如何判断一颗二叉树是否是搜索二叉树
什么是搜索二叉树?
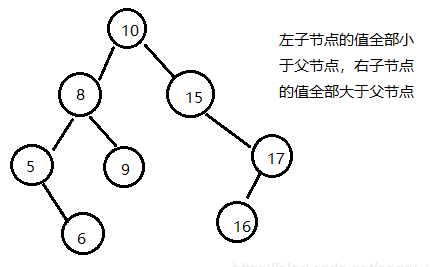
可知,如果对二叉搜索树进行中序排列(左中右),那么会得到一个从小到大的序列。
因此,如果用中序遍历搜索二叉树,肯定是一个升序的过程
判断一颗二叉树是否是搜索二叉树可以用中序遍历(递归/非递归)代码进行改写
package Algorithms.tree; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Stack; public class IsBST { public static void main(String[] args) { Node head = new Node(10); head.left = new Node(8); head.right = new Node(15); head.left.left = new Node(5); head.left.right = new Node(9); head.right.right = new Node(17); head.left.left.right = new Node(6); head.right.right.left = new Node(16); System.out.println(isBST1(head)); //true System.out.println(isBST2(head)); //true System.out.println(isBST3(head)); //true System.out.println(isBST(head)); //true } public static class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } public static int preValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE; //方式1:递归动态遍历比较(中序递归遍历代码改写) public static boolean isBST1(Node head) { if (head == null) { //空树,是搜索二叉树 return true; } boolean isLeftBST = isBST1(head.left); //检查左数是不是搜索二叉树 if (!isLeftBST) { return false; } //由打印变成比较 if (head.value <= preValue) { return false; } else { preValue = head.value; } return isBST1(head.right); //进行上面操作之后,如果右树是搜索二叉树那就返回true } //方式2:中序遍历添加到LinkedList中,再for循环遍历比较 public static boolean isBST2(Node head) { if (head == null) { return true; } LinkedList<Node> inOrderList = new LinkedList<>(); //用来存中序遍历的Node process(head, inOrderList); int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE; //记录上一次处理的数 for (Node cur : inOrderList) { if (cur.value <= pre) { return false; } pre = cur.value; } return true; } //中序遍历二叉树,把遍历的结果放在inOrderList中 public static void process(Node node, LinkedList<Node> inOrderList) { if (node == null) { return; } process(node.left, inOrderList); inOrderList.add(node); process(node.right, inOrderList); } //方式3:非递归 public static boolean isBST3(Node head) { if (head != null) { int preValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE; Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) { if (head != null) { //1、把当前节点所有的左节点压栈 stack.push(head); head = head.left; } else { //所有左节点压栈之后 head = stack.pop(); //2、弹出一个节点,比较 if (head.value <= preValue) { return false; } else { preValue = head.value; } head = head.right; //3、然后移动到弹出节点的右节点上面,循环以上步骤 } } } return true; } //方式4:递归处理二叉树的套路来判断是否为搜索二叉树(树型DP) //如果是搜索二叉树(头节点head),要满足: //1、左子树是二叉树 //2、右子树是二叉树 //3、左子树的最大值max < head.value //4、右子树的最小值min > head.value //使用递归完成的话左右子树的要求得一样,但条件3/4明显有冲突, //因此我们一律返回三个要素:当前树是否为搜索二叉树、当前树的最大值与最小值 //定义返回值的类型 public static class ReturnData { public boolean isBST; public int min; public int max; public ReturnData(boolean isBST, int min, int max) { this.isBST = isBST; this.min = min; this.max = max; } } public static ReturnData process(Node x) { if (x == null) { return null; } ReturnData leftData = process(x.left); //默认可以找左树要信息 ReturnData rightData = process(x.right);//默认可以找右树要信息 //利用左右树信息求整个树左右子树的最小值与最大值 int min = x.value; int max = x.value; if (leftData != null) { min = Math.min(min, leftData.min); max = Math.max(max, leftData.max); } if (rightData != null) { min = Math.min(min, rightData.min); max = Math.max(max, rightData.max); } //利用左右子树信息求整个子树是否为搜索二叉树 boolean isBST = true; //列举所有违规条件 if (leftData != null && (!leftData.isBST || leftData.max >= x.value)) { isBST = false; } if (rightData != null && (!rightData.isBST || x.value >= rightData.min)) { isBST = false; } // boolean isBST = false; // if ( // (leftData!=null?(leftData.isBST && leftData.max <x.value):true)&& // (rightData!=null?(rightData.isBST && rightData.min>x.value):true) // ){ // isBST = true; // } return new ReturnData(isBST, min, max); } //主函数 public static boolean isBST(Node head) { return process(head).isBST; } }


