Django-DRF中使用Elasticsearch ,使用IK分词
一.安装依赖
django-haystack==2.8.1 drf-haystack==1.8.6 Django==2.0.5 djangrestframework==3.8.2
elasticsearch==6.4.0
二.安装JAVA SDK
先到官网下载安装包:
下载链接:https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downloads-2133151.html
因为我装的Elasticsearch的版本是2.4.1,安装的JDK==1.8,ES 2.x后的版本使用haystack会有不兼容问题.

安装步骤:
# 首先:
cd /usr/local/
mkdir javajdk
# 将下载的文件上传到:
/usr/local/javajdk
# 将文件解压到此文件夹
tar -xzvf jdk-8u231-linux-i586.tar.gz
mv jdk1.8.0_231 java
# 配置环境变量:
vim /etc/profile
# 在文件最后添加这几行:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/javajdk/java
export JRE_HOME=${JAVA_HOME}/jre
export CLASSPATH=.:${JAVA_HOME}/lib:${JRE_HOME}/lib
export PATH=${JAVA_HOME}/bin:$PATH
# 然后
source /etc/profile
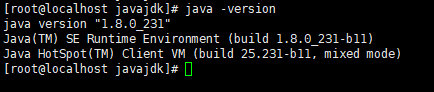
出现下面的提示则代表安装成功:
三.安装Elasticsearch
下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/past-releases#elasticsearch
要注意的是Elasticsearch在root用户下启动是会报错的!
首先要新建用户:
useradd -g elastic elastic # 在/home新建用户目录
mkdir elastic
# 将下载的安装包上传到 elastic 目录下
tar -xzvf elasticsearch-2.4.1.tar.gz -C /home/elastic/
# 给此目录授权 chown -R elastic:elastic elastic
# 切换用户
su - elastic
# 修改配置文件:
vim /home/elastic/elasticsearch-2.4.1/config/elasticsearch.yml
# 修改内容
path.data: /home/elastic/elasticsearch-2.4.1/data
path.logs: /home/elastic/elasticsearch-2.4.1/logs
network.host: 172.xxx.xxx.xxx
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
# 如果没有data与logs在相关目录下建立
# 启动ES,在elasticsearch的bin目录下:
./elasticsearch
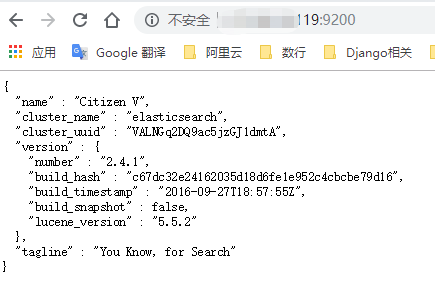
如果在浏览器中看到上面的内容,则表示安装成功!
如果出错解决方法:
1.最大文件描述符太少了,至少要65536,修改/etc/security/limits.conf文件 命令:vim /etc/security/limits.conf 内容修改为:* hard nofile 65536 2.一个进程可以拥有的VMA(虚拟内存区域)的数量太少了,至少要262144,修改文件 命令:vim /etc/sysctl.conf 增加内容为:vm.max_map_count=262144 3.最大线程太少了,至少要4096,修改/etc/security/limits.conf文件 命令:vim /etc/security/limits.conf 增加内容为:* hard nproc 65536
四.安装IK分词插件
下载安装包:
下载地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases?after=v5.0.0
所选版本应于ES版本对应:
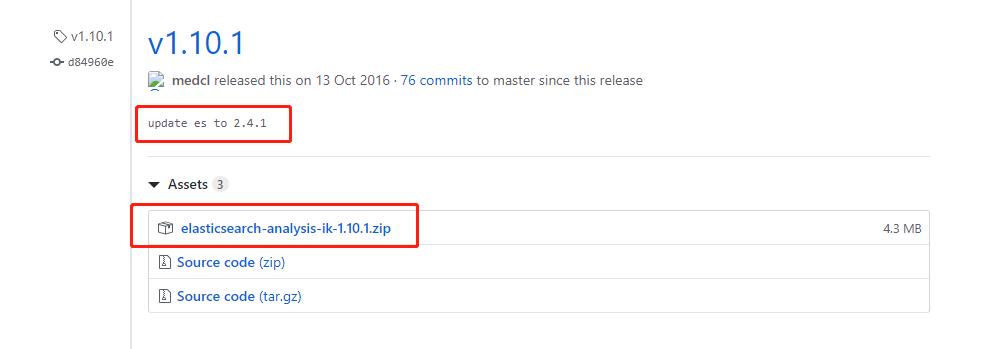
ES 2.4.1 对应 IK 版本是 1.10.1
将安装包解压到es的安装目录/plugin/ik
如果/plugin下面没有ik目录需要自己手动创建
五.可视化插件安装。
1.插件安装方式(推荐) #在Elasticsearch目录下 elasticsearch/bin/plugin install mobz/elasticsearch-head 2.下载安装方式 从https://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head下载ZIP包。 在 elasticsearch 目录下创建目录/plugins/head/_site 并且将刚刚解压的elasticsearch-head-master目录下所有内容COPY到当前创建的/plugins/head/_site/目录下即可。 需要注意的是在5.xx后的版本,安装方法与这个不一样! 3.重启elasticsearch访问: 访问地址是http://{你的ip地址}:9200/_plugin/head/ http 端口默认是9200
六.集群搭建
-
创建elasticsearch-cluster文件夹,在内部复制三个elasticsearch服务
-
修改每台服务器配置
修改elasticsearch-cluster\node*\config\elasticsearch.yml
如果在现有单机版本的基础上节点进行复制,需要注意的是,在当前节点的安装目录/elasticsearch/data中不能有数据,否则搭建集群会失败.需要删除data目录
# 节点1的配置信息
# 集群名称,保证唯一
cluster.name:my-elasticsearch
# 节点名称,必须不一样
node.name:node-1
# 必须为本机的ip地址
network.host:172.xxx.xxx.xxx
# 服务器端口号,在同一机器下必须不一样
http:port:9200
# 集群间通信端口号,在同一机器下必须不一样
transport.tcp.port:9300
# 设置集群自动发现机器ip集合
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.host:["172.xxx.xxx.xxx:9300",'172.xxx.xxx.xxx:9301',"172.xxx.xxx.xxx:9303"]
将服务启动即可
七.在Django中配置
首先要在app中创建一个 search_indexes.py 文件这是这django-haystack规定的
django-haystack:文档地址:https://django-haystack.readthedocs.io/en/master/tutorial.html#configuration
drf-haystack:文档地址:https://drf-haystack.readthedocs.io/en/latest/07_faceting.html#serializing-faceted-results
创建模型类:
from django.db import models
class Article(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=128)
files = models.FileField(upload_to='%Y/%m/')
content = models.TextField(default='')
创建索引类:
from haystack import indexes
from app001.models import Article
class DocsIndex(indexes.SearchIndex, indexes.Indexable):
# 1.构建的索引字段
text = indexes.CharField(document=True, use_template=True)
files = indexes.CharField(model_attr='files')
content = indexes.CharField(model_attr='content')
# 2.指定模型类
def get_model(self):
return Article
# 3.提供数据集
def index_queryset(self, using=None):
"""Used when the entire index for model is updated."""
return self.get_model().objects.all()
view视图:
mport os
import datetime
import uuid
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework import serializers
from rest_framework.response import Response
from django.conf import settings
from drf_haystack.serializers import HaystackSerializer
from drf_haystack.viewsets import HaystackViewSet
from .models import Article
from .search_indexes import DocsIndex
class DemoSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
"""
序列化器
"""
class Meta:
model = Article
fields = ('id', 'title','files')
class LocationSerializer(HaystackSerializer):
object = DemoSerializer(read_only=True) # 只读,不可以进行反序列化
class Meta:
# The `index_classes` attribute is a list of which search indexes
# we want to include in the search.
index_classes = [DocsIndex]
# The `fields` contains all the fields we want to include.
# NOTE: Make sure you don't confuse these with model attributes. These
# fields belong to the search index!
fields = [
"text","files","id","title"
]
class LocationSearchView(HaystackViewSet):
# `index_models` is an optional list of which models you would like to include
# in the search result. You might have several models indexed, and this provides
# a way to filter out those of no interest for this particular view.
# (Translates to `SearchQuerySet().models(*index_models)` behind the scenes.
index_models = [Article]
serializer_class = LocationSerializer
setting配置:
INSTALLED_APPS = [ 'django.contrib.admin', 'django.contrib.auth', 'django.contrib.contenttypes', 'django.contrib.sessions', 'django.contrib.messages', 'django.contrib.staticfiles', 'rest_framework', 'silk', 'debug_toolbar', 'haystack', 'app001', ]
# 搜索引擎配置:
# haystack配置
HAYSTACK_CONNECTIONS = {
'default': {
# 'ENGINE': 'haystack.backends.elasticsearch_backend.ElasticsearchSearchEngine',
'ENGINE': 'app001.elasticsearch_ik_backend.IKSearchEngine', # 如果配置分词需要重新制定引擎,下面会写到
'URL': 'http://172.16.xxx.xxx:9200/', # elasticseach 服务地址
'INDEX_NAME': 'haystack', # 索引名称
},
}
# 保持索引都是最新的
HAYSTACK_SIGNAL_PROCESSOR = 'haystack.signals.RealtimeSignalProcessor'
# 搜索显示的最多条数
HAYSTACK_SEARCH_RESULTS_PER_PAGE = 50
重写ik分词配置引擎:
在app中建立 elasticsearch_ik_backend.py 文件:
from haystack.backends.elasticsearch_backend import ElasticsearchSearchBackend from haystack.backends.elasticsearch_backend import ElasticsearchSearchEngine class IKSearchBackend(ElasticsearchSearchBackend): DEFAULT_ANALYZER = "ik_max_word" # 这里将 es 的 默认 analyzer 设置为 ik_max_word def __init__(self, connection_alias, **connection_options): super().__init__(connection_alias, **connection_options) def build_schema(self, fields): content_field_name, mapping = super(IKSearchBackend, self).build_schema(fields) for field_name, field_class in fields.items(): field_mapping = mapping[field_class.index_fieldname] if field_mapping["type"] == "string" and field_class.indexed: if not hasattr( field_class, "facet_for" ) and not field_class.field_type in ("ngram", "edge_ngram"): field_mapping["analyzer"] = getattr( field_class, "analyzer", self.DEFAULT_ANALYZER ) mapping.update({field_class.index_fieldname: field_mapping}) return content_field_name, mapping class IKSearchEngine(ElasticsearchSearchEngine): backend = IKSearchBackend
在django中使用drf-haystack对查询还不是很全:
在这我使用python 的 elasticsearch 进行查询:def-haystack的查询我觉得并不是很好用:
class EsSearch(APIView): def get(self,request): es = Elasticsearch(["http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:9200"]) query = request.GET.get("query")
# 这里面的搜索方式可以定制你自己想要用的查询:
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/match-query.html
body = { "query":{ "multi_match": { "query": "%s" % query, "fields": [ "text", "content" ] } }, "highlight":{ "fields":{ "content":{}, "text":{} } } } result = es.search(index="haystack", doc_type="modelresult", body=body) return Response(result)
url配置:
"""tool_bar URL Configuration The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/topics/http/urls/ Examples: Function views 1. Add an import: from my_app import views 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', views.home, name='home') Class-based views 1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', Home.as_view(), name='home') Including another URLconf 1. Import the include() function: from django.urls import include, path 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('blog/', include('blog.urls')) """ from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path from django.conf import settings from django.conf.urls import url,include from django.conf.urls.static import static from django.conf import settings from app001.views import Index,Uploads from rest_framework import routers from app001.views import LocationSearchView,EsSearch from app002.views import BlogView # drf-haystack查询 router = routers.DefaultRouter() router.register("search", LocationSearchView,base_name="location-search") urlpatterns = [ # 使用自定义查询 url(r'elastic_search/',EsSearch.as_view()),
url(r"api/", include(router.urls)),
]
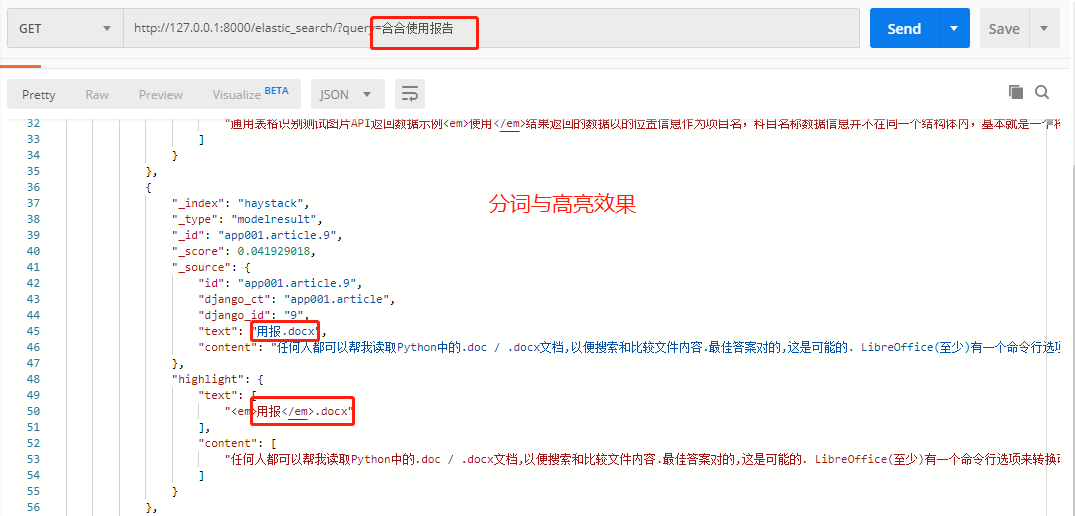
查询展示: