查找算法总结
一、顺序查找
public int sequenceSearch(int[] a, int value){ for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){ if(a[i] == value) return i; } return -1; }
二、二分查找
要求:元素必须是有序的。如果是无序的,则要先进行排序操作。
1. 使用循环实现
public int binarySearch2(int[] a, int value) { int low = 0, high = a.length - 1, mid; while (low <= high) { mid = (low + high) / 2; if (a[mid] == value) return mid; else if (a[mid] > value) high = mid - 1; else low = mid + 1; } return -1-low; //-1-low表示value应插入的位置? }
2. 使用递归实现
public int binarySearch(int[] a, int value, int low, int high) { int mid = (low + high) / 2; if (a[mid] == value) return mid; else if (a[mid] < value) return binarySearch(a, value, mid + 1, high); else return binarySearch(a, value, low, mid - 1); }
3. 二分查找的变种:插值查找
基本思想:基于二分查找算法,将查找点的选择改进为自适应选择,可以提高查找效率。它是二分查找的改进版。
二分查找:
mid = (low+high)/2 , 即 mid = low + (high-low)/2;
改进后:
mid = low + (high - low) * (key - a[low]) / (a[high] - a[low]);
前提条件:适合表长较大,而关键字分布又比较均匀的查找表。
public class InsertValueSearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {-4, -1, 0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10};
System.out.println(insertValueSearch(arr, 1, 0, arr.length - 1));
}
public static int insertValueSearch(int[] arr, int key, int low, int high) {
if (low > high) {
return -1;
}
int mid = low + (high - low) * (key - arr[low]) / (arr[high] - arr[low]);
if (key < arr[mid]) {
return insertValueSearch(arr, key, low, mid - 1);
} else if (key > arr[mid]) {
return insertValueSearch(arr, key, mid + 1, high);
} else {
return mid;
}
}
}
三、斐波那契查找
基本思想:斐波那契查找是二分查找的一种提升算法,通过运用黄金比例的概念在数列中选择查找点进行查找,提高查找效率。注意同时属于一种有序查找算法
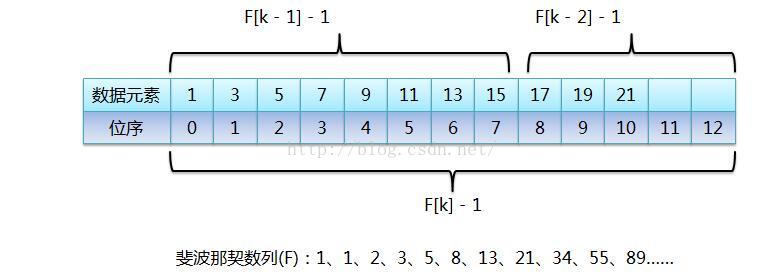
public class FibonacciSearch { private static final int size = 20; public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {-4, -1, 0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10}; System.out.println(fibonacciSearch(arr, 7)); } public static int fibonacciSearch(int[] arr, int key) { int len = arr.length; int low = 0; int mid = 0; int high = len - 1; int n = 0; int[] f = getFib(); //找到等于或刚刚大于high的斐波那契值 while (len > f[n] - 1) { n++; } //创建一个长度为f[n]-1的临时数组,超出arr长度的部分用最后一个元素补齐 int[] temp = Arrays.copyOf(arr, f[n] - 1); for (int i = high + 1; i < temp.length; i++) { temp[i] = arr[high]; } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(temp)); while (low <= high) { //mid = low + f[n - 1] - 1 mid = low + f[n - 1] - 1; //f[n] = f[n - 1] + f[n - 2] //总 = 前 + 后 if (key < temp[mid]) { high = mid - 1; n -= 1; } else if (key > temp[mid]) { low = mid + 1; n -= 2; } else { if (mid <= high) { return mid; } else { return high; } } } return -1; } public static int[] getFib() { int[] f = new int[size]; f[0] = 1; f[1] = 1; for (int i = 2; i < size; i++) { f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2]; } return f; } }
四、二叉排序树查找
基本思想:二叉查找树是先对待查找的数据进行生成树,确保树的左分支的值小于右分支的值,然后在就行和每个节点的父节点比较大小,查找最适合的范围。
注意:前提条件要首先创建树。
二叉查找树或者是一棵空树,特点如下:
1)若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
2)若任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
3)任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树。
public class SearchBST { //全局变量, 存放查找到的关键字所在的父节点 static BinTree parentNode = new BinTree(); public static void main(String[] args) { //主要是表达查询,所以手动构造一棵二叉排序树 BinTree bt1 = new BinTree(); bt1.data = 62; BinTree bt2 = new BinTree(); bt1.lchild = bt2; bt2.data = 58; BinTree bt3 = new BinTree(); bt2.lchild = bt3; bt3.data = 47; BinTree bt4 = new BinTree(); bt3.lchild = bt4; bt4.data = 35; BinTree bt5 = new BinTree(); bt4.rchild = bt5; bt5.data = 37; BinTree bt6 = new BinTree(); bt3.rchild = bt6; bt6.data = 51; BinTree bt7 = new BinTree(); bt1.rchild = bt7; bt7.data = 88; BinTree bt8 = new BinTree(); bt7.lchild = bt8; bt8.data = 73; BinTree bt9 = new BinTree(); bt7.rchild = bt9; bt9.data = 99; BinTree bt10 = new BinTree(); bt9.lchild = bt10; bt10.data = 93; boolean search = searchBST(bt1, 88, null); System.out.println(search == true ? "查找成功:" + parentNode.data : "查找失败!"); } /** * 二叉排序树 * * @param bt 待查询二叉排序树 * @param key 查找关键字 * @param parent 指向bt的双亲,其初始调用值为null * @return 查找关键字key成功 返回true,并把树结点赋值给全局变量result,查找失败,返回false */ public static boolean searchBST(BinTree bt, int key, BinTree parent) { // 树节点不存在,返回 if (null == bt || 0 == bt.data) { parentNode = parent; return false; } else if (key == bt.data) {// 查找成功 parentNode = bt; return true; } else if (key < bt.data) {// 关键字小于根节点则查找左子树 return searchBST(bt.lchild, key, bt); } else {// 关键字大于根节点则查找右子树 return searchBST(bt.rchild, key, bt); } } /** * 二叉树 数据结构 */ private static class BinTree { int data; BinTree lchild; BinTree rchild; } }
五、哈希表查找
1. 定义
哈希表查找又叫散列表查找,通过查找关键字,不需要比较就可以获得需要记录的存储位置。它是通过记录的存储位置和它的关键字之间建立一个确定的对应关系f,使得每个关键字key对应一个存储位置f(key)。
即:存储位置=f(关键字),其中f为哈希函数。
2. 哈希函数的构造方法
(1). 直接定址法(取关键字的某个线性函数值为哈希地址)
例:f(key)= a*key + b (其中a,b均为常数)
(2). 数字分析法(通过关键字的整体情况来判断去关键字的某一段或者某一种形式):
原则:尽量选择关键字出现随机且相互独立的区段。
(3). 除留余数法
这是最为常用的构造哈希函数的方法,对于哈希表长度为m的哈希函数为:
f(key)=key mod p (p<=m)通常p为小于或者等于表长的最小质数(只能被1和其自身整除的数)
3. 解决冲突的方法
(1). 开放定址法:
1):线性探测再散列:即从冲突的地址开始往后找,直至找到‘空’的哈希地址。
2):二次探测再散列:一次取1的二次方,-1的二次方,2的二次方,-2的二次方……让当前冲突的哈希地址与这些数字一次相加知道找到‘空地址’,其实我们可以看做在冲突的地方两边波动并逐渐远离。
3):伪随机数序列: 使用随机函数计算
(2). 再哈希法:H = R(H(key)):即在同义词产生地址冲突时通过另一个哈希函数计算哈希地址。
(3). 链地址法:创建一个链表,将所有关键字为同义词的记录存储在此线性表中。
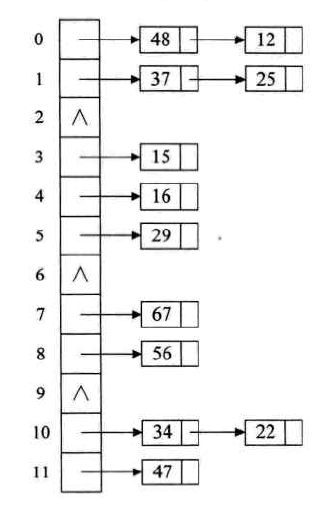
public class HashTableSearch { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1, 3, 5, 65, 6, 34, 67, 343, 56}; System.out.println(hashSearch(arr,34)); System.out.println(hashSearch(arr,100)); } /*** * * 哈希结点 */ private static class Node { int key; // 链表中的键 Node next; // 下一个同义词 } /*** * 在哈希表中查找关键字key * @param data * @param key * @return */ public static boolean hashSearch(int[] data, int key) { int p = 1; // 寻找小于或等于最接近表长的素数 for (int i = data.length; i > 1; i--) { if (isPrimes(i)) { p = i; break; } } // 构建哈希表 Node[] hashtable = createHashTable(data, p); // 查找key是否在哈希表中 int k = key % p; Node cur = hashtable[k]; while (cur != null && cur.key != key) { cur = cur.next; } if (cur == null) { return false; } else { return true; } } /*** * 用求余,链表法构建哈希表 * @param data * @param p * @return */ public static Node[] createHashTable(int[] data, int p) { Node[] hashtable = new Node[p]; int k; //哈希函数计算的单元地址 for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) { Node node = new Node(); node.key = data[i]; k = data[i] % p; if (hashtable[k] == null) { hashtable[k] = node; } else { Node current = hashtable[k]; while (current.next != null) { current = current.next; } current.next = node; } } return hashtable; } /*** * 除余法构建哈希函数 用链表法解决哈希冲突 * @param n * @return */ public static boolean isPrimes(int n) { for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i++) { if (n % i == 0) { return false; } } return true; } }
参考:
https://xie.infoq.cn/article/996cf8899930ae467cc790035
https://blog.csdn.net/smile_from_2015/article/details/72190562



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号