C# LinQ基础
LinQ基础
什么是LINQ
引出
LINQ能够解决什么问题
NET平台开发中一直存在如下情况
- 面向对象编程语言与数据访问方法长期分离,以嵌入式的方式开发。例如:

- 编程语言中的数据类型与数据库中的数据类型形成两套体系。
- 例如:C#中字符串string在SQL中用NVarchar/Varchar/Char来表示。
- SQL和XML都有各自的查询语言,而对象没有自己的查询语言。
- 比如要从List<T>集合或数组中找到符合要求的元素,非常困难。
LINQ将重点解决以上问题
定义
LINQ(Language Integrated Query,语言集成查询)
- 是微软公司提供的一项新技术,能够将查询功能直接引入到C#、VB.NET等变成语言中。
- 查询操作可以通过编程语言自身来表示,而不是嵌入字符串SQL语句。
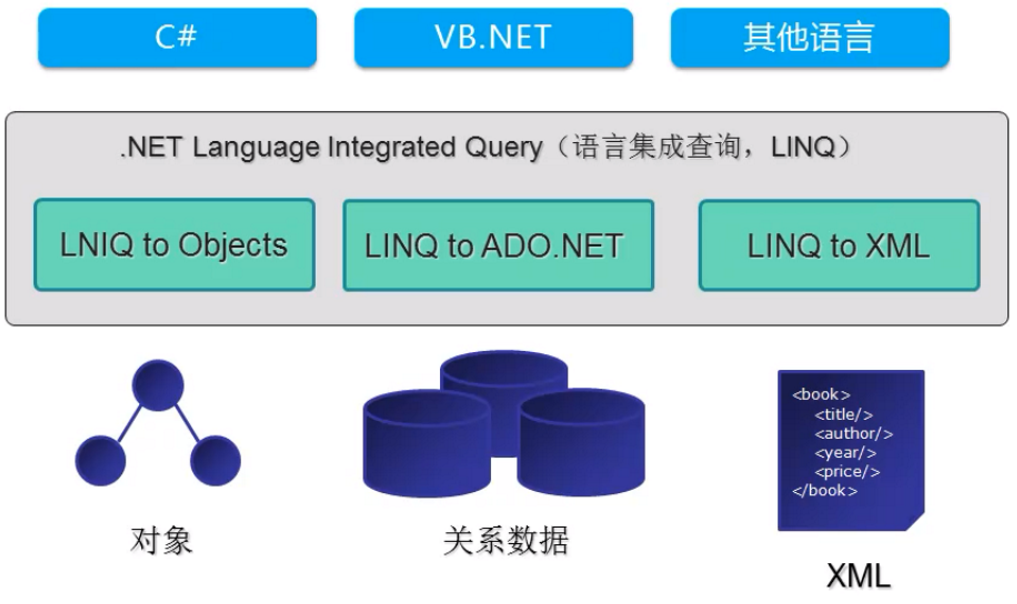
LINQ主要包含以下三个部分
- LINQ to Objects主要负责对象的查询
- LINQ to XML主要负责XML的查询
- LINQto ADO.NET主要负责数据库的查询
- (1)LINQ to SQL(目前已经没有人在使用)
- (2)LINQ to DataSet
- (3)LINQ to Entities(重点学习)
LINQ所在命名空间
- System.Linq;该命名空间已经由系统自动引入
- 因此微软默认建议你多使用Linq技术查询
LINQ的组成架构
对比:
| 不采用LINQ技术的查询方法 | 使用LINQ查询方法PK刚才的查询方法 |

|
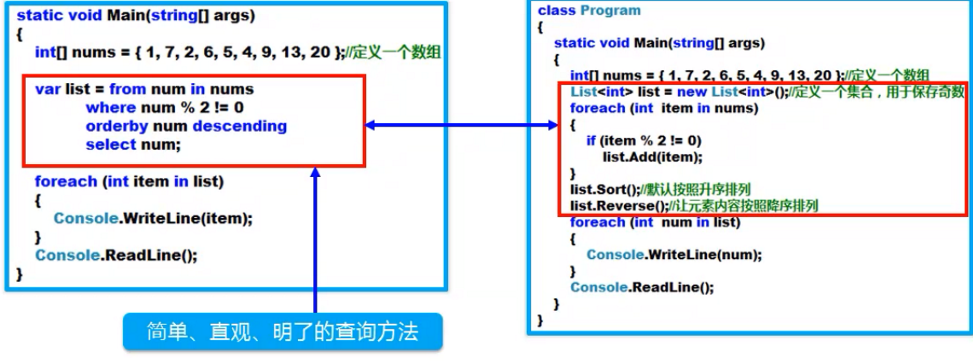
|
LinQ查询方法
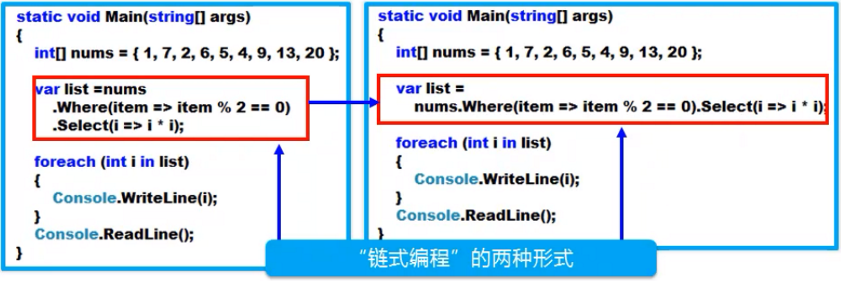
获取数据:扩展方法Select()
- Select()是一个泛型扩展方法
- Select()方法使用的时候,要求传递一个委托实例(委托实例就是一个方法)
Select()方法应用

提示:数组、泛型集合都可以使用扩展方法Select()
筛选数据:Where()方法
- Where()方法是一个扩展泛型方法
- Where()方法使用的时候要求传递一个委托实例,但该实例是一个判断条件,因此返回的类型必须是bool类型
Where()方法应用
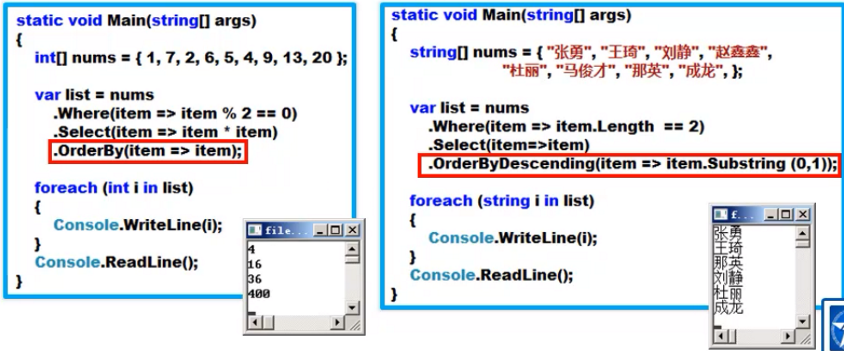
排序数据:OrderBy()
- OrderBy()是一个扩展方法
- OrderBy()里面的参数要求传递一个排序的字段,默认按照升序排列
- 如果想降序排列可以使用OrderByDescending方法
OrderBy()方法应用
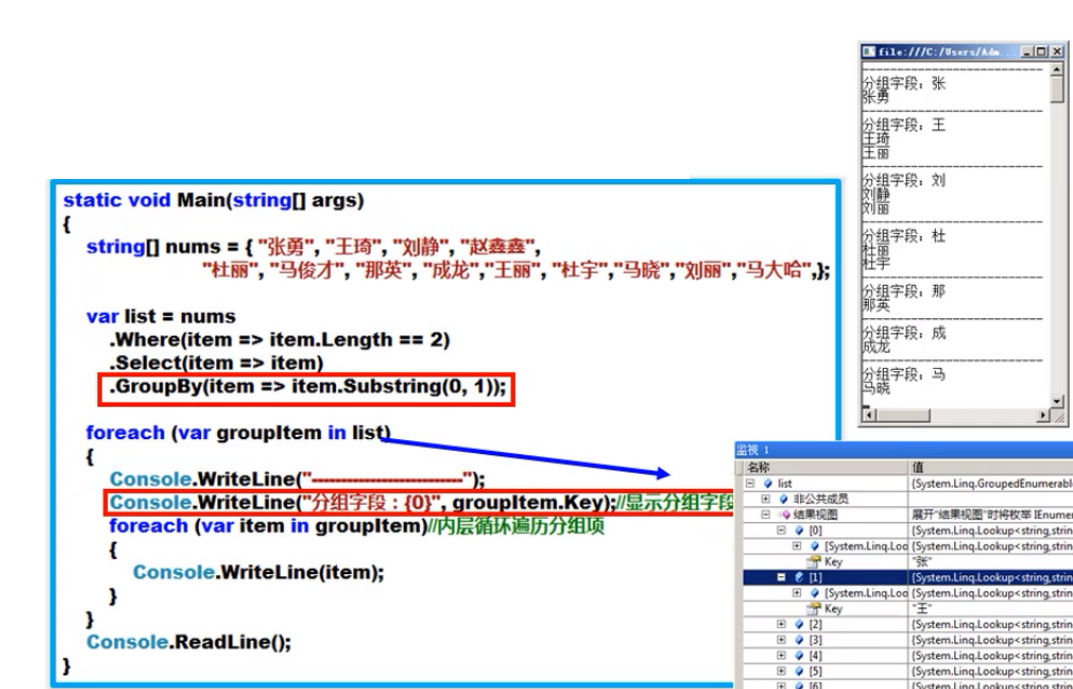
分组数据:GroupBy()方法
- OrderBy()是一个扩展方法
- OrderBy()里面的参数要求传递一个分组的字段
GroupBy()方法应用
LinQ查询实际和查询形式
查询实际
观察如下代码的执行顺序
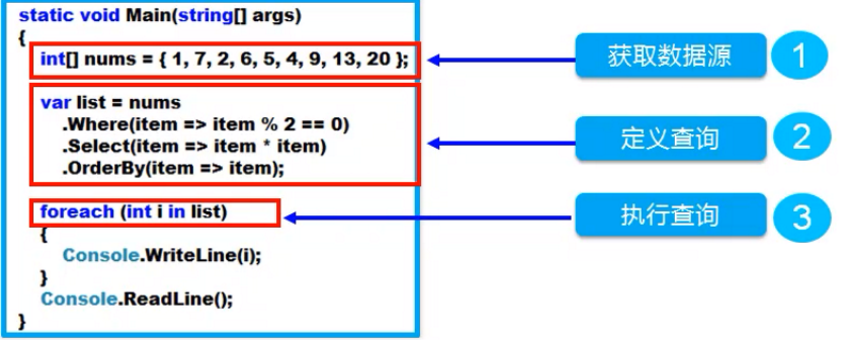
查询步骤
- 获取数据源、定义查询、执行查询
观察结论
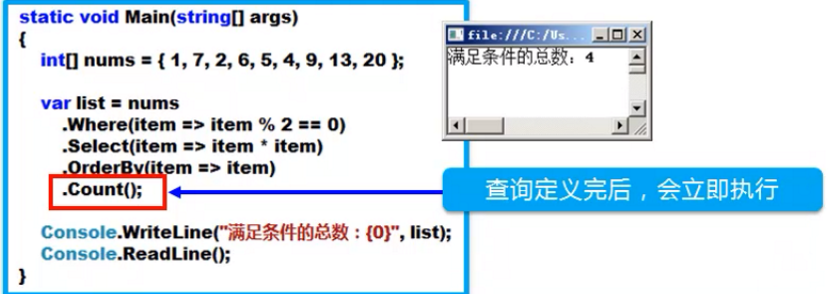
- 定义查询后,查询并没有立即执行,而是直到需要枚举结果(遍历)时才被真正执行
- 这种方式称为“延迟执行(deferred execution)”
使用“聚合扩展方法”返回单一结果,强制查询立即执行
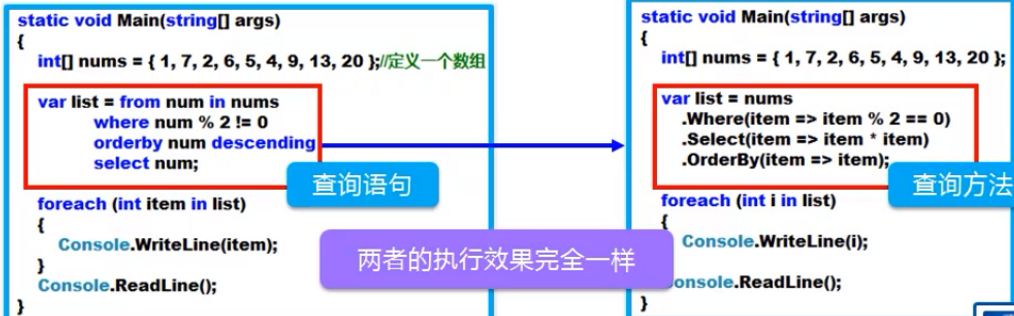
LINQ查询的两种形式
Method Syntax,查询方法方式
- 主要利用System.Linq.Enumerable类中定义的扩展方法和Lambda表达式方式进行查询
- 在此之前所用的查询都是这种方法
Query Syntax,查询语句方式
- 一种更接近SQL语法的查询方式,可读性更好
- 查询语句最后还是要被翻译成查询方法
LINQ查询子句概述
查询表达式
- 是一种用查询语法表示的表达式,由一组用类似于SQL的语法编写的句子组成
- 每一个子句可以包含一个或多个C#表达式

LINQ查询表达式包含的子句
- from子句:指定查询操作的数据源和范围变量
- where子句:筛选元素的逻辑条件,返回值是一个bool类型
- select子句:指定查询结果的类型和表现形式
- orderby子句:对查询结果进行排序(升序或降序)
- group子句:对查询结果进行分组
- into子句:提供一个临时标识符,该表示可充当对join/group/select子句结果的引用
- join子句:连接多个查询操作的数据源
- let子句:引入用于存储查询表达式中的子表达式结果的范围变量
from子句
from子句概述
- LINQ查询表达式必须包含from子句,并且必须以from子句开头
- from子句指定的数据源类型必须为IEnumerable、Ienumerable<T>或者两者的派生类型(例如:数组、 List<T>、ArrayList等)
关于数据源
- 如果数据源是泛型类型,则编译器可以自动推断出范围变量的类型,比如上面的num类型为int类型
- 如果数据源是非泛型类型,如ArrayList,则必须显示的指定范围变量的数据类型

复合from子句查询
- 如果数据源(本身是一个序列)的元素还包含子数据源(如序列、列表等),如果要查询子数据源中的元素,则需要使用复合from子句

多个from子句查询
- 若LINQ查询表达式包含两个或两个以上的独立数据源时,可以使用多个from子句查询所有数据源中的数据

其他常用子句
where子句概述
- 用于指定筛选元素的逻辑条件
- 一个查询表达式可以不包含where子句
- 如果查询表达式包含where子句,则where子句不能放在最后一个子句
select子句
- 用于指定查询结果的类型和表现形式
- LINQ查询表达式或者以select子句结束或者以group子句结束
group子句
- 用于对查询结果分组
- 返回元素类型为Igrouping<Tkey,TElement>对象序列
orderby子句
- 用于对查询结果排序,默认“升序”
- 在排序字段后面加上descending可以实现降序
其他子句:into/join/let(略)
LinQ高级查询
高级查询方法
聚合类
- Count , Max/Min , Average
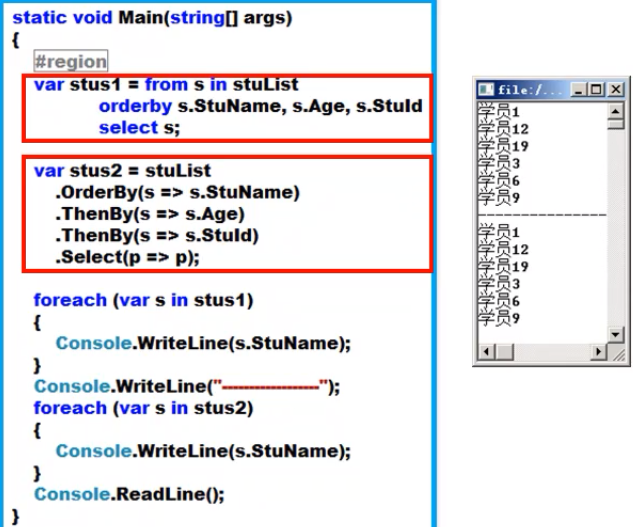
排序类
- ThenBy
分区类
- Take , TakeWhile , Skip , SkipWhile
集合类
- Distinct
生成类
- Range, Repeat
聚合类查询
- Count返回集合项的数目
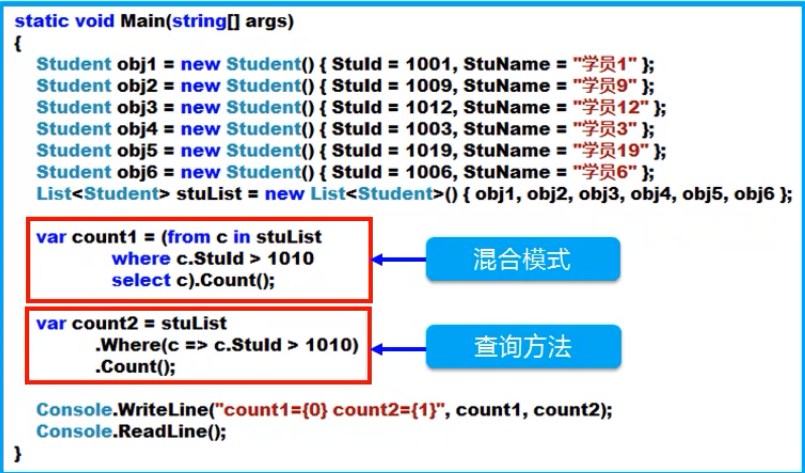
- Max/Min求最大值、最小值
- Average 返回集合的平均值
- Sum返回集合的总数
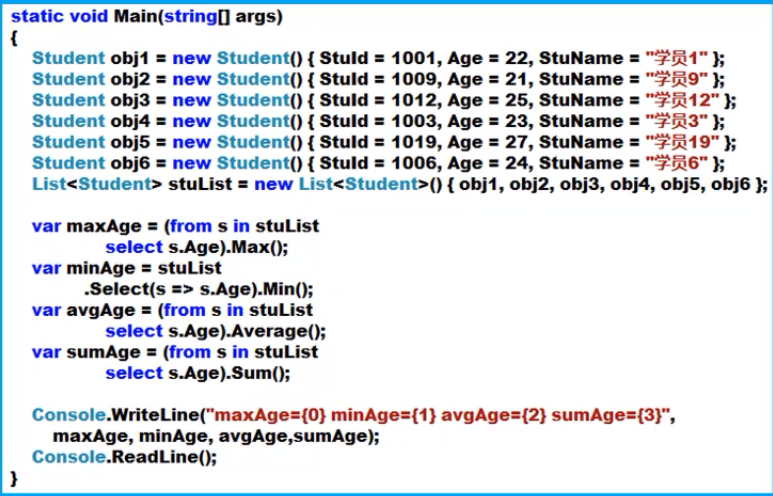
排序类
- ThenBy提供复合排序条件
分区类
- Take提取指定数量的项
- Skip跳过指定数量的项并获取剩余的项
- TakeWhile只要满足指定的条件,就会返回序列的元素,然后跳过剩余的元素
- SkipWhile只要满足指定的条件,就跳过序列中的元素,然后返回剩余元素

集合类查询Distinct
- Distinct去掉集合中的重复项

生成类查询
- Range生成一个整数序列
- Repeat生成一个重复项的序列
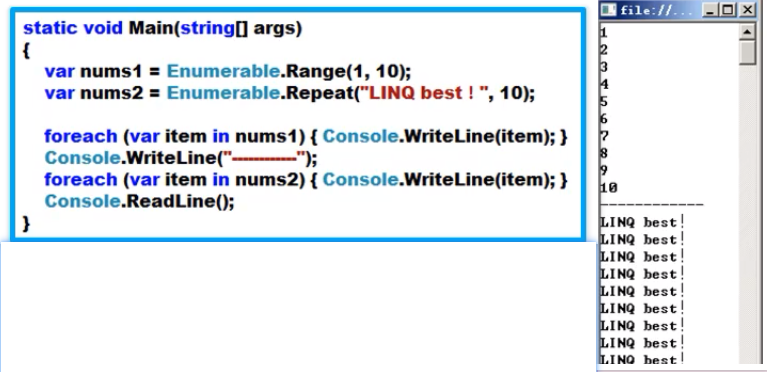
注意问题:
- Range/Repeat不是扩展方法,而是普通的静态方法
- Range只能产生整数序列
- Repeat可以产生泛型序列
- 所有的查询方法都存放在System.Linq.Enumerable 静态类中
示例

1 using System; 2 using System.Collections; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 namespace LinqDemo 7 { 8 class Program 9 { 10 #region 示例1:不使用LINQ查询数组 11 static void Main(string[] args) 12 { 13 int[] nums = { 1, 7, 2, 6, 5, 4, 9, 13, 20 }; 14 List<int> list = new List<int>(); 15 foreach (int item in nums) 16 { 17 if (item % 2 != 0) 18 list.Add(item); 19 } 20 list.Sort(); 21 list.Reverse(); 22 foreach (int item in list) 23 { 24 Console.WriteLine(item); 25 } 26 Console.ReadLine(); 27 } 28 #endregion 29 #region 示例2:使用LINQ技术查询数组 30 //static void Main(string[] args) 31 //{ 32 // int[] nums = { 1, 7, 2, 6, 5, 4, 9, 13, 20 }; 33 // var list = from num in nums 34 // where num % 2 != 0 35 // orderby num descending 36 // select num; 37 // foreach (int item in list) 38 // { 39 // Console.WriteLine(item); 40 // } 41 // Console.ReadLine(); 42 //} 43 #endregion 44 #region 示例3:扩展方法Select()应用 45 //static void Main(string[] args) 46 //{ 47 // int[] nums = { 1, 7, 2, 6, 5, 4, 9, 13, 20 }; 48 // var list = nums.Select(item => item * item); 49 // foreach (int item in list) 50 // { 51 // Console.WriteLine(item); 52 // } 53 // Console.ReadLine(); 54 //} 55 #endregion 56 #region 示例4:扩展方法Where()应用 57 //static void Main(string[] args) 58 //{ 59 // int[] nums = { 1, 7, 2, 6, 5, 4, 9, 13, 20 }; 60 // var list = nums 61 // .Where(item => item % 2 == 0) 62 // .Select(i => i * i); 63 // Console.ReadLine(); 64 //} 65 #endregion 66 #region 示例5:扩展方法OrderBy()应用 67 //static void Main(string[] args) 68 //{ 69 // int[] nums = { 1, 7, 2, 6, 5, 4, 9, 13, 20 }; 70 // var list = nums 71 // .Where(item => item % 2 == 0) 72 // .Select(i => i * i) 73 // .OrderBy(item => item); 74 // foreach (int i in list) 75 // { 76 // Console.WriteLine(i); 77 // } 78 // Console.ReadLine(); 79 //} 80 //static void Main(string[] args) 81 //{ 82 // string[] nums = { "张勇", "王琦", "刘静", "赵鑫鑫", 83 // "杜丽", "马俊才", "那英", "成龙", }; 84 // var list = nums 85 // .Where(item => item.Length == 2) 86 // .Select(item => item) 87 // .OrderByDescending(item => item.Substring(0, 1)); 88 // foreach (string item in list) 89 // { 90 // Console.WriteLine(item); 91 // } 92 // Console.ReadLine(); 93 //} 94 #endregion 95 #region 示例6:扩展方法GroupBy()应用 96 //static void Main(string[] args) 97 //{ 98 // string[] nums = { "张勇", "王琦", "刘静", "赵鑫鑫", 99 // "杜丽", "马俊才", "那英", "成龙","王丽", "杜宇","马晓","刘丽","马大哈",}; 100 // var list = nums 101 // .Where(item => item.Length == 2) 102 // .Select(item => item) 103 // .GroupBy(item => item.Substring(0, 1)); 104 // foreach (var groupItem in list) 105 // { 106 // Console.WriteLine("-------------------"); 107 // Console.WriteLine("分组字段:{0}", groupItem.Key); 108 // foreach (var item in groupItem) 109 // { 110 // Console.WriteLine(item); 111 // } 112 // } 113 114 115 // Console.ReadLine(); 116 //} 117 #endregion 118 #region 示例7:断点调试LINQ的查询时机 119 //static void Main(string[] args) 120 //{ 121 // int[] nums = { 1, 7, 2, 6, 5, 4, 9, 13, 20 }; 122 // var list = nums 123 // .Where(item => item % 2 == 0) 124 // .Select(item => item * item) 125 // .OrderBy(item => item); 126 // foreach (int i in list) 127 // { 128 // Console.WriteLine(i); 129 // } 130 // Console.ReadLine(); 131 //} 132 #endregion 133 #region 示例8:查询的立即执行 134 //static void Main(string[] args) 135 //{ 136 // int[] nums = { 1, 7, 2, 6, 5, 4, 9, 13, 20 }; 137 // var list = nums 138 // .Where(item => item % 2 == 0) 139 // .Select(item => item * item) 140 // .OrderBy(item => item) 141 // .Count(); 142 // Console.WriteLine(list.ToString ()); 143 // Console.ReadLine(); 144 //} 145 #endregion 146 #region 示例9:from子句的简单使用 147 //static void Main(string[] args) 148 //{ 149 // ArrayList values = new ArrayList(); 150 // for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { values.Add(i); } 151 // var list = from int item in values 152 // where item % 2 == 0 153 // select item; 154 // foreach (int item in list) { Console.WriteLine(item); } 155 // Console.ReadLine(); 156 //} 157 #endregion 158 #region 示例10:复合from子句的使用 159 //static void Main(string[] args) 160 //{ 161 // Student obj1 = new Student() 162 // { 163 // StuId = 1001, 164 // StuName = "学员1", 165 // ScoreList = new List<int>() { 90, 78, 54 } 166 // }; 167 // Student obj2 = new Student() 168 // { 169 // StuId = 1002, 170 // StuName = "学员2", 171 // ScoreList = new List<int>() { 95, 88, 90 } 172 // }; 173 // Student obj3 = new Student() 174 // { 175 // StuId = 1003, 176 // StuName = "学员3", 177 // ScoreList = new List<int>() { 79, 76, 89 } 178 // }; 179 // //将学员封装到集合中 180 // List<Student> stuList = new List<Student>() { obj1, obj2, obj3 }; 181 // //查询成绩包含95分以上的学员 182 // var result = from stu in stuList 183 // from score in stu.ScoreList 184 // where score >= 95 185 // select stu; 186 // //显示查询结果 187 // foreach (var item in result) 188 // { 189 // Console.WriteLine(item.StuName); 190 // } 191 192 // Console.ReadLine(); 193 //} 194 #endregion 195 #region 示例11:多个from子句查询的使用 196 //static void Main(string[] args) 197 //{ 198 // Student obj1 = new Student() { StuId = 1001, StuName = "学员1" }; 199 // Student obj2 = new Student() { StuId = 1009, StuName = "学员9" }; 200 // Student obj3 = new Student() { StuId = 1012, StuName = "学员12" }; 201 // Student obj4 = new Student() { StuId = 1003, StuName = "学员3" }; 202 // Student obj5 = new Student() { StuId = 1019, StuName = "学员19" }; 203 // Student obj6 = new Student() { StuId = 1006, StuName = "学员6" }; 204 // List<Student> stuList1 = new List<Student>() { obj1, obj2, obj3 }; 205 // List<Student> stuList2 = new List<Student>() { obj4, obj5, obj6 }; 206 // //查询学好大于1010的学员 207 // var result = from stu1 in stuList1 208 // where stu1.StuId >= 1010 209 // from stu2 in stuList2 210 // where stu2.StuId >= 1010 211 // select new { stu1, stu2 }; 212 // //显示查询结果 213 // foreach (var item in result ) 214 // { 215 // Console.WriteLine(item.stu1.StuName+" "+item.stu1.StuId); 216 // Console.WriteLine(item.stu2.StuName + " " + item.stu2.StuId); 217 // } 218 // Console.ReadLine(); 219 //} 220 #endregion 221 #region 示例12:聚合函数Count 222 //static void Main(string[] args) 223 //{ 224 // Student obj1 = new Student() { StuId = 1001, StuName = "学员1" }; 225 // Student obj2 = new Student() { StuId = 1009, StuName = "学员9" }; 226 // Student obj3 = new Student() { StuId = 1012, StuName = "学员12" }; 227 // Student obj4 = new Student() { StuId = 1003, StuName = "学员3" }; 228 // Student obj5 = new Student() { StuId = 1019, StuName = "学员19" }; 229 // Student obj6 = new Student() { StuId = 1006, StuName = "学员6" }; 230 // List<Student> stuList = new List<Student>() { obj1, obj2, obj3, obj4, obj5, obj6 }; 231 // var count1 = (from c in stuList 232 // where c.StuId > 1010 233 // select c).Count(); 234 // var count2 = stuList.Where(c => c.StuId > 1010).Count(); 235 // Console.WriteLine("count1={0} count2={1}",count1,count2); 236 237 // Console.ReadLine(); 238 //} 239 #endregion 240 #region 示例13:聚合函数Max、Min、Average 241 //static void Main(string[] args) 242 //{ 243 // Student obj1 = new Student() { StuId = 1001, Age = 22, StuName = "学员1" }; 244 // Student obj2 = new Student() { StuId = 1009, Age = 21, StuName = "学员9" }; 245 // Student obj3 = new Student() { StuId = 1012, Age = 25, StuName = "学员12" }; 246 // Student obj4 = new Student() { StuId = 1003, Age = 23, StuName = "学员3" }; 247 // Student obj5 = new Student() { StuId = 1019, Age = 27, StuName = "学员19" }; 248 // Student obj6 = new Student() { StuId = 1006, Age = 24, StuName = "学员6" }; 249 // List<Student> stuList = new List<Student>() { obj1, obj2, obj3, obj4, obj5, obj6 }; 250 // var maxAge = (from s in stuList 251 // select s.Age).Max(); 252 // var minAge = stuList 253 // .Select(s => s.Age).Min(); 254 // var avgAge = (from s in stuList 255 // select s.Age).Average(); 256 // var sumAge = (from s in stuList 257 // select s.Age).Sum(); 258 // Console.WriteLine("maxAge={0} minAge={1} avgAge={2} sumAge={3}", 259 // maxAge, minAge, avgAge,sumAge); 260 // Console.ReadLine(); 261 //} 262 #endregion 263 #region 示例14:排序类ThenBy的使用 264 //static void Main(string[] args) 265 //{ 266 // Student obj1 = new Student() { StuId = 1001, Age = 22, StuName = "学员1" }; 267 // Student obj2 = new Student() { StuId = 1009, Age = 21, StuName = "学员9" }; 268 // Student obj3 = new Student() { StuId = 1012, Age = 25, StuName = "学员12" }; 269 // Student obj4 = new Student() { StuId = 1003, Age = 23, StuName = "学员3" }; 270 // Student obj5 = new Student() { StuId = 1019, Age = 27, StuName = "学员19" }; 271 // Student obj6 = new Student() { StuId = 1006, Age = 24, StuName = "学员6" }; 272 // List<Student> stuList = new List<Student>() { obj1, obj2, obj3, obj4, obj5, obj6 }; 273 // var stus1 = from s in stuList 274 // orderby s.StuName, s.Age, s.StuId 275 // select s; 276 // var stus2 = stuList 277 // .OrderBy(s => s.StuName) 278 // .ThenBy(s => s.Age) 279 // .ThenBy(s => s.StuId) 280 // .Select(p => p); 281 // foreach (var s in stus1) 282 // { 283 // Console.WriteLine(s.StuName); 284 // } 285 // Console.WriteLine("----------------------"); 286 // foreach (var s in stus2) 287 // { 288 // Console.WriteLine(s.StuName); 289 // } 290 // Console.ReadLine(); 291 //} 292 #endregion 293 #region 示例15:分区类查询 294 //static void Main(string[] args) 295 //{ 296 // int[] nums = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 }; 297 // var list1 = nums.Skip(1).Take(3); 298 // var list2 = nums.SkipWhile(i => i % 3 != 0) 299 // .TakeWhile(i => i % 2 != 0); 300 // foreach (var item in list1) { Console.WriteLine(item); } 301 // Console.WriteLine("------------"); 302 // foreach (var item in list2) { Console.WriteLine(item); } 303 // Console.ReadLine(); 304 //} 305 #endregion 306 #region 示例16:集合类查询Distinct 307 //static void Main(string[] args) 308 //{ 309 // int[] nums = { 1, 2, 2, 6, 5, 6, 7, 8, 8 }; 310 // var list = nums.Distinct(); 311 // foreach (var item in list) { Console.WriteLine(item); } 312 // Console.ReadLine(); 313 //} 314 #endregion 315 #region 示例17:生成类查询 316 //static void Main(string[] args) 317 //{ 318 //var nums1 = Enumerable.Range(1, 10); 319 // var nums2 = Enumerable.Repeat("LINQ best!", 10); 320 // foreach (var item in nums1) { Console.WriteLine(item); } 321 // Console.WriteLine("------------"); 322 // foreach (var item in nums2) { Console.WriteLine(item); } 323 324 // Console.ReadLine(); 325 //} 326 #endregion 327 } 328 }
END



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号