一、基本操作
1 r = np.ones(3)
2 r = np.zeros(3)
3 r = np.full(shape=[3,2],fill_value="5")
4 r = np.arange(start=0,stop=5,step=2)
5 r = np.random.randint(low=1,high=10,size=3)
6 r2 = np.random.random((2,3)) # 0~1
7 r = np.random.rand(5) # 正态分布
8 r = np.random.randn(5) # 正态分布
9 r = np.array([2,1,3])
二、查看操作
1 r = r2.shape
2 r = r2.size
3 r = r2.dtype
三、文件IO操作
1 r = np.random.randint(1,10,10)
2 r2 = np.array([1,23,4])
3 np.savez("LianXi.npz",key1=r2,k2=r)
4 np.savetxt("lx.txt",r2)
5 np.savetxt("lx.csv",r2,delimiter=',')
四、读取
1 f = np.load('Lianxi.npz')
2 print(f["key1"])
3 print(f["k2"])
4 f =np.loadtxt("lx.csv",delimiter=',',dtype=np.int32)
5 print(f)
五、拷贝
# 浅拷贝
n = np.array([1,2,3])
n2 = n
print(id(n)) # 173227424
print(id(n2)) # 173227424
n[2]=4
print(n,n2) # [1 2 4] [1 2 4]
# 深拷贝
n2 = n.copy()
print(id(n)) # 173218432
print(id(n2)) # 173218352
n[2]=4
print(n,n2)
六、变形
n = np.random.randint(1,10,(3,2))
n = np.array([1,2,3,4]*3).reshape([3,4])
print(n.T) # 转置
print(n) # 变维度
七、堆叠
n1 = np.array([1,2,3,4])
n2 = np.array([4,5,6,5])
c = np.concatenate([n1,n2],axis=0) # 水平连接
c= np.hstack([n1,n2]) # 水平连接
c= np.vstack([n1,n2]) # 垂直连接
八、拆分
n2 = np.random.randint(1,10,(6,5))
print(n2)
n = np.split(n2,indices_or_sections=2,axis=0)
n = np.split(n2,indices_or_sections=[3,5],axis=0) # 以索引2,3为断点分割成3份
n22 = np.hsplit(n2,indices_or_sections=[1,2])
n = np.vsplit(n2,indices_or_sections=2)
九、函数
1 n = np.array([4,16,25])
2 n2 = np.array([-2.4,2.2,2.5])
3 n = np.sqrt(n) # 开平⽅
4 n = np.square(n) # 平⽅
5 nn = np.clip(n,5,21) # <=5的改成5,>=21的改成21
6 n = np.abs(n)
7 n = np.max(n)
8 n = np.maximum(n,n2) # 多个数组比较,返回最大的一列数组
9 n = np.all(n) # 满足所有条件返回True
10 n = np.any(n) # 满足其一条件返回True
11 n = np.round(n2,1)
12 n = np.floor(n2) # 向下取整
13 n = np.ceil(n2) # 向上取整
14 n = np.array([4,16,25])
15 nn = np.where(n>10,n,0) # 大于10为本身,否则为0
十、计算
1 c = np.max(m1)
2 c = np.min(m1)
3 c = np.mean(m1) # 平均値
4 c = np.median(m1) # 中位数
5 c = np.sum(m1) #和
6 c = np.cumsum(m1) # 累加求和【1,2,3】->【1,3,6】
7 c = np.argmax(m1) # 最大值的的索引
8 c = np.argwhere(m1>2) # 大于2的索引
十一、排序
1 n = np.array([24,16,25])
2 np.sort(n) # 返回深拷⻉排序结果
3 n.sort() # 直接改变原数组,从小到大
4 abs(np.sort(-n)) # 直接改变原数组,从大到小
5 nn = np.argsort(nn) # 返回从⼩到⼤排序索引
十二、交、并、差集
1 m1 = np.array([1,2,3])
2 m2 = np.array([2,3,4])
3 cc = np.intersect1d(m1,m2) # 交集
4 cc = np.union1d(m1,m2)# 并集
5 cc = np.setdiff1d(m1,m2) #差集
十三、其他
cond = data[:,3]==0 # 从全部数据里取索引为3
print(socre[cond].max(axis=0))
十四、笔试题
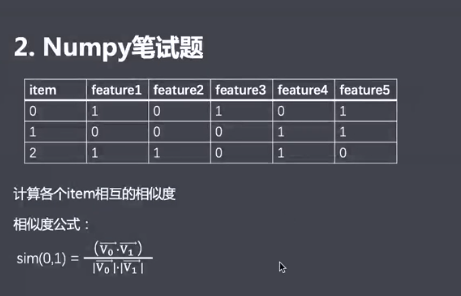

1 r = np.array([[1,0,1,0,1],
2 [0,0,0,1,1],
3 [1,1,0,1,0]
4 ])
5 r = np.mat(r)
6 fenzi = r*r.T
7 fenmu = np.sqrt(r.sum(axis=1)*r.sum(axis=1).T)
8 print(np.around(fenzi/fenmu,3))





