10@mysql数据库多表查询查询语句(union、内连接、外连接)
1|0mysql数据库多表查询
1|1一、多表查询分类
1》多表连接查询 2》复合条件连接查询 3》子查询
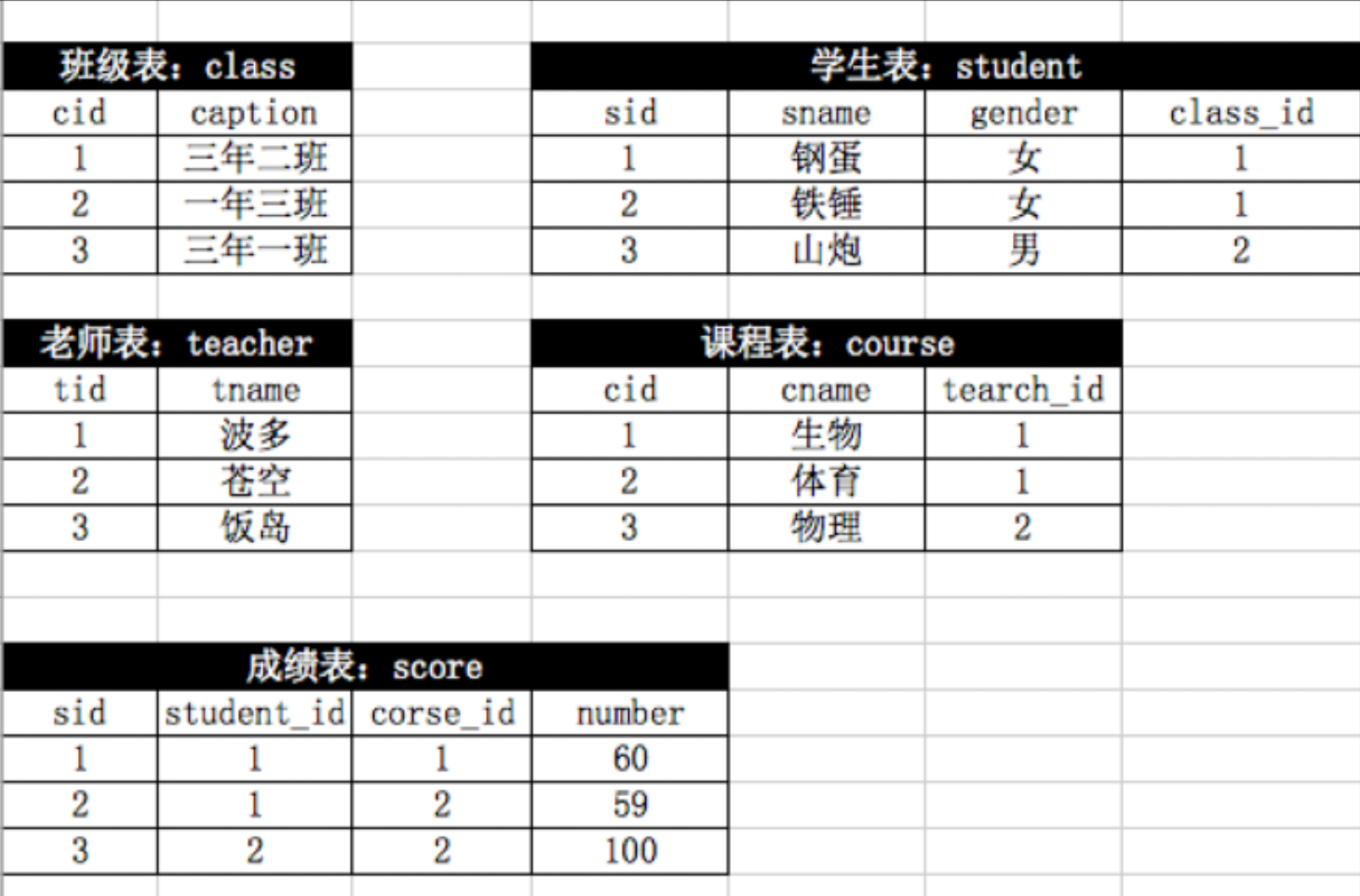
1|2二、多表查询准备
1|3三、多表连接查询
1|01、 交叉连接( 笛卡尔积查询 )
不适用任何匹配条件,生成笛卡尔积
1|01)笛卡尔积查询介绍
1|02)笛卡尔积查询使用
1|02、内连接(inner join on)
只连接匹配的行
1|01)inner join on介绍
在写sql语句的时候,让我们对语句有一个清晰的区分,增强代码的可读性,联表的操作和查询的操作有个明确的区分,就用到了内连接,左链接,右链接的方式inner join on就是内连接的意思,内连接的方式就一个弊端就是,当两个表的数据中无法通过联表指定的字段对应上的时候,就无法显示这些数据,类似集合中交集的意思
1|02)inner join on的使用
1|03、外连接(左连接 left join on )
优先显示左表全部记录
1|01)left join on 介绍
左连接的意思就是在内连接的基础上增加左边有,右边没有的数据,将左边的表作为主表,右边的表作为辅表,当辅表的数据没办法对应上左表的数据时,就通过null来表示(把左表的所有数据都显示)
1|02)left join on的使用
1|04、外连接(右连接 right join on )
优先显示右表全部记录
1|01)right join on介绍
右连接于左连接的用法使一样的,不过右连接是将右表作为主表,左表作为辅表
1|02)right join on的使用
1|05、全外连接( union )
显示左右两个表全部记录
1|01)union介绍
不管是内连接还是左连接,右连接,都会由一些数据使无法显示出来的,那么就可以用全连接的方式来链接,写法是写一个左连接,一个右链接,中间用union 来连接
1|02)union的使用
1|4四、符合条件连接查询
1|5五、子查询
子查询是将一个查询的结果作为另一个查询的条件
1|01、带in关键字的子查询
1|02、带any关键字的子查询
1|03、带all关键字的子查询
1|04、带比较运算符的子查询
1|05、带exists关键字的子查询
EXISTS关字键字表示存在
在使用EXISTS关键字时,内层查询语句不返回查询的记录
而是返回一个真假值 : True或False当返回True时,外层查询语句将进行查询;当返回值为False时,外层查询语句不进行查询
1|01)in与exists
1|02) not in与 not exists
1|03)示例:
1|06、案列
查询每个部门最新入职的那位员工
1|6六、综合练习
1|01、实列准备
1|02、表结构
!!!重中之重:练习之前务必搞清楚sql逻辑查询语句的执行顺序
1|03、sql的使用
【参考案列解析】
__EOF__
本文作者:ଲ小何才露煎煎饺
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zeny/p/15121495.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zeny/p/15121495.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!
本文来自博客园,作者:ଲ小何才露煎煎饺,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zeny/p/15121495.html



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报