hystrix-go
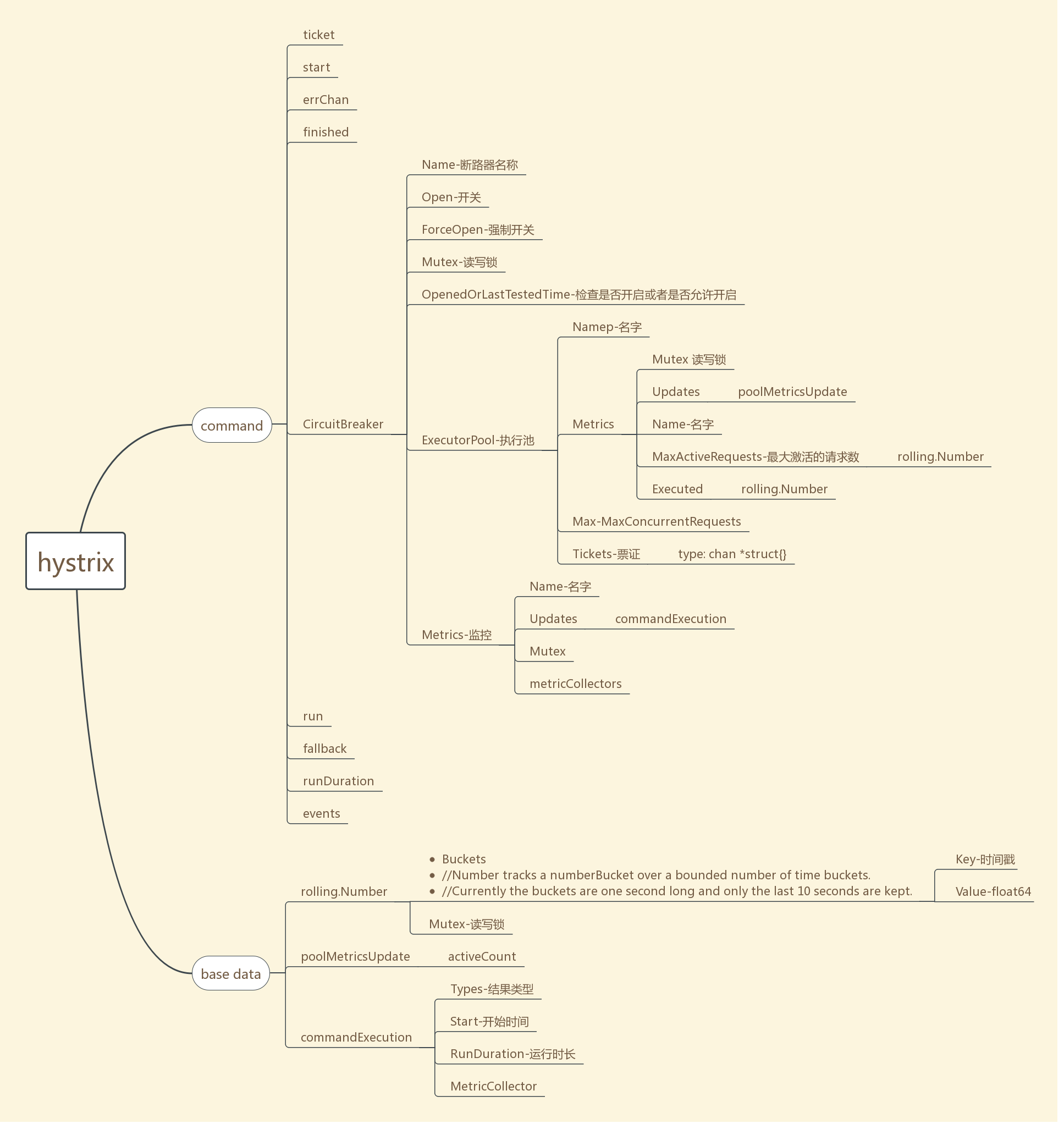
hystrix-go 源码分析
统计器
- 默认统计器
type DefaultMetricCollector struct {
mutex *sync.RWMutex
numRequests *rolling.Number
errors *rolling.Number
successes *rolling.Number //调用次数
failures *rolling.Number //失败次数
rejects *rolling.Number //拒绝次数
shortCircuits *rolling.Number
timeouts *rolling.Number
contextCanceled *rolling.Number
contextDeadlineExceeded *rolling.Number
fallbackSuccesses *rolling.Number
fallbackFailures *rolling.Number
totalDuration *rolling.Timing
runDuration *rolling.Timing
}
计数
type Number struct {
Buckets map[int64]*numberBucket //key 当前时间 value:次数
Mutex *sync.RWMutex
}
type numberBucket struct {
Value float64
}
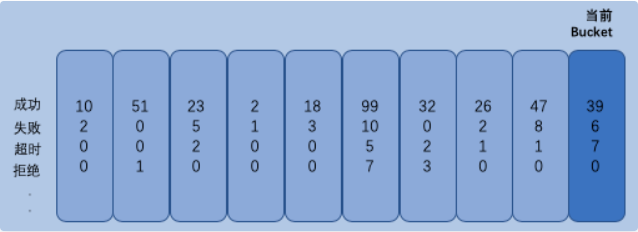
10秒统计原理(rolling window)
字典字段Buckets map[int64]*numberBucket 中的Key保存的是当前时间
可能你会好奇Number是如何保证只保存10秒内的数据的。每一次对熔断器的状态进行修改时,Number都要先得到当前的时间(秒级)的Bucket不存在则创建。
- 获取当前bucket
func (r *Number) getCurrentBucket() *numberBucket {
now := time.Now().Unix()
var bucket *numberBucket
var ok bool
if bucket, ok = r.Buckets[now]; !ok {
bucket = &numberBucket{}
r.Buckets[now] = bucket
}
return bucket
}
- 移除过期bucket
func (r *Number) removeOldBuckets() {
now := time.Now().Unix() - 10
for timestamp := range r.Buckets {
// TODO: configurable rolling window
if timestamp <= now {
delete(r.Buckets, timestamp)
}
}
}
- 增加当前bucket 计数
// Increment increments the number in current timeBucket.
func (r *Number) Increment(i float64) {
if i == 0 {
return
}
r.Mutex.Lock()
defer r.Mutex.Unlock()
b := r.getCurrentBucket() //获取当前bucket(没有则创建)
b.Value += i // 计数++
r.removeOldBuckets() // 移除过期bucket
}
流量控制
hystrix-go对流量控制的代码是很简单的。用了一个简单的令牌算法,能得到令牌的就可以执行后继的工作,执行完后要返还令牌。得不到令牌就拒绝,拒绝后调用用户设置的callback方法,如果没有设置就不执行。
结构体executorPool就是hystrix-go流量控制的具体实现。字段Max就是每秒最大的并发值。
type executorPool struct {
Name string
Metrics *poolMetrics
Max int
Tickets chan *struct{} // 并发控制
}
-
在创建
executorPool的时候,会根据Max值来创建令牌。Max值如果没有设置会使用默认值10p.Max = getSettings(name).MaxConcurrentRequests //添加var circuitSettings map[string]*Settings
记录
func newExecutorPool(name string) *executorPool {
p := &executorPool{}
p.Name = name
p.Metrics = newPoolMetrics(name)
p.Max = getSettings(name).MaxConcurrentRequests
p.Tickets = make(chan *struct{}, p.Max)
for i := 0; i < p.Max; i++ {
p.Tickets <- &struct{}{}
}
return p
}
- 返回令牌
func (p *executorPool) Return(ticket *struct{}) {
if ticket == nil {
return
}
p.Metrics.Updates <- poolMetricsUpdate{
activeCount: p.ActiveCount(),
}
p.Tickets <- ticket
}
- 通过channel 获取拿到令牌,使用完在返回到channel中
select {
case cmd.ticket = <-circuit.executorPool.Tickets:
ticketChecked = true
ticketCond.Signal()
cmd.Unlock()
default:
ticketChecked = true
ticketCond.Signal()
cmd.Unlock()
returnOnce.Do(func() {
returnTicket()
cmd.errorWithFallback(ctx, ErrMaxConcurrency)
reportAllEvent()
})
return
}
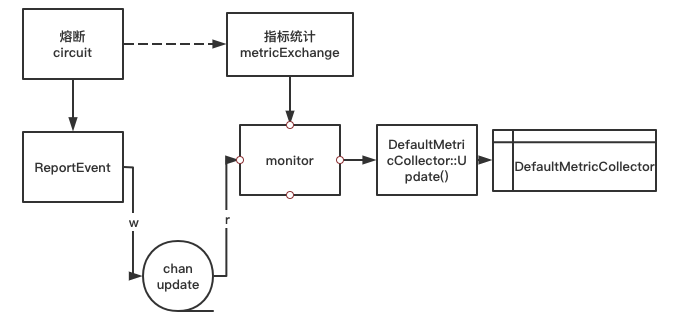
上报执行状态信息
- 指标
type metricExchange struct {
Name string
Updates chan *commandExecution
Mutex *sync.RWMutex
metricCollectors []metricCollector.MetricCollector
}
circuit.metrics.Updates这个信道就是处理上报信息的,上报执行状态自信的结构是metricExchange,结构体很简单只有4个字段。要的就是- 断路器circuit 通过channel 信息传输
func newMetricExchange(name string) *metricExchange {
m := &metricExchange{}
m.Name = name
m.Updates = make(chan *commandExecution, 2000)
m.Mutex = &sync.RWMutex{}
m.metricCollectors = metricCollector.Registry.InitializeMetricCollectors(name)
m.Reset()
go m.Monitor()
return m
}
- 启动一个协程
go m.Monitor()去监控Updates的数据,然后上报给metricCollectors保存执行的信息数据比如前面提到的调用次数,失败次数,被拒绝次数,熔断次数等等
func (m *metricExchange) Monitor() {
for update := range m.Updates {
// we only grab a read lock to make sure Reset() isn't changing the numbers.
m.Mutex.RLock()
totalDuration := time.Since(update.Start)
wg := &sync.WaitGroup{}
for _, collector := range m.metricCollectors {
wg.Add(1)
go m.IncrementMetrics(wg, collector, update, totalDuration)
}
wg.Wait()
m.Mutex.RUnlock()
}
}
go m.IncrementMetrics解析
func (m *metricExchange) IncrementMetrics(wg *sync.WaitGroup, collector metricCollector.MetricCollector, update *commandExecution, totalDuration time.Duration) {
// granular metrics
r := metricCollector.MetricResult{
Attempts: 1,
TotalDuration: totalDuration,
RunDuration: update.RunDuration,
ConcurrencyInUse: update.ConcurrencyInUse,
}
// ...
collector.Update(r)
wg.Done()
}
collector.Update(r)统计保存
command
type command struct {
sync.Mutex
ticket *struct{} // 票、令牌(令牌桶)
start time.Time //开始时间
errChan chan error
finished chan bool //是否执行完成
circuit *CircuitBreaker // 断路器
run runFuncC //执行函数(自定义)
fallback fallbackFuncC //失败回调函数
runDuration time.Duration //耗时
events []string //执行结果存储信息
}
command config
type CommandConfig struct {
Timeout int `json:"timeout"` // 超时时间定义
MaxConcurrentRequests int `json:"max_concurrent_requests"` // 最大并发请求数
RequestVolumeThreshold int `json:"request_volume_threshold"` // 一个统计窗口10秒内请求数量。达到这个请求数量后才去判断是否要开启熔断
SleepWindow int `json:"sleep_window"` // 熔断后可以重试的时间
ErrorPercentThreshold int `json:"error_percent_threshold"` // 请求出错比
}
- Timeout: 执行command的超时时间。
默认时间是1000毫秒 - MaxConcurrentRequests:command的最大并发量
默认值是10 - SleepWindow:当熔断器被打开后,SleepWindow的时间就是控制过多久后去尝试服务是否可用了。
默认值是5000毫秒 - RequestVolumeThreshold: 一个统计窗口10秒内请求数量。达到这个请求数量后才去判断是否要开启熔断。
默认值是20 - SleepWindow::熔断后可以重试的时间
- ErrorPercentThreshold:错误百分比,请求数量大于等于
RequestVolumeThreshold并且错误率到达这个百分比后就会启动熔断默认值是50
流程
func GoC(ctx context.Context, name string, run runFuncC, fallback fallbackFuncC) chan error {
cmd := &command{
run: run,
fallback: fallback,
start: time.Now(),
errChan: make(chan error, 1),
finished: make(chan bool, 1),
}
// dont have methods with explicit params and returns
// let data come in and out naturally, like with any closure
// explicit error return to give place for us to kill switch the operation (fallback)
circuit, _, err := GetCircuit(name) //得到断路器,不存在则创建
if err != nil {
cmd.errChan <- err
return cmd.errChan
}
cmd.circuit = circuit
ticketCond := sync.NewCond(cmd)
ticketChecked := false
// When the caller extracts error from returned errChan, it's assumed that
// the ticket's been returned to executorPool. Therefore, returnTicket() can
// not run after cmd.errorWithFallback().
returnTicket := func() { // 返还ticket
cmd.Lock()
// Avoid releasing before a ticket is acquired.
for !ticketChecked {
ticketCond.Wait()
}
cmd.circuit.executorPool.Return(cmd.ticket)
cmd.Unlock()
}
// Shared by the following two goroutines. It ensures only the faster
// goroutine runs errWithFallback() and reportAllEvent().
returnOnce := &sync.Once{} //最后执行结束阶段
reportAllEvent := func() { // 上报执行状态
err := cmd.circuit.ReportEvent(cmd.events, cmd.start, cmd.runDuration)
if err != nil {
log.Printf(err.Error())
}
}
go func() {
defer func() { cmd.finished <- true }()
// Circuits get opened when recent executions have shown to have a high error rate.
// Rejecting new executions allows backends to recover, and the circuit will allow
// new traffic when it feels a healthly state has returned.
if !cmd.circuit.AllowRequest() { // 查看断路器是否已打开
cmd.Lock()
// It's safe for another goroutine to go ahead releasing a nil ticket.
ticketChecked = true
ticketCond.Signal()
cmd.Unlock()
returnOnce.Do(func() {
returnTicket()
cmd.errorWithFallback(ctx, ErrCircuitOpen)
reportAllEvent()
})
return
}
// As backends falter, requests take longer but don't always fail.
//
// When requests slow down but the incoming rate of requests stays the same, you have to
// run more at a time to keep up. By controlling concurrency during these situations, you can
// shed load which accumulates due to the increasing ratio of active commands to incoming requests.
cmd.Lock()
select { // 获取ticket 如果得不到就限流
case cmd.ticket = <-circuit.executorPool.Tickets:
ticketChecked = true
ticketCond.Signal()
cmd.Unlock()
default: //未得到令牌,则返回错误
ticketChecked = true
ticketCond.Signal()
cmd.Unlock()
returnOnce.Do(func() {
returnTicket()
cmd.errorWithFallback(ctx, ErrMaxConcurrency)
reportAllEvent()
})
return
}
// 执行我们自已的方法,并上报执行信息
runStart := time.Now()
runErr := run(ctx)
returnOnce.Do(func() {
defer reportAllEvent()
cmd.runDuration = time.Since(runStart)
returnTicket()
if runErr != nil {
cmd.errorWithFallback(ctx, runErr)
return
}
cmd.reportEvent("success")
})
}()
go func() { // 等待context是否被结束,或执行者超时,并上报
timer := time.NewTimer(getSettings(name).Timeout)
defer timer.Stop()
select {
case <-cmd.finished:
// returnOnce has been executed in another goroutine
case <-ctx.Done():
returnOnce.Do(func() {
returnTicket()
cmd.errorWithFallback(ctx, ctx.Err())
reportAllEvent()
})
return
case <-timer.C: //超时 处理
returnOnce.Do(func() {
returnTicket()
cmd.errorWithFallback(ctx, ErrTimeout)
reportAllEvent()
})
return
}
}()
return cmd.errChan
}