微服务架构 | 服务监控与隔离 - [Sentinel]
§1 简介
下面内容摘要自 github alibaba/Sentinel 介绍
Sentinel 是用于 维护微服务架构稳定性 的组件,稳定性 包括:
- 流量控制
- 流量路由
- 熔断降级
- 系统自适应过载保护
- 热点流量防护
优点:
- 泛用性强:适用多种场景,秒杀(突发流量控制)、消息削峰填谷、集群流量控制、实时熔断等
- 实时监控:可以提供 500 台以下集群集群中每台集群的秒级监控数据
- 易用性高:与 Spring Cloud、Apache Dubbo、gRPC、Quarkus 的整合开箱即用
- 多语言支持: 提供 Java/Go/C++ 等多语言的原生实现
- 扩展性高:通过 SPI 扩展接口,快速实现定制逻辑,如定制规则管理、适配动态数据源等
与 Hystrix对比,Hystrix 传送门在此
| Hystrix | Sentinel | |
|---|---|---|
| 提供服务 | 耦合于项目 | 独立组件独立部署 |
| 提供管理 | 需要 dashboard 配合搭建管理端 | 默认提供页面化细粒度统一配置 |
| 隔离策略 | 信号量(并发线程数限流) | 信号量 / 线程池 |
| 熔断降级策略 | 基于RT / 异常比例 / 异常数 | 基于异常比例 |
| 实时统计实现 | 滑动窗口(LeapArray) | 滑动窗口(RxJava) |
| 动态规则配置 | 多种数据源 | 多种数据源 |
| 扩展性 | 多扩展点(Slot) | 插件的形式 |
| 注解 | √ | √ |
| 限流 | 基于 QPS,支持基于调用关系的限流(关联、链路) | 有限支持 |
§2 概念和原理
sentinel 的核心视角
sentinel 具有比较独特的核心视角
- 将微服务架构中所有需要被监控和控制的东西,全部视为 资源(resource)
- 将可以对 资源(resource) 施行的监控和控制的各个方面,全都视为 功能插槽(slot chain)
- 将具有控制行为的 功能插槽(slot chain) 的控制依据,全部视为 规则(rule)
资源(resource)
官网说明
资源(resource) 是 Sentinel 中的核心概念之一。最常用的资源是我们代码中的 Java 方法。 当然,您也可以更灵活的定义你的资源,例如,把需要控制流量的代码用 Sentinel API SphU.entry("HelloWorld") 和 entry.exit() 包围起来即可。
resource 的本体是服务中的接口,微服务架构中所有需要被监控和控制的都是其中的接口,包括
- 服务本身
- 服务中的一个方法
- 可以声明成方法,但省略了声明这一形式的一段逻辑(方法本身就是对逻辑的包装),这就是上文官网说明举的例子
resource 是 sentinel 看待 resource 的本体——即服务中的接口——的角度。
在 sentinel 的视角,服务中的接口是可以监控和进行隔离操作的,sentinel 的作用主要就是把这些接口,摆出十八般模样,因此称呼它们为 资源(resource)。类似厨师对待食材的视角。
resource 的声明
官网提供了 3 类、共计 5 种声明方式,
- 主流开源框架的资源可以被 sentinel 自动识别,比如 springcloud 中的 mvc 方法。
一些规则可能不生效,比如热点参数限流规则,同时不能使用自定义 fallback / blockHandler - 通过 @SentinelResource 声明
强烈建议,可以规避莫名其妙的问题(比如热点参数限流规则配置不生效) - 通过 SphU.entry(xxx) 和 entry.exit() 完成,包含 3 种具体方式
除非特殊场景,强烈不推荐,详细内容参考 SphU
功能插槽(slot chain)
官网说明
在 Sentinel 里面,所有的资源都对应一个资源名称以及一个 Entry。Entry 可以通过对主流框架的适配自动创建,也可以通过注解的方式或调用 API 显式创建
每一个 Entry 创建的时候,同时也会创建一系列功能插槽(slot chain)
官网描述中,一系列功能插槽是指如下一系列,这里按拆分成两个表格
表 2.1-1 主要用于收集信息的 slot,resource 的围观群众
| 名称 | 收集信息 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| NodeSelectorSlot | 资源的调用路径,以树状结构存储 | 根据调用路径来限流降级 |
| ClusterBuilderSlot | 资源的统计信息以及调用者信息(RT, QPS, thread count ) | 多维度限流,降级 |
| StatisticSlot | runtime 指标监控信息 |
表 2.1-2 主要用于控制的 slot,resource 的调教者
| 名称 | 依据 | 行为 |
|---|---|---|
| DegradeSlot | 统计信息 / 预设的规则 | 熔断降级 |
| FlowSlot | 预设的限流规则 / 上表 slot 统计的状态 | 流量控制 |
| AuthoritySlot | 黑白名单 / 调用来源信息 | 黑白名单控制 |
| SystemSlot | 系统的状态 | 入口流量 |
| ParamFlowSlot |
从下图看,功能插槽(slot chain) 也是按上面的区分成组
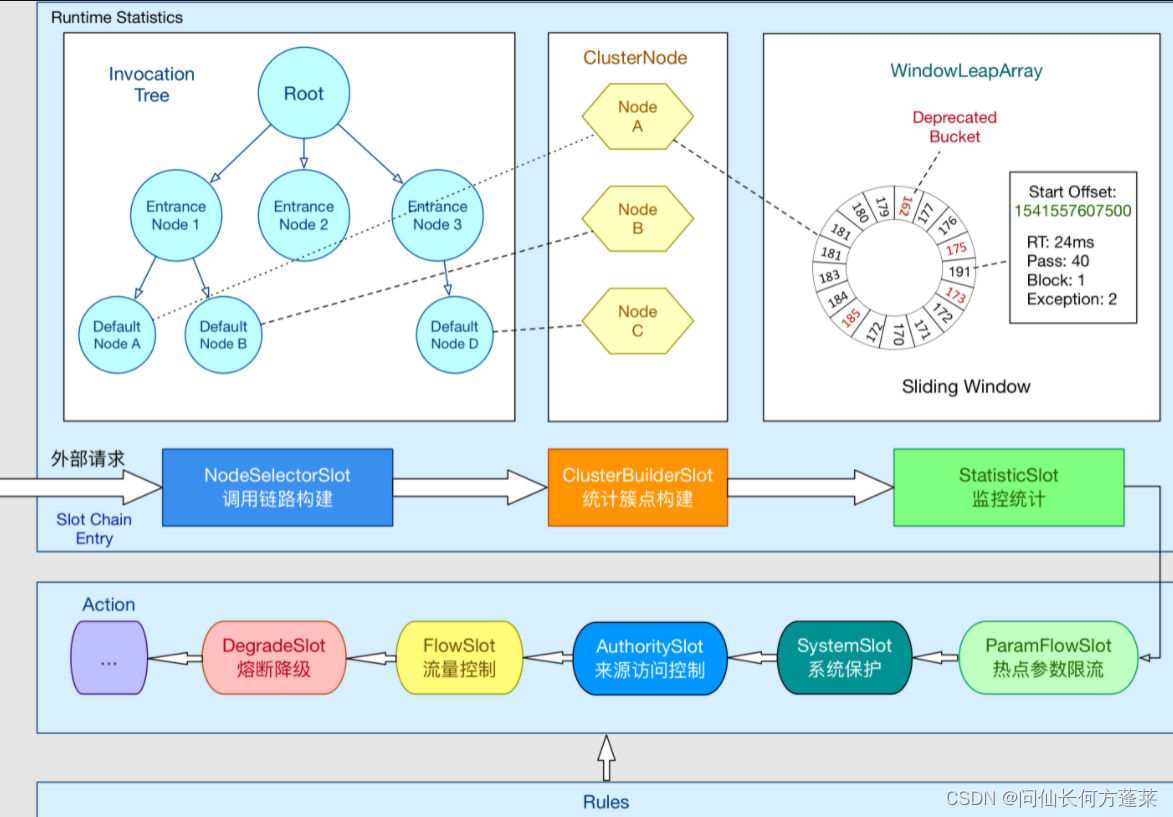
功能插槽(slot chain) 的扩展
通过 ProcessorSlot / SlotChainBuilder 可以实现功能插槽(slot chain) 的扩展
扩展插槽的位置如下图所示
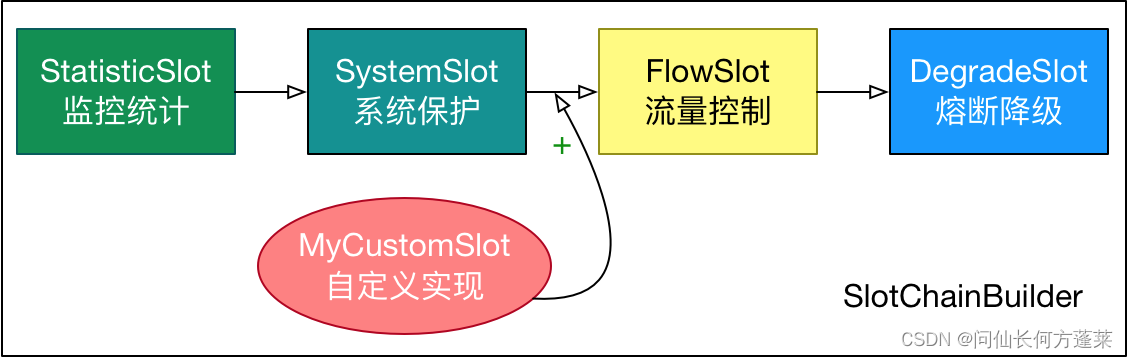
规则(rule)
Sentinel 的所有规则都可以在内存态中动态地查询及修改,修改之后立即生效。同时 Sentinel 也提供相关 API,供您来定制自己的规则策略。
Sentinel 支持以下几种规则,依次对应 表 2.1-2 中各个 slot
- 流量控制规则
- 熔断降级规则
- 系统保护规则
- 来源访问控制规则
- 热点参数规则
§3 简单使用
下载
可以从 github sentinel 直接下载
下载后是一个 jar 包
运行
nohup java -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.8.4.jar &
启动成功后可以通过 8080 看到登录页面

添加项目支持
依赖
<!--纯 sentinel -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--nacos + sentinel 时 额外引入-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置
server:
port: 8400
spring:
application:
name: nacos-sentinel-service
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: 192.168.3.10:8848
file-extension: yml
discovery:
server-addr: 192.168.3.10:8848
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: 192.168.3.10:8080 #配置Sentinel dashboard地址
port: 8719 #若有占用,它自己+1,再被占用,再+1
启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class NacosSentinelApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(NacosSentinelApplication.class,args);
}
}
启动并验证
依次完成如下操作
- 启动 sentinel
- 启动 nacos
- 启动服务
在 nacos 上检查服务注册
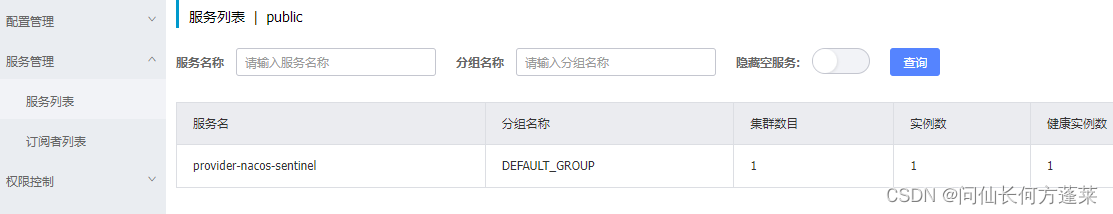
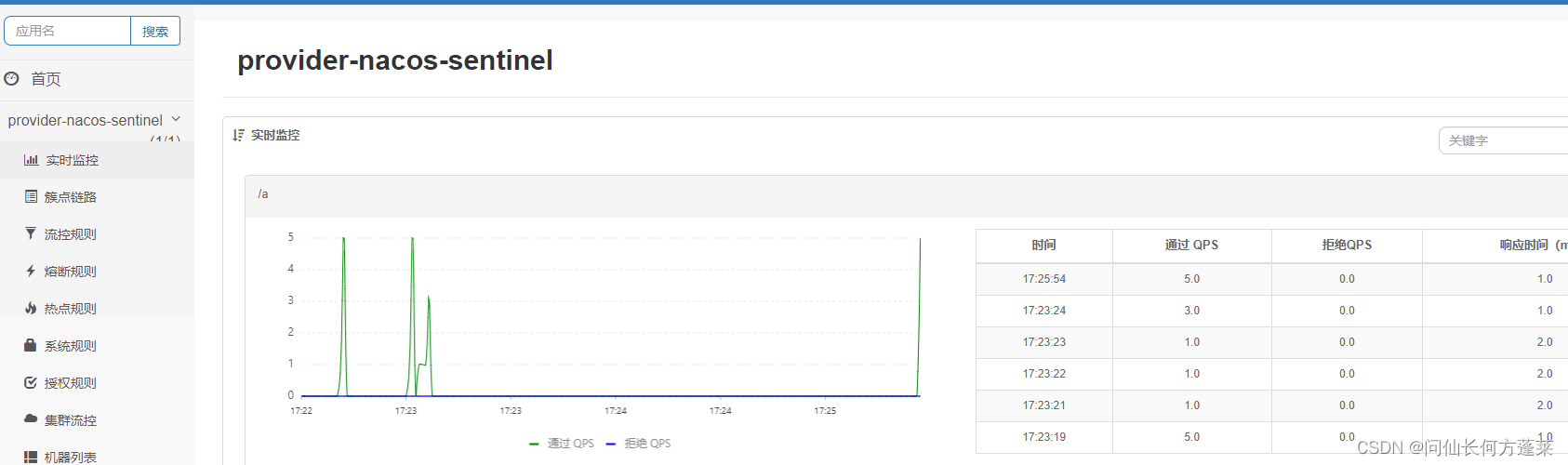
调用服务,sentinel 默认懒加载,不调用服务不触发监控
查看 sentinel dashboard 上的监控信息
§4 规则
§4.1 流量控制规则
流量控制规则的 通式 为
- 被控资源的监控项按流控模式进行统计
- 统计结果略达到阈值后触发规则
- 规则对被控资源施加流量控制行为
对套用了流量控制规则的 资源 A 而言
被控资源:A
监控项:
- QPS,每秒请求数
- 并发线程数,当前请求上下文的线程个数,与请求数无关,只统计有几个线程在调用 A
流控模式
-
直接
直接对 A 的监控项进行统计 -
关联
当另一个资源 B 与 A 存在竞争/依赖关系时,二者有关联。关联模式下,统计关联资源 B 的监控项,若触发条件,对 A 进行流量控制
用于 A 给资源 B 让渡流量的场景,比如 A 代表普通用户业务办理,而 B 代表 vip 用户 -
链路
链路可能有多个链路可以调用 A,链路模式可以只统计处于指定链路下的 A 的监控项,其余对 A 的调用不计入统计。通过链路入口指定链路
阈值
对监控项的统计达到此数值时,触发规则
触发规则意味着对 被控资源 施加 流量控制行为
流量控制行为
-
快速失败
新的请求就会被立即拒绝
拒绝方式为抛出FlowException,请求默认返回响应 Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)
监控项为 并发线程数 时,流量控制行为 默认并且只有 快速失败 -
预热(Warm Up)
从初始流速开始缓慢加大请求流速,经过预热时长达到最大流速。
长期不活跃的系统可能处于 "冷运行" 状态。若突发大流量,系统正常情况下会创建系统资源以适应骤增的流量。但是,资源的创建(比如在线程池中开辟新的线程)需要时间,系统可能在准备充足的资源之前就被压垮。预热可以通过缓冲流量放行速度,争取这个时间。其中具体设定如下:
- 冷运行因子(cold factor) 默认 = 3
- 请求最大流速 = 阈值
- 请求初始流速 = 阈值 / 冷运行因子(cold factoer) = 阈值 / 3
- 初始速度提升到最多速度的时间 = 预热时长
-
排队等待
新的请求放入漏桶(基于漏桶算法),并根据阈值严格限制单机请求的放行速度
在间歇性出现大流量的场景(某一秒有大量的请求到来,而接下来的几秒则处于空闲状态),可以使系统平稳的应对波动的流量,而不是马上丢弃一部分
单机请求的放行时间间隔为 (1000 / 阈值) ms
需要配置超时时间,在漏桶中存在超过超时时间的请求将被丢弃
§4.2 熔断/降级控制规则
熔断/降级控制规则的 通式 为
- 单位时间内,请求量达到一定级别后
- 被控资源的监控项按熔断策略进行统计
- 统计结果达到阈值后触发规则
- 规则对被控资源进行熔断 / 降级
对套用了熔断/降级控制规则的 资源 A 而言
被控资源:A
统计时长
即通式中的 单位时间,作为统计窗口
最小请求数
即通式中的 请求量达到一定级别
请求未达到此数量时,不考虑熔断 / 降级
最小请求数作用于每一个统计窗口,每轮统计都需要达到最小请求数才判断是否触发规则
监控项:
对 A 的调用的 健康状态
健康状态有多种描述方式或评估方法,对应 熔断策略 ,包括
- 单位时间内的 慢调用比例,用响应速度评估
- 单位时间内的 异常比例,用响应结果比例评估
- 单位时间内的 异常数,用响应结果数量评估
熔断策略和阈值
-
慢调用比例
调用时间超过 最大 RT(最大 Response Time) 的调用会被统计为慢调用
阈值为一个比例 -
异常比例
发生业务异常的调用会被统计为异常调用
阈值为一个比例 -
异常数
同上,但阈值为一个具体数字
熔断 / 降级和熔断时长
每次熔断都会使资源在一个熔断时长中不可用
度过一轮熔断时长后,进入探测恢复状态(HALF-OPEN 状态),放行一个请求
若此请求正常响应,则资源恢复,否则继续熔断一个熔断时长
按熔断策略不同,请求正常响应的判断标准也不同
- 慢调用比例:响应时间小于 最大 RT
- 异常比例 / 异常数:请求成功完成(没有业务异常)
§4.3 热点参数限流规则
热点参数限流规则的 通式 为
- 在单位时间内
- 对被控资源进行的带参访问进行统计
- 统计结果达到阈值后触发规则
- 规则对被控系统进行阻塞访问
对套用了热点参数限流规则的 资源 A 而言
被控资源:
A
统计窗口时长
即通式中的 单位时间
带参访问
-
带参访问需要通过 @SentinelResource 声明资源,否则可能不生效
-
以下情况被认为带参访问
访问资源时,携带了指定的参数
访问资源时,携带了指定的参数,且值为指定值 -
参数通过在资源参数表中的索引进行指定,从 0 开始计数,1 表示 A 的第二个参数
-
参数可以设置例外项
每个例外项都是这个参数的一个指定值
每个例外项都具有参数类型,但类型仅支持 数字、字符 和 字符串
每个例外项都可以有自己的独立阈值
阈值
阈值是一个 Qps 值
对监控项的统计达到此数值时,触发规则
触发规则意味着对 被控资源 阻塞访问
阻塞访问
效果等同 §4.1 流量控制规则 中的快速失败
§4.4 系统自适应保护规则
系统自适应保护规则的 通式 为
- 对被控系统的入口流量进行统计
- 统计结果达到阈值后触发规则
- 规则对被控系统进行阻塞访问
对套用了系统自适应保护规则的 系统 A 而言
被控系统:
A
入口流量
所有进入系统 A,需要被 A 处理的流量
入口流量有多种描述方式或评估方法,包括
-
Load(仅对 Linux/Unix-like 机器生效)
A 的负载超过阈值,且系统当前的并发线程数超过 系统容量 时才会触发
系统容量由系统的 maxQps * minRt
设定参考值一般是 CPU cores * 2.5
存疑:详见 系统容量 -
CPU 使用率
当系统 CPU 使用率超过阈值(取值范围 0.0-1.0)。 -
RT (响应时间)
当单台机器上所有入口流量的平均 RT 达到阈值,单位是毫秒。 -
线程数
当单台机器上所有入口流量的并发线程数达到阈值 -
入口 QPS
当单台机器上所有入口流量的 QPS 达到阈值
阈值
对监控项的统计达到此数值时,触发规则
触发规则意味着对 被控资源 阻塞访问
阻塞访问
效果等同 §4.1 流量控制规则 中的快速失败
系统容量(不确定,但能说通)
官网提供的计算方式:系统容量 = maxQps * minRt
系统容量是一个用于评估当前系统处理能力的值,这个值的含义大约可以理解为:
按系统的处理能力,需要长时间保持 (系统容量)根 线程同时作业,才能消化掉当前的业务访问
或者可以把这个系统容量理解成 由实际观测数据估算的系统当前常驻线程数
- 系统容量可以达到的值越大,说明系统处理能力越强,1 秒能当 系统容量秒 使
- 系统容量的当前值越小,说明系统越不饱和
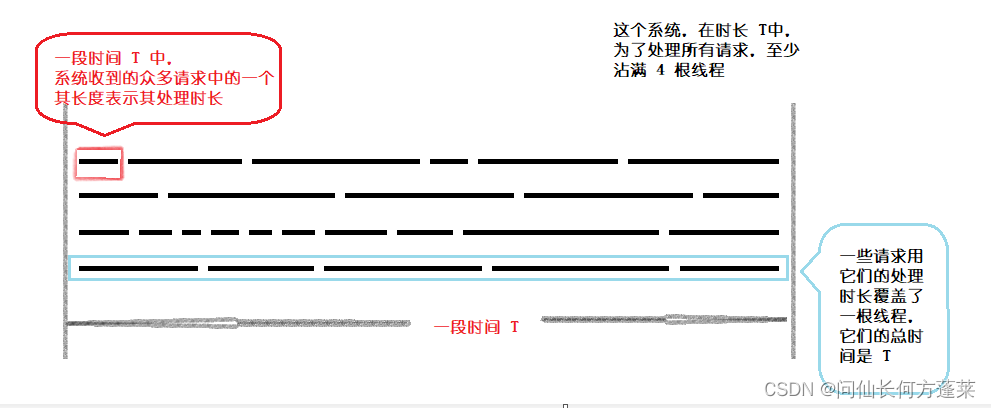
我们很好理解系统容量的单位是 个,一个 对应 一根线程:
令 maxQps = y个/秒(Qps是个速度,不是纯数值),minRt = x 秒
则,系统容量 = y个/秒 * x 秒 = xy个
官网上的计算方式可能是按下面的思路得来的:
在一段时长 T 里,
系统在源源不断的处理业务,业务可以理解为请求的集合,
每个请求都需要一个时长t 才能处理完,系统实际处理了 Ttotal = ∑ t 时长的业务
那么如何在一个时长 T 里,处理了明显更多时长 TTotal 的业务 —— 通过多线程
所以,用时长 T 处理总时长为 Ttotal 的业务需要系统常驻 (Ttotal / T) 根线程
问:现在有一盘包子,正常人吃得吃 60 分钟,现在只有 15 分钟,怎么吃完?
答:4人同时吃
假设上面的时长 T 就是 1 秒,则 Ttotal 也相应的成为 Tsecond (Ttotal / T = Tsecond / 1s)
Tsecond 不太好估算,于是把所有的请求都进行折算
每个请求都折算成 1-n 个特别简单的单位请求,相当于每个请求都是对单位请求的 1-n 倍加权,1 秒内的所有请求 可以折算成 1 秒内的所有单位请求的总和,记为 C
在此前提下,我们可以认为每个单位请求的处理时间一样并且很短,作为单位请求处理时间 t'
则有 Tsecond = ( ∑ Random(n) ) * t' = Ct'
C 也不好计算,于是只能认为在某个时段,系统里处理的请求都是单位请求级别,此时请求数量最多。所以将单位时间内请求数量的最大值作为 C,因为时长是 1 秒,所以这个值实际就是一秒内请求数的最大值,即 maxQps * 1秒(qps 的单位是 个/秒)
t' 也不好计算,于是只能认为单位请求处理时间就是系统中出现的最短的响应时间,即 minRt
于是有下表
| 原始 | 折算 | 对折算的估算取值 |
|---|---|---|
| 请求数量 | 单位请求总量 | maxQps * 1s |
| 请求响应时间 | 单位请求处理时间 | minRt |
| ∑ 求和 | 乘法 | 乘法 |
| Tsecond | ( ∑ Random(n) ) * t' = Ct' | maxQps * 1s * minRt |
| Tsecond / 1s | Ct' / 1s | maxQps * minRt |
疑问:
官网描述
Load(仅对 Linux/Unix-like 机器生效):当系统 load1 超过阈值,且系统当前的并发线程数超过系统容量时才会触发系统保护。系统容量由系统的 maxQps * minRt 计算得出。设定参考值一般是 CPU cores * 2.5
从上面的计算推导看 maxQps * minRt 其实是估算了一个线程数,而官网上对阈值的推荐配置 CPU cores * 2.5 明显也是个线程数。load1 超过用户设置的值(CPU cores * 2.5 )和 当前的并发线程数超过系统容量难道不是一回事?还是说系统容量是通过压测数据计算的,而不是实时数据? 有看到这里的大佬请解惑。
§5 @SentinelResource
§5.1 属性明细
value
资源名称,必需项,不能为空
entryType
entry 类型,可选项,默认为 EntryType.OUT
blockHandler
当资源发生 BlockException 时,对应处理的方法名称,可选项
blockHandler 方法
- blockHandler 方法只用于处理 BlockException
- BlockException 是 Sentinel 规则触发后反馈的异常,比如触发了热点参数限流规则等
- 访问范围需要是 public
- 返回类型需要与原方法相同
- 参数表在原方法参数表基础上追加一个 BlockException 类型参数
- 默认声明在原方法所在的类中
- 可以通过 blockHandlerClass 声明在非原方法所在类,但需要追加 static 修饰,否则解析失败
fallback
当资源发生 Exception 时,对应处理方法名称,可选项
fallback 方法
- fallback 方法可以处理所有异常
- 返回类型需要与原方法相同
- 参数表在原方法参数表基础上可选的追加一个 Throwable 类型参数,即触发的异常
- 默认声明在原方法所在的类中
- 可以通过 fallbackClass 声明在非原方法所在类,但需要追加 static 修饰,否则解析失败
defaultFallback
当资源发生 Exception 时且没有指定 fallback 方法时,缺省 fallback 方法名,可选项
缺省 fallback 方法
- 缺省 fallback 方法可以处理所有异常
- 是可以用于很多服务或方法的、通用的默认 fallback 方法
- 优先级低于 fallback ,若某资源同时存在二者时,则只有 fallback 会生效
- 返回类型需要与原方法相同
- 参数表在空白的基础上可选的追加一个 Throwable 类型参数,即触发的异常
- 默认声明在原方法所在的类中
- 可以通过 fallbackClass 声明在非原方法所在类,但需要追加 static 修饰,否则解析失败
exceptionsToIgnore
忽略异常
当资源抛出被此属性涵盖的异常时,
- 不会计入异常统计中
- 不会进入 fallback 逻辑中
- 但是会原样抛出
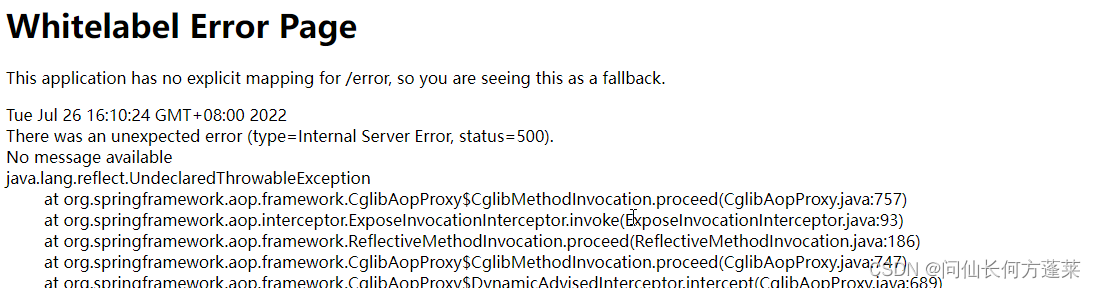
需注意
使用 @SentinelResource 声明的资源,必须至少声明 blockHandler、fallback 或 defaultFallback 之一,否则发生异常时会抛出白页,如下图
§5.2 使用
§6 SphU / Tracer
使用 SphU 声明资源
SphU 工具可以声明 Sentinel 资源,但可读性相对 @SentinelResource 较差,同时不能自动完成对上层业务异常的统计,因此不推荐
SphU 工具提供了 3 种资源声明方法,三种方法的区别不在于声明资源本身
而是处理 block 或 fallback 的位置随三种声明方式,出现格式上的变化,细节如下
基于 try-catch-finally 或 try-with-resource
// 1.5.0 版本开始可以利用 try-with-resources 特性
// 资源名可使用任意有业务语义的字符串,比如方法名、接口名或其它可唯一标识的字符串。
try (Entry entry = SphU.entry("resourceName")) {
// 被保护的业务逻辑
// do something here...
} catch (BlockException ex) {
// 资源访问阻止,被限流或被降级
// 在此处进行相应的处理操作
}
基于 if-try-finally-else
// 资源名可使用任意有业务语义的字符串
if (SphO.entry("自定义资源名")) {
// 务必保证finally会被执行
try {
/**
* 被保护的业务逻辑
*/
} finally {
SphO.exit();
}
} else {
// 资源访问阻止,被限流或被降级
// 进行相应的处理操作
}
基于异步调用
try {
AsyncEntry entry = SphU.asyncEntry(resourceName);
// 异步调用.
doAsync(userId, result -> {
try {
// 在此处处理异步调用的结果.
} finally {
// 在回调结束后 exit.
entry.exit();
}
});
} catch (BlockException ex) {
// Request blocked.
// Handle the exception (e.g. retry or fallback).
}
SphU 声明资源的套路
- 通过 SphU.entry("resourceName") 开启资源的声明,同时给资源命名
- 通过 entry.exit() 标注资源声明的结束,同时释放资源,可以通过 try-with-resource 自动释放
- try 中包围的是需要保护的逻辑,相当于被 @SentinelResource 注解的方法的方法体
- catch 或 else 中包围的是 block / fallback 的处理逻辑,相当于 @SentinelResource 中blockhandler 或 fallback 对应方法的方法体
- 这和声明一个数据库连接资源 -> 使用资源 -> 释放连接 的套路基本一致
使用 Tracer 统计业务异常(非 BlockException 异常)
Tracer 用于记录用户通过 SphU 或 SphO 手动定义的资源的业务异常。
因上述资源,不能由 Sentinel 感知上层业务异常并自动记录,所以,只能手动调用如下 API
- trace(Throwable e)
资源为当前线程 context 下 entry 对应的资源 - trace(Throwable e, int count)
资源同上,但统计的数量按 count 记录 - traceEntry(Throwable, int, Entry)
资源为传入的 entry 对应的资源
统计的数量按 count 记录
上述 API 不能在 try-with-resources 形式的 SphU.entry(xxx) 中使用,否则会统计不上
§7 Sentinel 整合 Ribbon / OpenFeign
完整示例
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--SpringCloud ailibaba sentinel-datasource-nacos 后续做持久化用到-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--SpringCloud ailibaba sentinel -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- hi用 open feign 时添加 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置
server:
port: 8800
spring:
application:
name: nacos-sentinel-ribbon-sentinel-comsumer
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 192.168.3.10:8848
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: 192.168.3.10:8080 #配置Sentinel dashboard地址
port: 8719 #若有占用,它自己+1,再被占用,再+1
#使用 OpenFeign 并需要日志时添加
logging:
config: classpath:logback.cfg.dev.xml
level:
# 对服务类进行正常的接口配置,否则对应类根本不输出日志,就无所谓其中的接口日志记录到什么程度了
com.fc.sprcloudlearning.order.service.PaymentOpenfeignClient: debug
@Configuration
public class RestTemplateConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplateBuilder()
.setConnectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(2))
.setReadTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(2))
.messageConverters(new GsonHttpMessageConverter(new GsonBuilder().serializeNulls().create())).build();
}
}
//使用 OpenFeign 并需要日志时添加
@Configuration
public class OpenFeignConfig {
@Bean
Logger.Level openFeignLoggerLevel(){
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}
消费方法+ fallback + block 代码
//ribbon 调用
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@SentinelResource(value = "find",fallback = "getout",blockHandler = "getoutBlock")
public CommonResult<PaymentEntity> find(@PathVariable Long id){
if(3 < id)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("查无此单");
return restTemplate.getForObject(BASE_URL+"/payment/"+id ,CommonResult.class);
}
//OpenFeign 调用
@RequestMapping(value = "/f/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@SentinelResource(value = "find",fallback = "getout",blockHandler = "getoutBlock")
public CommonResult<PaymentEntity> finds(@PathVariable Long id){
if(3 < id)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("查无此单");
return paymentOpenfeignClient.findById(id);
}
//@Component
@FeignClient(value = "nacos-sentinel-ribbon-sentinel-provider",fallback = PaymentOpenfeignClientFallback.class)
public interface PaymentOpenfeignClient {
@RequestMapping(value = "/payment/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
CommonResult<PaymentEntity> findById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
/* *******************************
* 以下是两种方式通用的 fallback / block
******************************* */
public CommonResult<PaymentEntity> getout(@PathVariable Long id ,Throwable e){
return new CommonResult<PaymentEntity>(500,e.getClass().getName()+" | "+e.getMessage()+" GET OUT!!!");
}
public CommonResult<PaymentEntity> getoutBlock(Long id , BlockException e){
return new CommonResult<PaymentEntity>(500,e.getClass().getName()+" | "+e.getMessage()+" Block OUT!!!");
}
blockhandler 和 fallback
- blockhandler 用于处理 BlockException 的逻辑处理,BlockException 由 Sentinel 在被触发规则时反馈
- fallback 用于处理 业务异常(非 BlockException 异常) 的逻辑处理
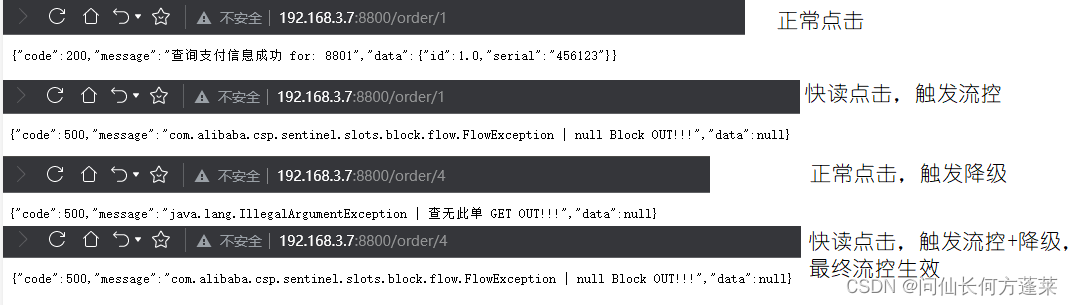
- blockhandler 与 fallback 可以同时生效于一个资源,且 blockhandler 具有更高的优先级,验证见下面示例
规则

效果
§8 正式环境 Sentinel 整合 Nacos
§8.1 要求
- sentinel dashboard 进行增删规则操作时,自动同步到 nacos,并自动入库
- 服务重启后,具体接口调用结束前,自动拉取规则并生效
- 配置简单
§8.2 思路和依据
通过下面操作可以实现上述要求的一部分
- 服务启动后可以自动获取各种规则并生效
- 无法同步 Sentinel 的操作到 nacos
- 规则报文需要手动入库
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
spring:
application:
name: nacos-sentinel-ribbon-sentinel-comsumer
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 192.168.3.10:8848
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: 192.168.3.10:8080 #配置Sentinel dashboard地址
port: 8719 #若有占用,它自己+1,再被占用,再+1
datasource:
ds1:
nacos:
server-addr: 192.168.3.10:8848
dataId: nacos-sentinel-ribbon-sentinel-comsumer.flow
groupId: Sentinel
data-type: json
rule-type: FLOW
ds2:
nacos:
server-addr: 192.168.3.10:8848
dataId: nacos-sentinel-ribbon-sentinel-comsumer.degrade
groupId: Sentinel
data-type: json
rule-type: DEGRADE
对于 Sentinel 整合 nacos 的完整需求,Sentinel 的官网 给出了一套基于数据源 datasource 的方案
- 通过 datasource 来实现 Sentinel 和 nacos 的连接(但如何具体实现的并没有说明,比如数据源如何监听 Sentinel 的操作)
- 提供两种模式 Pull / Push,两种模式分别对应不同的 datasource
- Pull: AutoRefreshDataSource
- Push: AutoRefreshDataSource
- 写数据源的部分逻辑需要参考 nacos 官方 API
- 将数据源注册至指定的规则管理器
- 将对应的类名添加到位于资源目录
resources/META-INF/services/com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc
下面的案例中选用 Push 进行实现和改造(更好的易用性),Push 模式是生产环境普遍选用的方案。
并在此基础上分离定义、注册、参数,简化生效配置
§8.3 准备和使用
准备
需要依次完成下面的步骤,这些步骤完成一个通用模块
这个 module 完全可以单独提取出去,成为一个独立的 jar 存在,以做到多项目/模块引用
以下代码可以从 https://gitee.com/unfixed/sprcloudlearning.git 获取
增加通用 module: sentinel-nacos-auto
sentinel-nacos-auto 的依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--SpringCloud ailibaba sentinel -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
实现读写数据源
也可以 参考官方代码
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.concurrent.NamedThreadFactory;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.AbstractDataSource;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.Converter;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.log.RecordLog;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.util.AssertUtil;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.util.StringUtil;
import com.alibaba.nacos.api.NacosFactory;
import com.alibaba.nacos.api.config.ConfigService;
import com.alibaba.nacos.api.config.listener.Listener;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource<T> extends AbstractDataSource<String, T> {
private static final int DEFAULT_TIMEOUT = 3000;
//只有一条线程的线程池,线程阻塞时丢弃老任务
private final ExecutorService pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(1), new NamedThreadFactory("sentinel-nacos-ds-update", true),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());
private final Listener configListener;
protected final String groupId;
protected final String dataId;
private final Properties properties;
protected ConfigService configService;
public ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource(String serverAddr, String groupId, String dataId, Converter<String, T> parser) {
this(buildProperties(serverAddr), groupId, dataId, parser);
}
//创建了一个仅针对 server.groupId.dataId 的读数据源
public ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource(final Properties properties, final String groupId, final String dataId, Converter<String, T> parser) {
super(parser);
this.configService = null;
if (StringUtil.isBlank(groupId) || StringUtil.isBlank(dataId)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("Bad argument: groupId=[%s], dataId=[%s]", groupId, dataId));
}
AssertUtil.notNull(properties, "Nacos properties must not be null, you could put some keys from PropertyKeyConst");
this.groupId = groupId;
this.dataId = dataId;
this.properties = properties;
//通过此监听器与 nacos 相连
this.configListener = new Listener() {
@Override
public Executor getExecutor() {
return pool;
}
@Override
public void receiveConfigInfo(String configInfo) {
RecordLog.info("[ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource] New property value received for (properties: {}) (dataId: {}, groupId: {}): {}"
, properties, dataId, groupId, configInfo);
T newValue = ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource.this.parser.convert(configInfo);
getProperty().updateValue(newValue);
}
};
this.initNacosListener();
this.loadInitialConfig();
}
private void loadInitialConfig() {
try {
T newValue = this.loadConfig();
if (newValue == null) {
RecordLog.warn("[ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource] WARN: initial config is null, you may have to check your data source");
}
this.getProperty().updateValue(newValue);
} catch (Exception e) {
RecordLog.warn("[ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource] Error when loading initial config", e);
}
}
private void initNacosListener() {
try {
this.configService = NacosFactory.createConfigService(this.properties);
this.configService.addListener(this.dataId, this.groupId, this.configListener);
} catch (Exception e) {
RecordLog.warn("[ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource] Error occurred when initializing Nacos data source", e);
}
}
@Override
public String readSource() throws Exception {
if (this.configService == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Nacos config service has not been initialized or error occurred");
} else {
return this.configService.getConfig(this.dataId, this.groupId, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
}
}
@Override
public void close() {
if (this.configService != null) {
this.configService.removeListener(this.dataId, this.groupId, this.configListener);
}
this.pool.shutdownNow();
}
private static Properties buildProperties(String serverAddr) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("serverAddr", serverAddr);
return properties;
}
}
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.Converter;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.WritableDataSource;
import com.fc.sprcloudlearning.sentinelnacos.datasource.ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class WritableSentineNacoslDatasource<T> extends ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource implements WritableDataSource<T> {
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
private final Converter<T, String> configEncoder;
public WritableSentineNacoslDatasource(String serverAddr, String groupId, String dataId, Converter<T, String> configEncoder) {
super(serverAddr, groupId, dataId, configEncoder);
this.configEncoder = configEncoder;
}
@Override
public void write(T value) throws Exception {
lock.lock();
try {
String convertResult = configEncoder.convert(value);
configService.publishConfig(dataId, groupId, convertResult);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public void close() {
super.close();
}
}
实现数据源注册
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.command.handler.ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.ReadableDataSource;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.WritableDataSource;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.transport.util.WritableDataSourceRegistry;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;
import com.fc.sprcloudlearning.sentinelnacos.config.SentinelNacosDatasourceConfig;
import com.fc.sprcloudlearning.sentinelnacos.datasource.ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource;
import com.fc.sprcloudlearning.sentinelnacos.datasource.WritableSentineNacoslDatasource;
import java.util.List;
public class Sentinel4NacosInitor implements InitFunc {
private final SentinelNacosDatasourceConfig config;
public Sentinel4NacosInitor(SentinelNacosDatasourceConfig config) {
this.config = config;
init();
}
@Override
public void init() {
//流控规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleDataSource =
new ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource<>(config.server(), config.groupId(), config.flow(),
source -> JSON.parseObject(source, new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>() {}));
FlowRuleManager.register2Property(flowRuleDataSource.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>> writableFlowRuleDataSource =
new WritableSentineNacoslDatasource<>(config.server(), config.groupId(), config.flow(), JSON::toJSONString);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(writableFlowRuleDataSource);
//降级规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleDataSource =
new ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource<>(config.server(), config.groupId(), config.degrade(),
source -> JSON.parseObject(source, new TypeReference<List<DegradeRule>>() {}));
DegradeRuleManager.register2Property(degradeRuleDataSource.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<DegradeRule>> writableDegradeRuleDataSource =
new WritableSentineNacoslDatasource<>(config.server(), config.groupId(), config.degrade(), JSON::toJSONString);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerDegradeDataSource(writableDegradeRuleDataSource);
//系统规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleDataSource =
new ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource<>(config.server(), config.groupId(), config.system(),
source -> JSON.parseObject(source, new TypeReference<List<SystemRule>>() {
}));
SystemRuleManager.register2Property(systemRuleDataSource.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<SystemRule>> writableSystemRuleDataSource =
new WritableSentineNacoslDatasource<>(config.server(), config.groupId(), config.system(), JSON::toJSONString);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerSystemDataSource(writableSystemRuleDataSource);
//授权规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleDataSource =
new ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource<>(config.server(), config.groupId(), config.authority(),
source -> JSON.parseObject(source, new TypeReference<List<AuthorityRule>>() {}));
AuthorityRuleManager.register2Property(authorityRuleDataSource.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<AuthorityRule>> writableAuthorityRuleDataSource =
new WritableSentineNacoslDatasource<>(config.server(), config.groupId(), config.authority(), JSON::toJSONString);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerAuthorityDataSource(writableAuthorityRuleDataSource);
//热点参数规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleDataSource =
new ReadableSentinelNacosDatasource<>(config.server(), config.groupId(), config.param(),
source -> JSON.parseObject(source, new TypeReference<List<ParamFlowRule>>() {
}));
ParamFlowRuleManager.register2Property(paramFlowRuleDataSource.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<ParamFlowRule>> writableParamFlowRuleDataSource =
new WritableSentineNacoslDatasource<>(config.server(), config.groupId(), config.param(), JSON::toJSONString);
ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler.setWritableDataSource(writableParamFlowRuleDataSource);
}
}
实现配置
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "config.sentinel.datasource.nacos")
public class SentinelNacosDatasourceConfig {
private String server;
private String groupId;
private String dataId;
private String flowSuffix = "flow";
private String authoritySuffix = "authority";
private String degradeSuffix = "degrade";
private String paramSuffix = "param";
private String systemSuffix = "system";
private String separator = ".";
/* *******************************
* 以下是 setter/getter
******************************* */
public String getServer() {
return server;
}
public void setServer(String server) {
this.server = server;
}
public String getGroupId() {
return groupId;
}
public void setGroupId(String groupId) {
this.groupId = groupId;
}
public String getDataId() {
return dataId;
}
public void setDataId(String dataId) {
this.dataId = dataId;
}
public String getFlowSuffix() {
return flowSuffix;
}
public void setFlowSuffix(String flowSuffix) {
this.flowSuffix = flowSuffix;
}
public String getAuthoritySuffix() {
return authoritySuffix;
}
public void setAuthoritySuffix(String authoritySuffix) {
this.authoritySuffix = authoritySuffix;
}
public String getDegradeSuffix() {
return degradeSuffix;
}
public void setDegradeSuffix(String degradeSuffix) {
this.degradeSuffix = degradeSuffix;
}
public String getParamSuffix() {
return paramSuffix;
}
public void setParamSuffix(String paramSuffix) {
this.paramSuffix = paramSuffix;
}
public String getSystemSuffix() {
return systemSuffix;
}
public void setSystemSuffix(String systemSuffix) {
this.systemSuffix = systemSuffix;
}
public String getSeparator() {
return separator;
}
public void setSeparator(String separator) {
this.separator = separator;
}
public String server() {
return server;
}
public String groupId() {
return groupId;
}
public String dataId() {
return dataId;
}
public String flow() {
return StringUtils.join(dataId, separator, flowSuffix);
}
public String authority() {
return StringUtils.join(dataId, separator, authoritySuffix);
}
public String degrade() {
return StringUtils.join(dataId, separator, degradeSuffix);
}
public String param() {
return StringUtils.join(dataId, separator, paramSuffix);
}
public String system() {
return StringUtils.join(dataId, separator, systemSuffix);
}
}
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc;
import com.fc.sprcloudlearning.sentinelnacos.Sentinel4NacosInitor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
public class Sentinel4NacosInitorConfig {
@Bean
public InitFunc sentinel4NacosInitor(SentinelNacosDatasourceConfig config){
return new Sentinel4NacosInitor(config);
}
}
实现@Enable
import com.fc.sprcloudlearning.sentinelnacos.config.Sentinel4NacosInitorConfig;
import com.fc.sprcloudlearning.sentinelnacos.config.SentinelNacosDatasourceConfig;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import({SentinelNacosDatasourceConfig.class,
Sentinel4NacosInitorConfig.class})
public @interface EnableSentinel4Nacos {
}
使用
经过上面准备,下面的使用在手感上接近,用 sentinel-nacos-auto 平替此依赖即可(配置还是要改的)
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
引入模块 sentinel-nacos-auto
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fc.sprcloudlearning</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-nacos-auto</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>
启动类注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableSentinel4Nacos //这里
public class OrderComsummerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderComsummerApplication.class,args);
}
}
配置
以下为最简配置,使用下面配置后,会自动生成 5 个 dataId
每个完整 dataId = {dataId}{separator}{rule-type-suffix},如 appName.flow
-
{separator} 默认值为 .
可以通过 config.sentinel.datasource.nacos.separator 进行修改 -
{rule-type-suffix} 默认为 flow / authority / degrade / param / system
可以通过如 config.sentinel.datasource.nacos.flow-suffix 配置进行修改
config:
sentinel:
datasource:
nacos:
server: http://192.168.3.10:8848
group-id: Sentinel
data-id: nacos-sentinel-ribbon-sentinel-comsumer
效果
已有规则可以自动拉取
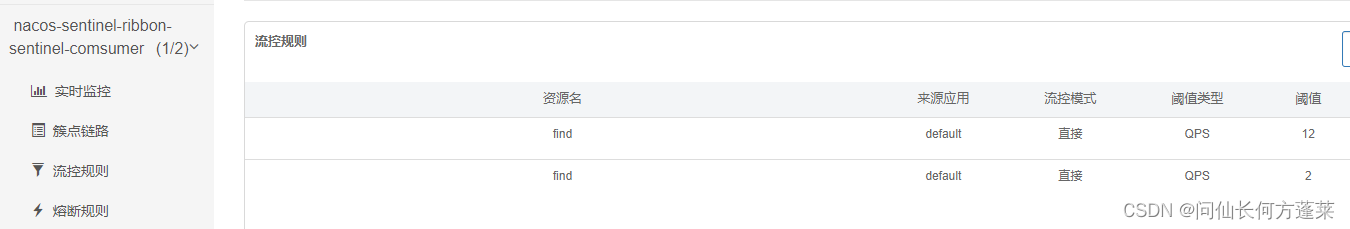
规则可生效
sentinel dashboard 的操作自动同步 nacos



进阶优化方案
可以在 @EnableSentinel4Nacos 注解中增加参数 server / groudId / dataId,以实现最简配置场景的无配置化
对应的,需要增加从启动类上获取 注解以及获取参数的逻辑,此逻辑可能可以通过 Environment 自动完成,此时需要额外补充填充逻辑
本文部分内容参考自
sentinel的限流操作:快速失败、Warm UP、排队等待
实战流控效果-WarmUp
生产环境下sentinel规则持久化方案
传送门:
微服务架构 | 组件目录





