python写入excel数据xlwt模块
xlwt模块介绍
把内容写入excel表的模块
xlwt模块的使用
创建excel文件
#导入模块
import xlwt
# 创建一个workbook 设置编码
workbook = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8')
# 创建一个worksheet
file = workbook.add_sheet('POS运营简报')
保存写入的excel数据
# 保存excel文件
workbook.save(excel_filepath)
写入
一个单元格写入
file.write(row, column,content)
# 注: row和colum从0开始
例子:
file.write(1,1,'zezhou')
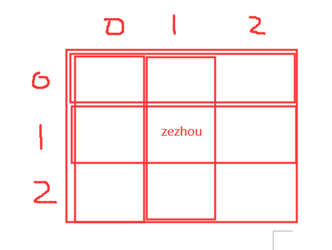
合并单元格写入
file.write_merge(row1,row2,column1,column2,content)
例子:
file.write_merge(1,3,0,1,'zezhou')

设置样式
加边框
style = XFStyle()
# 边框
borders = Borders()
borders.left = 1
borders.right = 1
borders.top = 1
borders.bottom = 1
# 赋值
style.borders = borders
# 写入
file.write(1,1,'zezhou',style)
居中
style = XFStyle()
al = xlwt.Alignment()
al.horz = 0x02 # 设置水平居中
al.vert = 0x01 # 设置垂直居中
# 赋值
style.alignment = al
file.write(1,1,'zezhou',style)
字体样式
1.调整字体大小
# 创建一个文本格式,包括字体、字号和颜色样式特性
fnt = Font()
fnt.height = 20 * 20 # 第一个20默认,第二个字号
# 赋值
style.font = fnt
file.write(1,1,'zezhou',style)
2.加粗字体
fnt.blod = True
自动换行
# 默认用xlwt写入的内容是不会换行的
# 设置后内容超出自动换行或者是遇到\n自动换行
style.alignment.wrap = 1 # 自动换行
设置行高
tall_style = xlwt.easyxf('font:height 700;')
file.row(0).set_style(tall_style) # 0表示第一行
设置列宽
file.col(0).width = 512 * 7 # 0表示第一行,256表示一个字符,512我试的差不多一个文字
把excel格式数据写入内存中的例子写法:
import xlwt from io import BytesIO def write_excel(data=[]): # print(data) # 操作内存的 stream = BytesIO() # 写入excel格式数据 workbook = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8') file = workbook.add_sheet('出行记录数据') # 标题 title = ["序号", "客人名称", "手机号", "体温", "餐厅名称", "进入时间", "出去时间"] for col_index in range(0, len(title)): file.write(0, col_index, title[col_index]) # 主体数据 for row_index in range(1, len(data)+1): temp = data[row_index-1] file.write(row_index, 0, row_index) for col_index in range(1, len(temp)+1): value = temp[col_index - 1] # datime数据转下格式 if isinstance(value, datetime.datetime): value = value.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') file.write(row_index, col_index, value) # 文件内容保存在内存中 workbook.save(stream) # 直接从内存中返回数据 return stream.getvalue() if __name__ == '__main__': value = write_excel() f = open(file="temp.xls", mode="wb") f.write(value) f.close()
# 使用场景: 当前端a标签请求后端拿excel文件,后端及时生成excel,不写入到硬盘时侯使用。



