Spring Boot(二):数据库操作
本文主要讲解如何通过spring boot来访问数据库,本文会演示三种方式来访问数据库,第一种是JdbcTemplate,第二种是JPA,第三种是Mybatis。之前已经提到过,本系列会以一个博客系统作为讲解的基础,所以本文会讲解文章的存储和访问(但不包括文章的详情),因为最终的实现是通过MyBatis来完成的,所以,对于JdbcTemplate和JPA只做简单演示,MyBatis部分会完整实现对文章的增删改查。
一、准备工作
在演示这几种方式之前,需要先准备一些东西。第一个就是数据库,本系统是采用MySQL实现的,我们需要先创建一个student的表:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(10) default NULL,
`age` varchar(10) default NULL,
`schoolName` varchar(55) default NULL,
`createTime` datetime default NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
后续的演示会对这个表进行增删改查。另外配置文件使用properties配置,即application.properties(你也可以使用application.yml配置文件,没什么太大的区别,如果对ymal不熟悉,有兴趣也可以查一下,比较简单)。
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/databasezfy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456
最后,我们还需要建立与数据库对应的POJO类,代码如下:
public class Student implements Serializable{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 5465872778586910807L; private String id; private String name; private String age; private String schoolName; private Date createTime; }
好了,需要准备的工作就这些,现在开始实现数据库的操作。
二、与JdbcTemplate集成
首先,我们先通过JdbcTemplate来访问数据库,这里只演示数据的插入,上一篇文章中我们已经提到过,Spring boot提供了许多的starter来支撑不同的功能,要支持JdbcTemplate我们需要引入下面的starter和连接mysql的驱动:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.34</version> </dependency>
现在我们就可以通过JdbcTemplate来实现数据的插入了:
public interface StudentDao { int insertStudent(Student student); }
@Repository public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{ @Autowired private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Override public int insertStudent(Student student) { String sql = "insert into student (id,name,age,schoolName,createTime) values (:id,:name,:age,:schoolName,:createTime)"; Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("id",student.getId()); map.put("name",student.getName()); map.put("age",student.getAge()); map.put("schoolName",student.getSchoolName()); map.put("createTime",student.getCreateTime()); int result = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, map); return result; } }
我们通过JUnit来测试上面的代码:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = DemoApplication.class) public class StudentDaoTest { @Autowired private StudentDao studentDao; @Test public void testInsert(){ Student student = new Student(); student.setId("1"); student.setName("zs"); student.setAge("10"); student.setSchoolName("一中"); student.setCreateTime(new Date()); studentDao.insertStudent(student); } }
测试结果:test passed
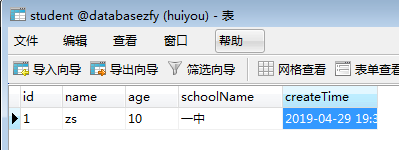
表中也插入了一条数据:
目录结构:

三、与JPA集成
JPA是Java Persistence API的简称,中文名Java持久层API,是JDK 5.0注解或XML描述对象-关系表的映射关系,并将运行期的实体对象持久化到数据库中。
现在我们开始讲解如何通过JPA的方式来实现数据库的操作。还是跟JdbcTemplate类似,首先,我们需要引入对应的starter:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
然后我们需要对POJO类增加Entity的注解,并指定表名(如果不指定,默认的表名为student),然后需要指定表主键ID所在的get方法,这些都是JPA的知识,与Spring boot无关,如果不熟悉的话可以看下JPA的知识点,注意注解所在的包,别引错包。
@Entity @Table(name = "student") public class Student implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 5465872778586910807L; private String id; private String name; private String age; private String schoolName; private Date createTime; @Id public String getId() { return id; } ................................. ................................. }
最后,我们需要继承JpaRepository这个类,这里我们实现了两个查询方法,第一个是符合JPA命名规范的查询(方法名写的时候会有提示),JPA会自动帮我们完成查询语句的生成,另一种方式是我们自己实现JPQL(JPA支持的一种类SQL的查询),这里举例使用第一种的查询
public interface StudentRepository extends JpaRepository<Student,String>{ public Student findStudentById(String id); }
JpaRepository<Student,String>中的参数表明实体和主键类型。
好了,我们可以再测试一下上面的代码:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = DemoApplication.class) public class StudentRepositoryTest { @Autowired private StudentRepository studentRepository; @Test public void testQuery(){ Student studentById = studentRepository.findStudentById("1"); System.out.println(studentById); } }
测试结果:报错
Caused by: com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.jdbc4.MySQLSyntaxErrorException: Unknown column 'student0_.create_time' in 'field list'
at sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.java:45)
at java.lang.reflect.Constructor.newInstance(Constructor.java:423)
at com.mysql.jdbc.Util.handleNewInstance(Util.java:377)
at com.mysql.jdbc.Util.getInstance(Util.java:360)
原因:类的属性,表字段命名是驼峰命名法(createTime),Spring data jpa 在操作表的时候,生成的sql语句中却是create_time, 表字段不对照,解决方法参见:jpa数据库表实体命名规则 Unknown column 'user0_.create_time' in 'field list',生成的sql语句时无修改命名,即在application.properties配置文件中加入
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.physical-strategy=org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.PhysicalNamingStrategyStandardImpl
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/databasezfy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.physical-strategy=org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.PhysicalNamingStrategyStandardImpl
在测试一下:test passed

四、与MyBatis集成
最后,我们再看看如何通过MyBatis来实现数据库的访问。同样我们还是要引入starter:
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.1.1</version> </dependency>
由于该starter不是spring boot官方提供的,所以版本号于Spring boot不一致,需要手动指定。
MyBatis一般可以通过XML或者注解的方式来指定操作数据库的SQL,个人比较偏向于XML,所以,本文中也只演示了通过XML的方式来访问数据库。首先,我们需要配置mapper的目录。我们在application.properties中进行配置:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/databasezfy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 mybatis.config-locations=mybatis/mybatis-config.xml mybatis.mapper-locations=mybatis/mapper/*.xml
这里配置主要包括两个部分,一个是mybatis自身的一些配置,例如基本类型的别名,是否支持缓存。第二个是指定mapper文件的位置。这个配置也可以通过 Java configuration来实现,由于篇幅的问题,我这里就不详述了,有兴趣的朋友可以自己实现一下。
配置完后,我们先编写mapper对应的接口:
@Service public interface StudentMapper { public int insertStudent(Student student); }
该接口暂时只定义了一个方法,即插入操作。这是一个接口,并且和JPA类似,可以不用实现类。接下来我们编写XML文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.example.demo.dao.StudentMapper"> <sql id="base_column"> id,name,age,schoolName,createTime </sql> <insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="com.example.demo.entity.Student"> INSERT INTO student(<include refid="base_column"/>) VALUES (#{id},#{name},#{age},#{schoolName},#{createTime}) </insert> </mapper>
好了,与MyBatis的集成也完成了,我们再测试一下:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoApplication.class)
public class StudentMapperTest {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Test
public void testInsert() {
Student student = new Student();
student.setId("2");
student.setName("ls");
student.setAge("11");
student.setSchoolName("erzhong");
student.setCreateTime(new Date());
studentMapper.insertStudent(student);
}
}
测试一下,会发现报错
org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException: Error creating bean with name 'com.example.demo.dao.StudentMapperTest': Unsatisfied dependency expressed through field 'studentMapper'; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.example.demo.dao.StudentMapper' available: expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate. Dependency annotations: {@org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true)}
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$AutowiredFieldElement.inject(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:596) ~[spring-beans-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata.inject(InjectionMetadata.java:90) ~[spring-beans-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
No qualifying bean of type 'com.example.demo.dao.StudentMapper' available,也就是说StudentMapperTest中依赖的StudentMapper unavaliable,即找不到StudentMapper类。所以在启动DemoApplication需要扫描StudentMapper类,加上@MapperScan注解扫描j将*Mapper扫描进来。@MapperScan注解
@SpringBootApplication @MapperScan("com.example.demo.dao") public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); } }
在测试一下:

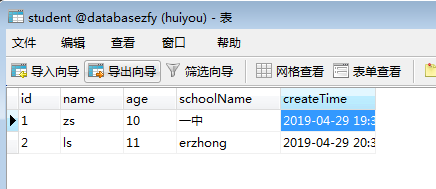
插入成功:
捋一下StudentMapperTest整个插入操作执行的过程:
①加载Application这个类,扫描com.example.demo.dao包下的所有Mapper
②这样就可以通过@Autowired注解引入StudentMapper,执行insertStudent方
③通过配置文件application.properties中的mybatis.mapper-locations=mybatis/mapper/*.xml定位到*.xml文件,最后通过nameSpace即StudentMapper所在的路径(com.example.demo.dao.StudentMapper)和SQL语句中的id即方法名(insertStudent)唯一标识对应的SQL语句。
附上目录结构:
五、总结
本文演示Spring boot与JdbcTemplate、JPA以及MyBatis的集成,整体上来说配置都比较简单,以前做过相关配置的同学应该感觉比较明显,Spring boot确实在这方面给我们提供了很大的帮助。后续的文章中我们只会使用MyBatis这一种方式来进行数据库的操作。
参考资料:




