| 参数 |
说明 |
| n_samples |
样本个数 |
| n_features |
样本特征个数,包括信息特征,冗余特征,重复特征,和除去以上特征的无用特征 |
| n_informative |
信息特征个数 |
| n_redundant |
冗余特征个数 |
| n_repeated |
重复特征个数 |
| n_classes |
样本类别个数 |
| n_clusters_per_class |
每个类的簇的个数 |
| random_state |
随机种子指定,以便生成同样的数据集 |
| shuffle |
bool, default=True,对样本和特征洗牌 |
| weights |
列表类型,每个属性的权重 |
| flip_y |
float, default=0.01,随机分配的样本的比例,增大会加大噪声,加大分类难度 |
| shift |
float, ndarray of shape (n_features,) or None, default=0.0,对每个属性值进行位移 |
| scale |
float, ndarray of shape (n_features,) or None, default=1.0,对每个属性值进行数乘 |
| class_sep |
将每个簇分隔开来,较大的值将使分类任务更加容易 |
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
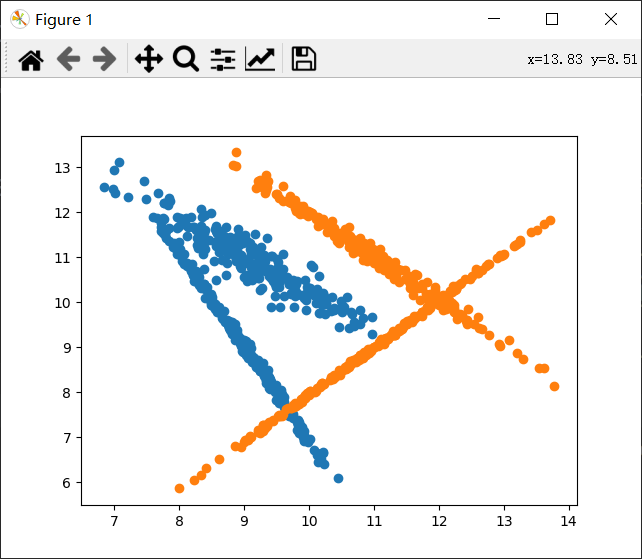
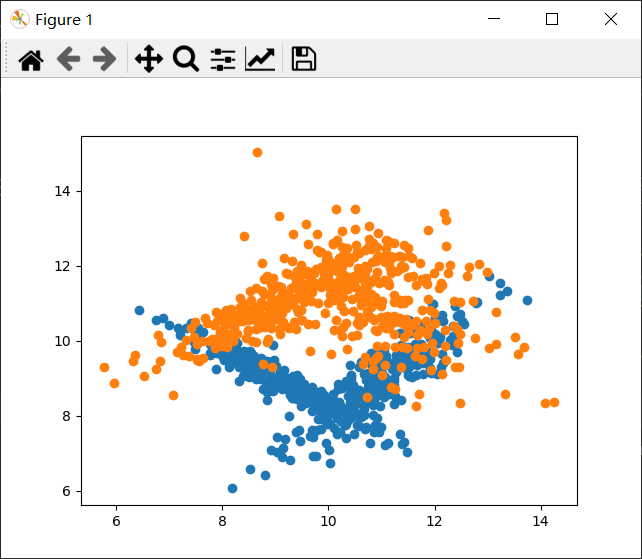
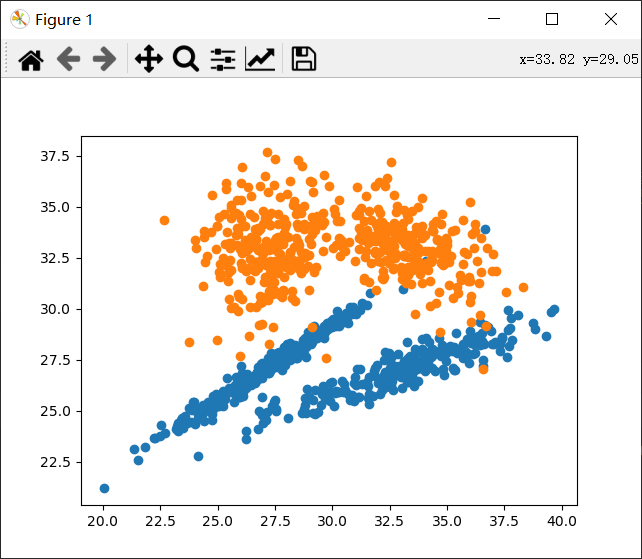
X,y=make_classification(n_samples=1000,#1000个样本
n_features=2,#两个特征,方便画图
n_informative=2,#信息特征(有用特征)
n_redundant=0,#冗余特征,它是信息特征的线性组合
n_repeated=0,#重复特征
n_classes=2,#分类样别
random_state=None,
n_clusters_per_class=2,#每个类别两簇
shuffle=True,
class_sep=1,#将每个簇分隔开来,较大的值将使分类任务更加容易
shift=10,
scale=3,
flip_y=0,)#没有噪声
#训练集与测试集分割函数
#x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(
# X,y,train_size=800,test_size=200,random_state=4)
data=np.concatenate((X,y.reshape(1000,1)),axis=1)
# data=pd.DataFrame(X)
# x0=data[0]
# x1=data[1]
x0=[]
x1=[]
y0=[]
y1=[]
for d in data:
if d[2]==0:
x0.append(d[0])
y0.append(d[1])
else:
x1.append(d[0])
y1.append(d[1])
plt.scatter(x0,y0)
plt.scatter(x1,y1)
plt.show()