MySQL和Python交互案例练习(2)
1. 数据库设计
创建 "商品分类" 表 |
创建 "商品品牌" 表 |
创建 "商品" 表 |
create table goods_cates( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null, name varchar(40) not null ); |
create table goods_brands ( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null, name varchar(40) not null ); |
create table goods( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null, name varchar(40) default '', price decimal(5,2), cate_id int unsigned, brand_id int unsigned, is_show bit default 1, is_saleoff bit default 0, foreign key(cate_id) references goods_cates(id), foreign key(brand_id) references goods_brands(id) ); |
创建 "顾客" 表 |
创建 "订单" 表 |
创建 "订单详情" 表 |
create table customer( id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null, name varchar(30) not null, addr varchar(100), tel varchar(11) not null ); |
create table orders( id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null, order_date_time datetime not null, customer_id int unsigned, foreign key(customer_id) references customer(id) ); |
create table order_detail( id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null, order_id int unsigned not null, goods_id int unsigned not null, quantity tinyint unsigned not null, foreign key(order_id) references orders(id), foreign key(goods_id) references goods(id) ); |
说明
- 以上创建表的顺序是有要求的,即如果goods表中的外键约束用的是goods_cates或者是goods_brands,那么就应该先创建这2个表,否则创建goods会失败
- 创建外键时,一定要注意类型要相同,否则失败
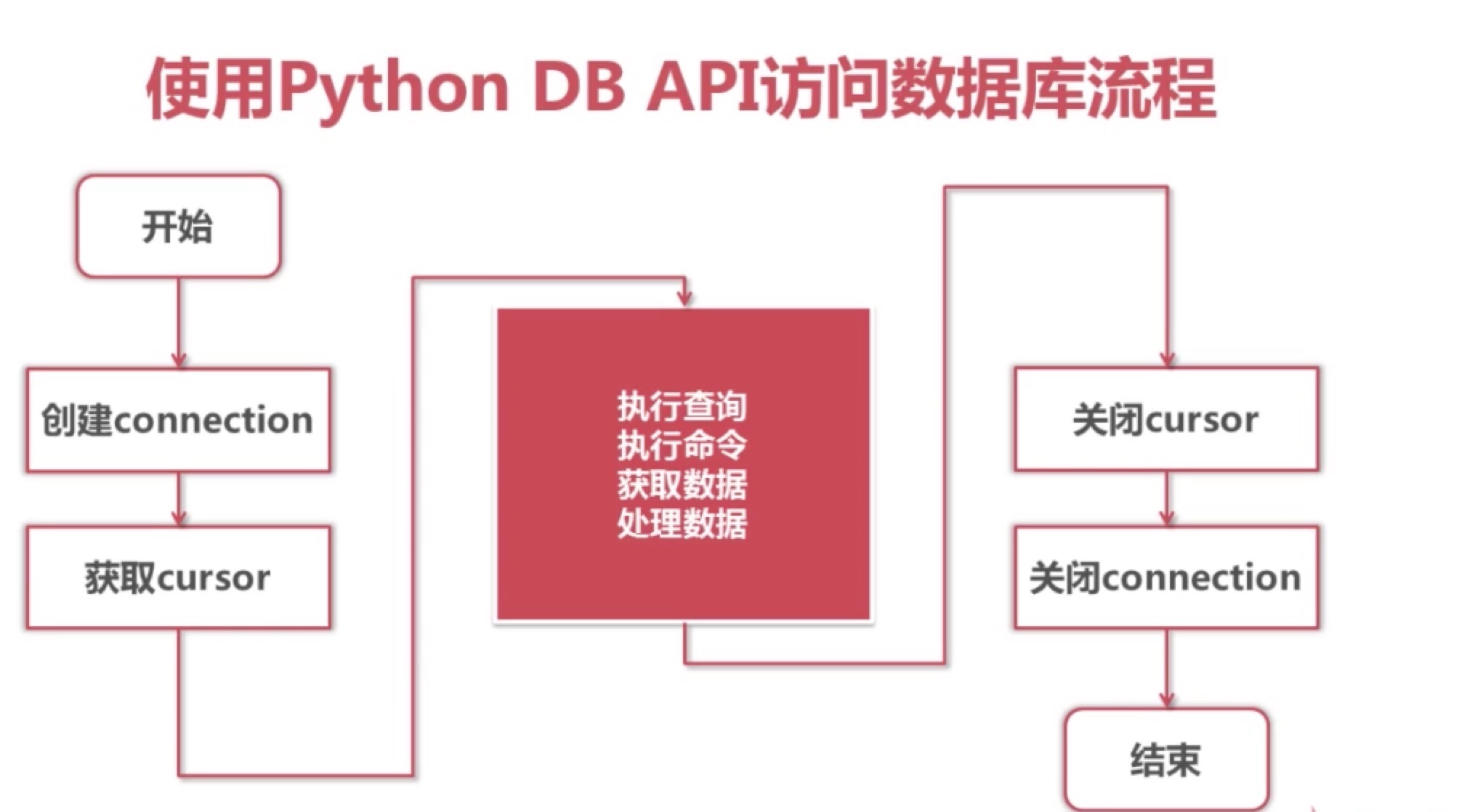
2. Python 中操作 MySQL 步骤
PyMySQL的使用
1. 思考
如何实现将100000条数据插入到MySQL数据库?
答案:
如果使用之前学习的MySQL客户端来完成这个操作,那么这个工作量无疑是巨大的,我们可以通过使用程序代码的方式去连接MySQL数据库,然后对MySQL数据库进行增删改查的方式,实现10000条数据的插入,像这样使用代码的方式操作数据库就称为数据库编程。
 |
2. Python程序操作MySQL数据库
安装pymysql第三方包:
sudo pip3 install pymysql |
说明:
- 安装命令使用 sudo pip3 install 第三方包名
- 卸载命令使用 sudo pip3 uninstall 第三方包
- 可以使用: pip3 show pymysql 命令查看第三方包的信息
- pip3 list 查看使用pip命令安装的第三方包列表
3.pymysql的使用:
1). 引入pymysql模块 |
2). 创建Connection 连接对象 |
3).获取Cursor 游标对象 |
from pymysql import * |
conn=connect(参数列表)
对象的方法
|
cs1=conn.cursor() 对象的方法
对象的属性
|
3. 增删改查
|
增删改 |
查询一行数据 |
查询多行数据 |
from pymysql import * def main(): # 创建Connection连接 conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,database='jing_dong',user='root',password='mysql',charset='utf8') # 获得Cursor对象 cs1 = conn.cursor() # 执行insert语句,并返回受影响的行数:添加一条数据 # 增加 count = cs1.execute('insert into goods_cates(name) values("硬盘")') #打印受影响的行数 print(count) count = cs1.execute('insert into goods_cates(name) values("光盘")') print(count) # # 更新 # count = cs1.execute('update goods_cates set name="机械硬盘" where name="硬盘"') # # 删除 # count = cs1.execute('delete from goods_cates where id=6') # 提交之前的操作,如果之前已经之执行过多次的execute,那么就都进行提交 conn.commit() # 关闭Cursor对象 cs1.close() # 关闭Connection对象 conn.close() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
from pymysql import * def main(): # 创建Connection连接 conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='mysql',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8') # 获得Cursor对象 cs1 = conn.cursor() # 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条数据 count = cs1.execute('select id,name from goods where id>=4') # 打印受影响的行数 print("查询到%d条数据:" % count) for i in range(count): # 获取查询的结果 result = cs1.fetchone() # 打印查询的结果 print(result) # 获取查询的结果 # 关闭Cursor对象 cs1.close() conn.close() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
from pymysql import * def main(): # 创建Connection连接 conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='mysql',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8') # 获得Cursor对象 cs1 = conn.cursor() # 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条数据 count = cs1.execute('select id,name from goods where id>=4') # 打印受影响的行数 print("查询到%d条数据:" % count) # for i in range(count): # # 获取查询的结果 # result = cs1.fetchone() # # 打印查询的结果 # print(result) # # 获取查询的结果 result = cs1.fetchall() print(result) # 关闭Cursor对象 cs1.close() conn.close() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
说明:
- conn.commit() 表示将修改操作提交到数据库
- conn.rollback() 表示回滚数据
4.防止SQL注入
什么是SQL注入?
用户提交带有恶意的数据与SQL语句进行字符串方式的拼接,从而影响了SQL语句的语义,最终产生数据泄露的现象。
如何防止SQL注入?
SQL语句参数化
- sql语句的参数化,可以有效防止sql注入
- SQL语言中的参数使用%s来占位,此处不是python中的字符串格式化操作
- 将SQL语句中%s占位所需要的参数存在一个列表中,把参数列表传递给execute方法中第二个参数
防止SQL注入的示例代码:
from pymysql import * def main(): find_name = input("请输入物品名称:") # 创建Connection连接 conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='mysql',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8') # 获得Cursor对象 cs1 = conn.cursor() # # 非安全的方式 # # 输入 " or 1=1 or " (双引号也要输入) # sql = 'select * from goods where name="%s"' % find_name # print("""sql===>%s<====""" % sql) # # 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询所有数据 # count = cs1.execute(sql) # 安全的方式 # 构造参数列表 params = [find_name] # 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询所有数据 count = cs1.execute('select * from goods where name=%s', params) # 注意: # 如果要是有多个参数,需要进行参数化 # 那么params = [数值1, 数值2....],此时sql语句中有多个%s即可 # 打印受影响的行数 print(count) # 获取查询的结果 # result = cs1.fetchone() result = cs1.fetchall() # 打印查询的结果 print(result) # 关闭Cursor对象 cs1.close() # 关闭Connection对象 conn.close() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
说明:
- execute方法中的 %s 占位不需要带引号
5. 小结
| 1. 导包 |
2. 创建连接对象
|
3. 获取游标对象 | 4. 执行SQL语句 |
import pymysql |
pymysql.connect(参数列表) |
cursor =conn.cursor() |
row_count = cursor.execute(sql) |
| 5. 获取查询结果集 | 6. 将修改操作提交到数据库 | 7. 回滚数据 | 8. 关闭游标 | 9. 关闭连接 |
result = cursor.fetchall() |
conn.commit()
|
conn.rollback()
|
cursor.close() |
|

