七、Mybatis 动态SQL和缓存
12、动态SQL
动态SQL就是根据不同的条件生成不同的SQL
- if
- choose (when, otherwise)
- trim (where, set)
- foreach
环境搭建
新建一个项目然后准备一张新表Blog,并插入数据。
CREATE TABLE blog( `id` VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL COMMENT '博客id', `title` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '博客标题', `author` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT '博客作者', `create_time` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT '创建时间', `views` int(30) NOT NULL COMMENT '浏览量' )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
pojo/Blog.java
@Data public class Blog { private String id; private String title; private String author; private Date createTime; private int views; }
dao/BlogMapper.java
public interface BlogMapper { //插入数据 int addBlog(Blog blog); }
dao/BlogMapper.xml
<insert id="addBlog" parameterType="blog"> insert into blog(id,title,author,create_time,views) values (#{id},#{title},#{author},#{createTime},#{views}) </insert>
在test下编写测试方法插入数据:
@Test public void testAddBlog() { Blog blog = new Blog(); blog.setId(IDUtils.getId()); blog.setTitle("Mybatis学习-03"); blog.setAuthor("小张"); blog.setCreateTime(new Date()); blog.setViews(9999); SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); int i = mapper.addBlog(blog); System.out.println(i); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
Tip: 在mybatis-config.xml中设置
可以自动映射数据库字段create_time到createTime(从下划线转换到驼峰)
IF
BlogMapper.xml
<select id="queryBlogByIF" resultType="blog" parameterType="map"> select * from blog <where> <if test="title != null"> title like concat('%',#{title},'%') </if> <if test="author != null"> and author = #{author} </if> </where> </select>
MyTest.java
@Test public void testQueryBlogByIF() { SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("author","小芳"); map.put("title","学习"); List<Blog> blogs = mapper.queryBlogByIF(map); for (Blog blog : blogs) { System.out.println(blog); } sqlSession.close(); }
上面的例子使用了IF关键字,如果map中包含title就在sql语句中添加title的查询条件,如果map中包含author,则在sql中添加author的查询条件。
choose(when、otherwise)
<select id="queryBlogByChoose" parameterType="map" resultType="blog"> select * from blog <where> <choose> <when test="title != null"> title like concat('%',#{title},'%') </when> <when test="author != null"> and author = #{author} </when> <otherwise> and views > #{views} </otherwise> </choose> </where> </select>
这里使用的choose标签与Java中的switch/case语句的效果是类似的,如果when中的条件成立则执行,不会在查看后面的when标签;如果所有的when标签都不满足,则执行otherwise中的语句。
CHOOSE和IF的区别就是,if的查询条件是叠加的,而choose的查询条件是多个当中取一个。
trim(where、set)
在数据库更新语句中,需要用到set关键字来更新sql的值。
<update id="updateBlog" parameterType="map"> update blog <set> <if test="title != null"> title = #{title} </if> <if test="author != null"> author = #{author} </if> <if test="views != null"> views = #{views} </if> </set> where id = #{id} </update>
SQL片段
SQL片段指的是,将一段xml配置抽取出来作为模版,方便对这段配置进行复用。我们将上面choose查询的配置抽取出来,简单的展示下:
<select id="queryBlogByChoose" parameterType="map" resultType="blog"> select * from blog <where> <include refid="chooseSql"> </include> </where> </select> <sql id="chooseSql"> <choose> <when test="title != null"> title like concat('%',#{title},'%') </when> <when test="author != null"> and author = #{author} </when> <otherwise> and views > #{views} </otherwise> </choose> </sql>
将要抽取的片段放在sql标签中,在需要使用的地方使用include引用。
Foreach
Foreach是mybatis中的一个强大的用法,它可以从一个可迭代的对象中取出元素,按照设定的规则拼装进sql语句中。比较常见的用法是in的查询场景:
select * from blog where id in (1,2,3)
<select id="queryBlogByForeach" parameterType="map" resultType="blog"> select * from blog where author in <foreach collection="authors" item="author" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{author} </foreach> </select>
这里可以看出来,我们设置了如下规则:
- 从authors中遍历取出元素,元素命名为author
- 每个元素以逗号分隔
- 所有的元素用括号包裹
MyTest.java
@Test public void testQueryBlogByForeach() { SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("小芳"); list.add("小张"); map.put("authors", list); List<Blog> blogs = mapper.queryBlogByForeach(map); for (Blog blog : blogs) { System.out.print(blog); } sqlSession.close(); }
我们在测试方法中,传入authors列表,即可查询出对应作者的博客信息。
面试高频
- MySQL引擎
- InnoDB底层原理
- 索引&索引优化
13、缓存
什么是缓存?
一般我们在系统中使用缓存技术是为了提升数据查询的效率。当我们从数据库中查询到一批数据后将其放入到缓存中(简单理解就是一块内存区域),下次再查询相同数据的时候就直接从缓存中获取数据就行了。这样少了一步和数据库的交互,可以提升查询的效率。
13.1、Mybatis缓存
在Mybatis中提供了一级缓存和二级缓存供我们使用。一级缓存是默认开启的,它针对的范围是sqlSession,二级缓存则需要我们手动开启。
13.2、一级缓存
Mybatis的一级缓存是sqlSession级别的,即在一个sqlSession创建出来到关闭结束这段期间。
@Test public void test(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User user1 = mapper.getUserById(1); System.out.println(user1); System.out.println("==================="); User user2 = mapper.getUserById(1); System.out.println(user2); System.out.println(user1==user2); sqlSession.close(); }
在上面的测试方法中,我们在一个sqlSession期间查询了两次id为1的用户信息,我们来看下查询的日志:
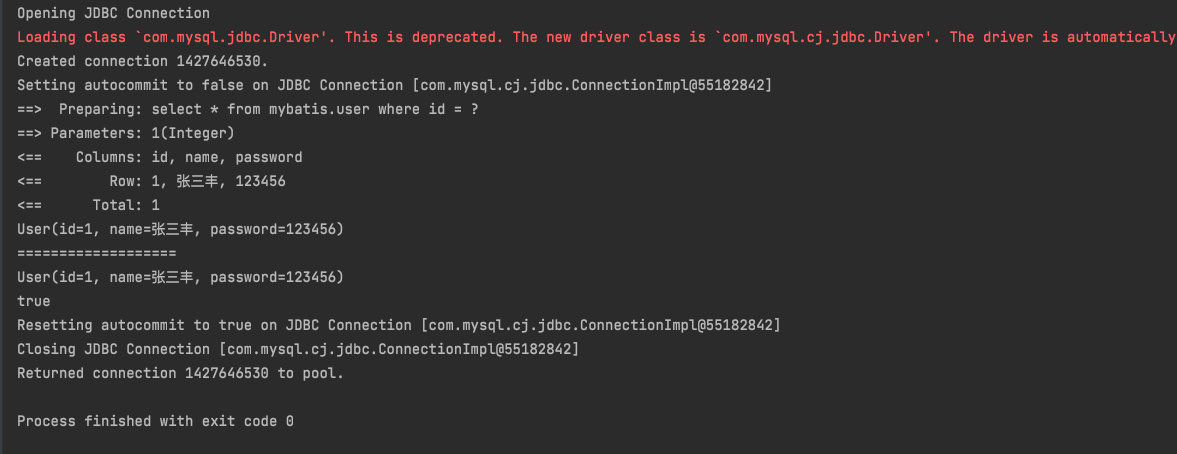
可以从日志中看到,查询的语句只执行了一次,第二次查询是直接获取到的结果,这就是从缓存中直接取出的;并且可以看到user1==user2返回的是true,说名两次查询的对象是同一个。
但是,一级缓存的作用域只在sqlSession中生效,如果是两个sqlSession查询了同样的语句,是不会共用缓存的。
@Test public void test(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); UserMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User user1 = mapper.getUserById(1); System.out.println(user1); System.out.println("==================="); User user2 = mapper2.getUserById(1); System.out.println(user2); System.out.println(user1==user2); sqlSession.close(); sqlSession2.close(); }
我们分别创建了两个sqlSession,分别去查询id=1的用户信息,我们看结果:
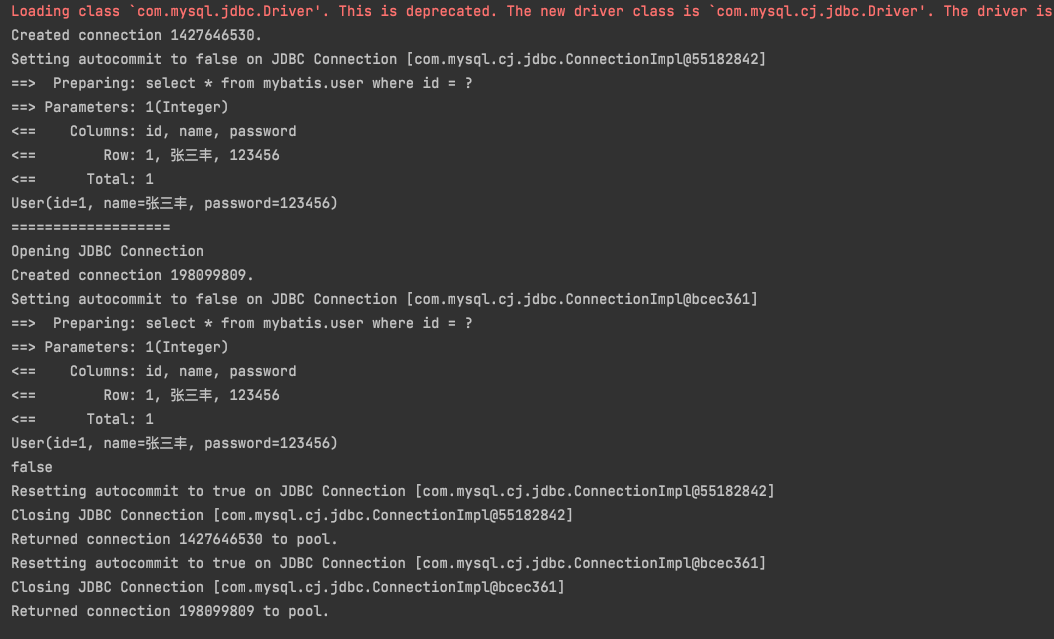
13.3、二级缓存
由于一级缓存的作用范围很小,可使用的场景很少;Mybatis提供了二级缓存的使用。
什么是二级缓存?
在一级缓存要被清理掉的时候,如果开启了二级缓存服务,则会将一级缓存中的信息存放到二级缓存中。二级缓存的作用域是namespace级别的,即一个Mapper.xml配置文件中的范围。
开启二级缓存
mybatis-config.xml
<settings> <setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/> <!--显式开启二级缓存--> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> </settings>
在需要开启二级缓存的Mapper.xml中增加cache标签
UserMapper.xml
<cache/> <cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>
上面是默认的配置,下面是使用自定义的配置:eviction是缓存的策略FIFO是先进先出策略,flushInterval刷新时间等等......
还有一点非常重要,要使用二级缓存,需要我们的实体类支持序列化
pojo/User.java
@Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class User implements Serializable { private int id; private String name; private String password; }
使用二级缓存
这样我们的二级缓存就可以使用了,我们还运行上面的2个sqlSession查询同样数据的测试。需要注意的是,只有在sqlSession关闭后才会将信息放入二级缓存,我们需要调整下顺序:
@Test public void test(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); UserMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User user1 = mapper.getUserById(1); System.out.println(user1); sqlSession.close(); System.out.println("==================="); User user2 = mapper2.getUserById(1); System.out.println(user2); sqlSession2.close(); System.out.println(user1==user2); }

可以看到日志中只查询了一次,二级缓存确实生效了。
需要注意的是,如果进行了更新操作(包含insert update delete)二级缓存会自动清空,因为查询的结果可能会有变化。例如在上面的例子中,增加一个更新id=2的用户密码的操作,那么在更新前后查询id=1的用户信息,仍会查询2次。
小结
- 只要开启了二级缓存,在同一个Mapper下都生效
- 所有的数据都会先放在一级缓存中
- 只有当会话提交或关闭的时候,才会提交到二级缓存中
13.4、Ehcache
略




【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步