Hibernate--对象关系
在hibernate中,关联关系映射分为单向关联和双向关联。共有七种关系
hibernate在维护这几种关系的时候,要不通过连接表,要不通过外键的方式。
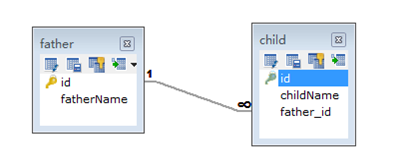
这是一种最常见的关系,hibernate是通过在many的一方加入one的一个主键作为外键的方式来管理关系的。
此时的多的一方和一的一方,需要各自管理,分别保存,也可以在many-to-one的配置中加入级联属性,则在保存多的一端的时候,会自动保存一的一端
先看配置文件版
package com.fuwh.model; //one public class Father { private int id; private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.model; //Many public class Child { private int id; private String name; //在many的一端中加入one作为一个属性变量 private Father father; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Father getFather() { return father; } public void setFather(Father father) { this.father = father; } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 --> <hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Father" table="t_father"> <id name="id" column="fatherId"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="fatherName"></property> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 --> <hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Child" table="t_child"> <id name="id" column="childId"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="childName"></property> <!-- 单向多(child)对一(father)的关系 会在多(child)的一方生成的表中添加一个外键,指向一(father)的主键 需要在多(child)的一方配置many-to-one name:指定类中的Father对象变量 column:指定外键名字
cascade:表示级联操作,包含以下集中取值 none(默认),all,persist, merge, delete, save-update, evict, replicate,lock and refresh,delete-orphan ; 可以用逗号隔开,表示几个取值,all代表所有的 -->
<many-to-one name="father" column="father_Id" cascade="all"></many-to-one> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- 数据库连接设置 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">mysqladmin</property> <!-- 指定方言,表明用的是哪种数据库,也可以不指定,hibernate默认会翻译成正确的数据库脚本 方言可以在 hibernate-release-xx.xx/project/etc/hibernate.properties 中查找 --> <property name="hibernate.dialect">MySQL5</property> <!-- 设定时候更新表结构,不存在或自动创建 --> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> <!-- 配置 在后台打印出sql语句 --> <property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property> <property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property> <!-- 引入实体类和表的映射文件 --> <mapping resource="/com/fuwh/model/Father.hbm.xml"/> <mapping resource="/com/fuwh/model/Child.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
执行空的测试语句,生成的sql文如下
Hibernate: create table t_child ( childId integer not null auto_increment, childName varchar(255), father_Id integer, primary key (childId) ) Hibernate: create table t_father ( fatherId integer not null auto_increment, fatherName varchar(255), primary key (fatherId) ) Hibernate: alter table t_child add constraint FKg4qwua9ltkkkfik7fsvubyou7 foreign key (father_Id) references t_father (fatherId)
操作表中的数据
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.model.Child; import com.fuwh.model.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); Father father=new Father(); father.setName("爸爸"); //因为在多的一断配置了级联属性为all,就表明把操作都交给了多的一端来维护关系,不需要保存father对象 //在保存child的时候,会自动保存father Child child1=new Child(); child1.setName("儿子1"); child1.setFather(father); Child child2=new Child(); child2.setName("儿子2"); child2.setFather(father); session.save(child1); session.save(child2);
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
}
}
生成的sql文
Hibernate: insert into t_father (fatherName) values (?) Hibernate: insert into t_child (childName, father_Id) values (?, ?) Hibernate: insert into t_child (childName, father_Id) values (?, ?)


注解版
package com.fuwh.mto; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity public class Father { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @Column(name="fatherName") private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.mto; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.ForeignKey; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.JoinColumn; import javax.persistence.ManyToOne; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity public class Child { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @Column(name="childName") private String name; /** * 定义多对一 * JoinCloumn中的name指定外键的列名,foreignkey中指定定义的外键的名字 * 这一列也可以不加,不加就是默认的设置 */ @ManyToOne(cascade=CascadeType.ALL) @JoinColumn(name="father_id",foreignKey=@ForeignKey(name="FATHER_ID_FK")) private Father father; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Father getFather() { return father; } public void setFather(Father father) { this.father = father; } }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.mto.Child; import com.fuwh.mto.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); Father father=new Father(); father.setName("爸爸"); Child child1=new Child(); child1.setName("儿子一"); child1.setFather(father); Child child2=new Child(); child2.setName("儿子二"); child2.setFather(father); session.save(child1); session.save(child2); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
@One To Many关系把一个父节点和多个子节点联系起来,如果在子节点没有一个@Many To One和@One To Many相匹配的话,那就是一个单向的@One To Many,否则的话就是一个多向的@One To Many,并且可以在任意一边来维护关系。
package com.fuwh.model; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Father { private int id; private String name; private List<Child> children=new ArrayList<Child>(); public List<Child> getChildren() { return children; } public void setChildren(List<Child> children) { this.children = children; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.model; public class Child { private int id; private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 --> <hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Child" table="t_child"> <id name="id" column="childId"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="childName"></property> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 --> <hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Father" table="t_father"> <id name="id" column="fatherId"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="fatherName"></property> <set name="children" cascade="true"> <key column="father_Id"></key> <one-to-many class="com.fuwh.model.Child"/> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
生成的sql文
Hibernate: create table t_child ( childId integer not null auto_increment, childName varchar(255),
father_Id integer,
primary key (childId) ) Hibernate: create table t_father ( fatherId integer not null auto_increment, fatherName varchar(255), primary key (fatherId) ) Hibernate: alter table t_child add constraint FKev9uk6ojrjsv10ba9qoa4yhsy foreign key (father_Id) references t_father (fatherId)
注解版

package com.fuwh.otm; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity public class Child { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @Column(name="childName") private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.otm; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.CascadeType; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.OneToMany; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity public class Father { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @Column(name="fatherName") private String name; //orphanRemoval:表示在删除集合中的child的时候,也会删除child表中的相应纪录 @OneToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL,orphanRemoval=true) private List<Child> children=new ArrayList<Child>(); public List<Child> getChildren() { return children; } public void setChildren(List<Child> children) { this.children = children; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.otm.Child; import com.fuwh.otm.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); Father father1=new Father(); father1.setName("爸爸1"); Father father2=new Father(); father2.setName("爸爸2"); Child child1=new Child(); child1.setName("儿子一"); Child child2=new Child(); child2.setName("儿子二"); father1.getChildren().add(child1); father1.getChildren().add(child2); session.save(father1); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
package com.fuwh.model; public class Child { private int id; private String name; private Father father; public Father getFather() { return father; } public void setFather(Father father) { this.father = father; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.model; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; public class Father { private int id; private String name; private Set<Child> children=new HashSet<Child>(); public Set<Child> getChildren() { return children; } public void setChildren(Set<Child> children) { this.children = children; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 --> <hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Father" table="t_father"> <id name="id" column="fatherId"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="fatherName"></property> <set name="children"> <key column="father_Id"/> <one-to-many class="com.fuwh.model.Child"/> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 --> <hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Child" table="t_child"> <id name="id" column="childId"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="childName"></property> <many-to-one name="father" column="father_Id" cascade="all"></many-to-one> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.model.Child; import com.fuwh.model.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); Father father=new Father(); father.setName("爸爸"); Child child1=new Child(); child1.setName("儿子1"); Child child2=new Child(); child2.setName("儿子2"); child1.setFather(father); child2.setFather(father); father.getChildren().add(child1); father.getChildren().add(child2); session.save(child1); session.save(child2); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
生成的sql
Hibernate: select father0_.fatherId as fatherId1_1_0_, father0_.fatherName as fatherNa2_1_0_ from t_father father0_ where father0_.fatherId=? Hibernate: select child0_.childId as childId1_0_0_, child0_.childName as childNam2_0_0_, child0_.father_Id as father_I3_0_0_ from t_child child0_ where child0_.childId=? Hibernate: select children0_.father_Id as father_I3_0_0_, children0_.childId as childId1_0_0_, children0_.childId as childId1_0_1_, children0_.childName as childNam2_0_1_, children0_.father_Id as father_I3_0_1_ from t_child children0_ where children0_.father_Id=? Hibernate: update t_child set childName=?, father_Id=? where childId=? Hibernate: update t_child set father_Id=? where childId=?
注解版
package com.fuwh.otmbi; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.CascadeType; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.OneToMany; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity public class Father { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @Column(name="fatherName") private String name; /** * orphanRemoval:表示在删除集合中的child的时候,也会删除child表中的相应纪录 * mappedBy/inverse:表示由另一方来维护关系 * */ @OneToMany(mappedBy="father",cascade=CascadeType.ALL,orphanRemoval=true) private List<Child> children=new ArrayList<Child>(); public List<Child> getChildren() { return children; } public void setChildren(List<Child> children) { this.children = children; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.otmbi; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.ManyToOne; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity public class Child { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @Column(name="childName") private String name; @ManyToOne private Father father; public Father getFather() { return father; } public void setFather(Father father) { this.father = father; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.otmbi.Child; import com.fuwh.otmbi.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); Father father1=new Father(); father1.setName("爸爸1"); Child child1=new Child(); child1.setName("儿子一"); child1.setFather(father1); Child child2=new Child(); child2.setName("儿子二"); child2.setFather(father1); father1.getChildren().add(child1); father1.getChildren().add(child2); session.save(father1); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
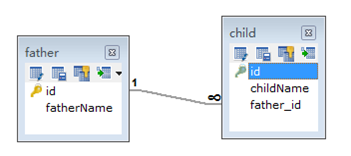
单向的关系又可以分为基于主键的关联和基于外键的关联。
基于外键
package com.fuwh.model; public class Wife { private int id; private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.model; public class Husband { private int id; private String name; private Wife wife; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Wife getWife() { return wife; } public void setWife(Wife wife) { this.wife = wife; } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 --> <hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Wife" table="t_wife"> <id name="id" column="wifeId"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="wifeName"></property> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 --> <hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Husband" table="t_husband"> <id name="id" column="husbandId"> <!-- 主键生成策略为 外键 指向 wife--> <generator class="foreign"> <param name="property">wife</param> </generator> </id> <property name="name" column="husbandName"></property> <one-to-one name="wife" constrained="true"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.model.Child; import com.fuwh.model.Father; import com.fuwh.model.Husband; import com.fuwh.model.Wife; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); Husband husband=new Husband(); Wife wife=new Wife(); wife.setName("老婆"); husband.setName("老公"); husband.setWife(wife); session.save(wife); session.save(husband); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
生成的sql文
Hibernate: create table t_husband ( husbandId integer not null, husbandName varchar(255), primary key (husbandId) ) Hibernate: create table t_wife ( wifeId integer not null auto_increment, wifeName varchar(255), primary key (wifeId) ) Hibernate: alter table t_husband add constraint FK2tae450lphjy8nciwyrxxlfkv foreign key (husbandId) references t_wife (wifeId) Hibernate: insert into t_wife (wifeName) values (?) Hibernate: insert into t_husband (husbandName, husbandId) values (?, ?)
在单向一对一中,hibernate默认是让client-side(上例的Husband)通过外键来管理关系的。
注解版

package com.fuwh.oto; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity public class Father { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @Column(name="fatherName") private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.oto; import javax.persistence.CascadeType; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.JoinColumn; import javax.persistence.OneToOne; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity public class Child { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @Column(name="childName") private String name; @OneToOne(cascade=CascadeType.ALL) @JoinColumn(name="father_id") private Father father; public Father getFather() { return father; } public void setFather(Father father) { this.father = father; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.oto.Child; import com.fuwh.oto.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); Father father1=new Father(); father1.setName("爸爸1"); Child child1=new Child(); child1.setName("儿子一"); child1.setFather(father1); session.save(child1); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
package com.fuwh.model; public class Wife { private int id; private String name; private Husband husband; public Husband getHusband() { return husband; } public void setHusband(Husband husband) { this.husband = husband; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 --> <hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Wife" table="t_wife"> <id name="id" column="wifeId"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="wifeName"></property> <one-to-one name="husband"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
Hibernate: create table t_husband ( husbandId integer not null, husbandName varchar(255), primary key (husbandId) ) Hibernate: create table t_wife ( wifeId integer not null auto_increment, wifeName varchar(255), primary key (wifeId) ) Hibernate: alter table t_husband add constraint FK2tae450lphjy8nciwyrxxlfkv foreign key (husbandId) references t_wife (wifeId) Hibernate: insert into t_wife (wifeName) values (?) Hibernate: insert into t_husband (husbandName, husbandId) values (?, ?)
注解版
package com.fuwh.otobi; import javax.persistence.CascadeType; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.FetchType; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.OneToOne; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity public class Father { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @Column(name="fatherName") private String name; @OneToOne(mappedBy="father",cascade=CascadeType.ALL,fetch=FetchType.LAZY) private Child child; public Child getChild() { return child; } public void setChild(Child child) { this.child = child; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.otobi; import javax.persistence.CascadeType; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.JoinColumn; import javax.persistence.OneToOne; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity public class Child { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @Column(name="childName") private String name; @OneToOne(cascade=CascadeType.ALL) @JoinColumn(name="father_id") private Father father; public Father getFather() { return father; } public void setFather(Father father) { this.father = father; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.otobi.Child; import com.fuwh.otobi.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); Father father1=new Father(); father1.setName("爸爸1"); Child child1=new Child(); child1.setName("儿子一"); child1.setFather(father1); session.save(child1); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
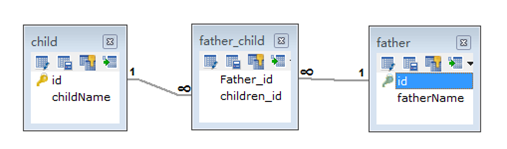
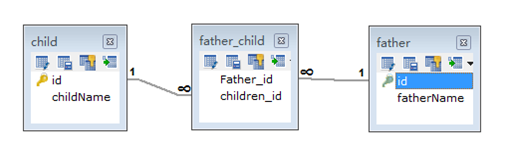
@Many-To-Many关系需要一个连接表来连接两张表。
package com.fuwh.model; public class Wife { private int id; private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
package com.fuwh.model; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; public class Husband { private int id; private String name; private Set<Wife> wives=new HashSet<Wife>(); public Set<Wife> getWives() { return wives; } public void setWives(Set<Wife> wives) { this.wives = wives; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 --> <hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Wife" table="t_wife"> <id name="id" column="wifeId"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="wifeName"></property> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 --> <hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Husband" table="t_husband"> <id name="id" column="husbandId"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <property name="name" column="husbandName"></property> <set name="wives" cascade="all"> <!-- key 指定连接表的主键列 many-to-many:中的列指定连接另一端的列,或对应的类 --> <key column="husband_id"></key> <many-to-many column="wife_id" class="com.fuwh.model.Wife"></many-to-many> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.model.Child; import com.fuwh.model.Father; import com.fuwh.model.Husband; import com.fuwh.model.Wife; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); Husband husband=new Husband(); husband.setName("老公"); Wife wife1=new Wife(); wife1.setName("老婆1"); Wife wife2=new Wife(); wife2.setName("老婆2"); husband.getWives().add(wife1); husband.getWives().add(wife2); // session.save(wife); session.save(husband); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
注解
package com.fuwh.model; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.CascadeType; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.ManyToMany; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity(name="person") public class Person { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @ManyToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL) private List<Address> addresses=new ArrayList<Address>(); public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public List<Address> getAddresses() { return addresses; } public void setAddresses(List<Address> addresses) { this.addresses = addresses; } }
package com.fuwh.model; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity(name="address") public class Address { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @Column(name="street") private String street; private String number; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getStreet() { return street; } public void setStreet(String street) { this.street = street; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.model.Address; import com.fuwh.model.Person; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); Person person=new Person(); Address address1=new Address(); address1.setNumber("1001"); address1.setStreet("java路"); Address address2=new Address(); address2.setNumber("1002"); address2.setStreet("php路"); person.getAddresses().add(address1); person.getAddresses().add(address2); session.save(person); session.flush(); //删除的时候会把所有的address的id的记录删除,在插入其他不用删除的 person.getAddresses().remove(address1); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
生成的SQL文
Hibernate: create table address ( id integer not null auto_increment, number varchar(255), street varchar(255), primary key (id) ) Hibernate: create table person ( id integer not null auto_increment, primary key (id) ) Hibernate: create table person_address ( person_id integer not null, addresses_id integer not null ) Hibernate: alter table person_address add constraint FKkvjdfs4jhjpxa6y3melormp0w foreign key (addresses_id) references address (id) Hibernate: alter table person_address add constraint FKnndfs0btabect8upo03uwgfxt foreign key (person_id) references person (id) Hibernate: insert into person values ( ) Hibernate: insert into address (number, street) values (?, ?) Hibernate: insert into address (number, street) values (?, ?) Hibernate: insert into person_address (person_id, addresses_id) values (?, ?) Hibernate: insert into person_address (person_id, addresses_id) values (?, ?) Hibernate: delete from person_address where person_id=? Hibernate: insert into person_address (person_id, addresses_id) values (?, ?)
package com.fuwh.model; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; public class Wife { private int id; private String name; private Set<Husband> husbands=new HashSet<Husband>(); public Set<Husband> getHusbands() { return husbands; } public void setHusbands(Set<Husband> husbands) { this.husbands = husbands; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 --> <hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Wife" table="t_wife"> <id name="id" column="wifeId"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="wifeName"></property> <!-- 这里必须参照Husband.hbm.xml文件中的连接表的配置,否则会默认生成两个连接表 也就是两个单向的多对多 --> <set name="husbands" inverse="true" table="husband_wife"> <key column="wife_id"></key> <many-to-many column="husband_id" class="com.fuwh.model.Husband" ></many-to-many> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.model.Child; import com.fuwh.model.Father; import com.fuwh.model.Husband; import com.fuwh.model.Wife; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); Husband husband1=new Husband(); husband1.setName("老公1"); Husband husband2=new Husband(); husband2.setName("老公2"); Wife wife1=new Wife(); wife1.setName("老婆1"); Wife wife2=new Wife(); wife2.setName("老婆2"); husband1.getWives().add(wife1); husband1.getWives().add(wife2); wife1.getHusbands().add(husband1); wife1.getHusbands().add(husband2); session.save(husband1); session.save(husband2); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
生成的SQL文
Hibernate: create table husband_wife ( husband_id integer not null, wife_id integer not null, primary key (husband_id, wife_id) ) Hibernate: create table t_husband ( husbandId integer not null auto_increment, husbandName varchar(255), primary key (husbandId) ) Hibernate: create table t_wife ( wifeId integer not null auto_increment, wifeName varchar(255), primary key (wifeId) ) Hibernate: alter table husband_wife add constraint FK56txr9ocpn1k0eyc7ax1a2smw foreign key (wife_id) references t_wife (wifeId) Hibernate: alter table husband_wife add constraint FKsiwjiutn6eoha0iv059pd75fc foreign key (husband_id) references t_husband (husbandId) Hibernate: insert into t_husband (husbandName) values (?) Hibernate: insert into t_wife (wifeName) values (?) Hibernate: insert into t_husband (husbandName) values (?) Hibernate: insert into t_wife (wifeName) values (?) Hibernate: insert into husband_wife (husband_id, wife_id) values (?, ?) Hibernate: insert into husband_wife (husband_id, wife_id) values (?, ?)
注解
package com.fuwh.mtmbi; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.CascadeType; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.ManyToMany; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity(name="person") public class Person { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @ManyToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL) private List<Address> addresses=new ArrayList<Address>(); public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public List<Address> getAddresses() { return addresses; } public void setAddresses(List<Address> addresses) { this.addresses = addresses; } }
package com.fuwh.mtmbi; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.ManyToMany; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity(name="address") public class Address { @Id @GeneratedValue(generator="_native") @GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native") private int id; @Column(name="street") private String street; private String number; @ManyToMany(mappedBy="address") private List<Person> owners=new ArrayList<Person>(); public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getStreet() { return street; } public void setStreet(String street) { this.street = street; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.mtmbi.Person; import com.fuwh.mtmbi.Address; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式 private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build(); try { sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry); } } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { if(sessionFactory != null){ sessionFactory.close(); } } @Test public void testAdd() { Session session=sessionFactory.openSession(); session.beginTransaction(); Person person1=new Person(); Person person2=new Person(); Address address1=new Address(); address1.setNumber("101"); Address address2=new Address(); address2.setNumber("102"); person1.getAddresses().add(address1); person1.getAddresses().add(address2); person2.getAddresses().add(address1); session.save(person1); session.save(person2); session.getTransaction().commit(); session.close(); } }
生成的SQL文
Hibernate: create table address ( id integer not null auto_increment, number varchar(255), street varchar(255), primary key (id) ) Hibernate: create table person ( id integer not null auto_increment, primary key (id) ) Hibernate: create table person_address ( owners_id integer not null, addresses_id integer not null ) Hibernate: alter table person_address add constraint FKkvjdfs4jhjpxa6y3melormp0w foreign key (addresses_id) references address (id) Hibernate: alter table person_address add constraint FKpts56mn8uttsyi3b63b2cihvo foreign key (owners_id) references person (id) Hibernate: insert into person values ( ) Hibernate: insert into address (number, street) values (?, ?) Hibernate: insert into address (number, street) values (?, ?) Hibernate: insert into person values ( ) Hibernate: insert into person_address (owners_id, addresses_id) values (?, ?) Hibernate: insert into person_address (owners_id, addresses_id) values (?, ?) Hibernate: insert into person_address (owners_id, addresses_id) values (?, ?)




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步