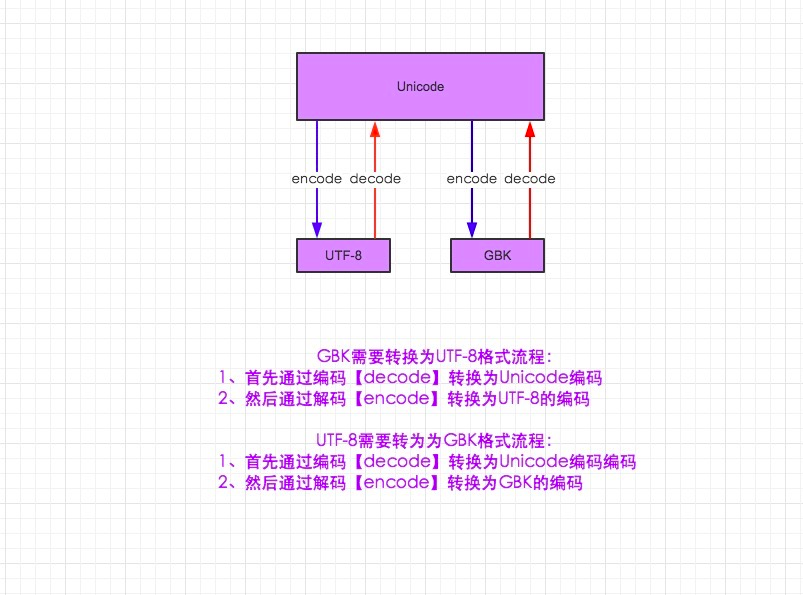
六、字符编码与转码
详细文章:
http://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/5956943.html
http://www.diveintopython3.net/strings.html
需知:
1.在python2默认编码是ASCII, python3里默认是unicode
2.unicode 分为 utf-32(占4个字节),utf-16(占两个字节),utf-8(占1-4个字节), so utf-16就是现在最常用的unicode版本, 不过在文件里存的还是utf-8,因为utf8省空间
3.在py3中encode,在转码的同时还会把string 变成bytes类型,decode在解码的同时还会把bytes变回string
python2转码(默认编码是ASCLL)
说明:先说从gbk转成utf-8(encode=解码,decode=编码)
流程:先encode("gbk")——unicode——decode("utf-8")

1 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 2 __author__ = 'Alex Li' 3 4 import sys 5 print(sys.getdefaultencoding()) 6 7 8 msg = "我爱北京天安门" 9 msg_gb2312 = msg.decode("utf-8").encode("gb2312") 10 gb2312_to_gbk = msg_gb2312.decode("gbk").encode("gbk") 11 12 print(msg) 13 print(msg_gb2312) 14 print(gb2312_to_gbk) 15 16 in python2
Python3转码(默认编码是Unicode)
说明:先说从gbk转成utf-8(encode=解码,decode=编码)
流程:先encode("gbk")——unicode——decode("utf-8")

1 #-*-coding:gb2312 -*- #这个也可以去掉 2 __author__ = 'Alex Li' 3 4 import sys 5 print(sys.getdefaultencoding()) 6 7 8 msg = "我爱北京天安门" 9 #msg_gb2312 = msg.decode("utf-8").encode("gb2312") 10 msg_gb2312 = msg.encode("gb2312") #默认就是unicode,不用再decode,喜大普奔 11 gb2312_to_unicode = msg_gb2312.decode("gb2312") 12 gb2312_to_utf8 = msg_gb2312.decode("gb2312").encode("utf-8") 13 14 print(msg) 15 print(msg_gb2312) 16 print(gb2312_to_unicode) 17 print(gb2312_to_utf8) 18 19 in python3