map集合和可变参数总结
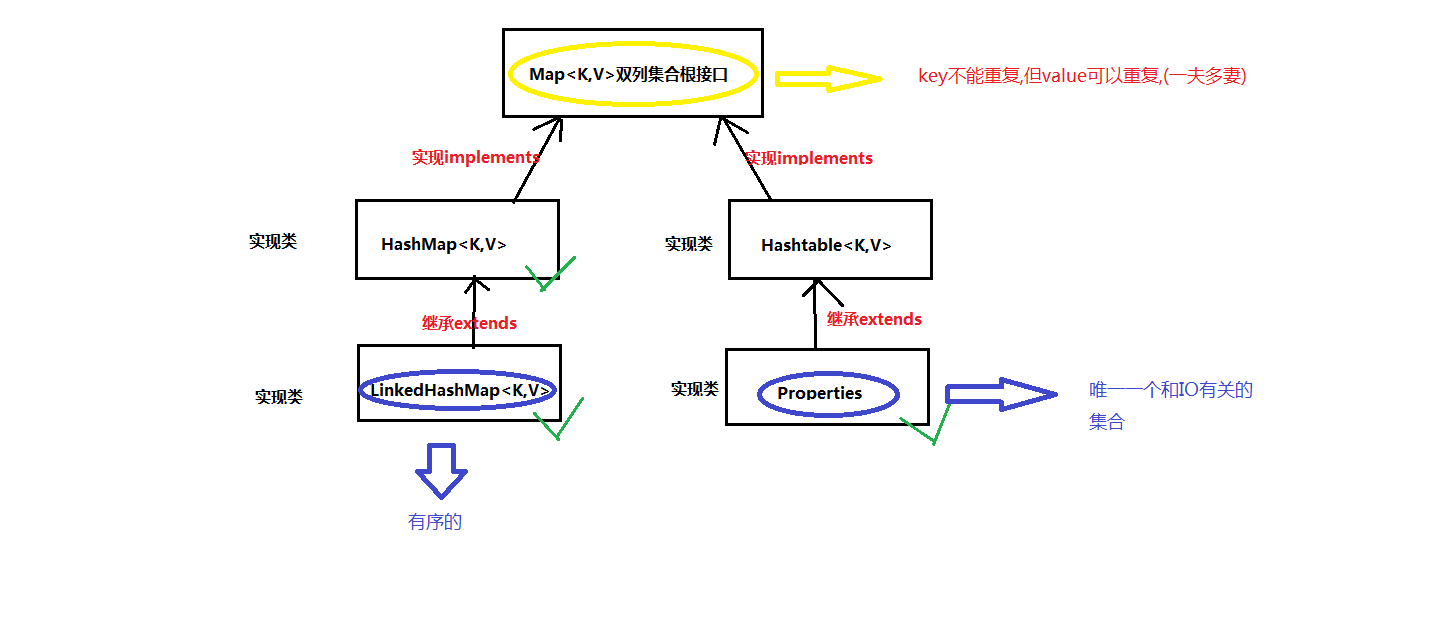
*① Map集合是所有双列集合的根接口,有如下特点:
* 1. 是以键值对的形式存储对象
* 2. 并且key值需要唯一
* 3. 值可以是多个
* 4. 是无序的, 存取的顺序不能保证
*
* 场景成员方法:
1. public V put(K key, V value);// 添加一组键值对,返回被替换的值.
2.public V get(K key);// 根据给定的key获取值
3.public V remove(K key);// 根据key删除键值对.
4.public void clear();//清除所有的键值对
5.public int size();// 获取集合的长度
6.public boolean containerKey(K key);//判断集合是否包含指定的key
7.public boolean containerValue(V value);// 判断集合是否包含指定的value
Map集合中常见的实现类: HashMap, LinkedHashMap, Properties
* 如何遍历Map集合?
* 由于Map集合并没有继承自java.lang.Iterable接口,所以不能使用迭代器和增强for;
* 但是, Map集合中提供了一个方法,keySet, 可以获取到所有key的Set集合.
*
* 获取到所有键的集合方法:
* public set<K> keySet();
*
* Map集合的遍历步骤:
* 1. 使用ketSet方法获取到所有的键的Set集合
* 2. 获取到Set集合的迭代器
* 3. 遍历迭代器,根据key获取到对应的value
* Map集合中提供了第二种遍历方式, 使用Entry内部接口的方式来实现.
* Entry<K, V>: Map集合的内部接口
* 有两个常用成员方法:
* public K getKey();
* public V getValue();
*
* 使用Entry的方式来遍历Map集合的步骤:
* 1. 创建Map集合
* 2. 添加元素, put
* 3. 调用map集合中的entrySet(), 获取到映射关系对象(结婚证)的Set集合
* 4. 获取到Set集合的迭代器
* 5. 使用增强for循环遍历
*② HashMap集合是Map集合的实现类,特点:
* 1. 完全符合map集合特点(无序,键唯一,值可以多个)
* 2. 可以存储null和null值, 比较少使用
* 3. 底层是通过哈希表实现
* 4. 线程不安全,效率高
1 package cn.itcast.demo01; 2 3 4 5 import java.util.HashMap; 6 7 import java.util.Iterator; 8 9 import java.util.Map; 10 11 import java.util.Map.Entry; 12 13 import java.util.Set; 14 15 16 17 public class Demo05HashMap { 18 19 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) { 22 23 24 25 HashMap<String, Integer>map = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); 26 27 //map.put(null, null);// 不能只有key为null 28 29 30 31 // 添加元素到hashMap集合中 32 33 map.put("AA", 100); 34 35 map.put("BB", 200); 36 37 map.put("EE", 500); 38 39 map.put("CC", 300); 40 41 map.put("DD", 400); 42 43 44 45 //methodLoop1(map); 46 47 methodLoop2(map); 48 49 } 50 51 52 53 /* 54 55 * 使用entrySet方式遍历 56 57 */ 58 59 public static void methodLoop2(Map<String, Integer>map){ 60 61 //1.获取到所有的映射关系对象的Set集合 62 63 Set<Entry<String, Integer>> set = map.entrySet(); 64 65 66 67 //2.获取到Set集合的迭代器 68 69 Iterator<Entry<String, Integer>> iter = set.iterator(); 70 71 72 73 //3.遍历迭代器 74 75 while(iter.hasNext()){ 76 77 Entry<String, Integer> next = iter.next(); 78 79 80 81 // 获取到结婚证的key,value 82 83 String key = next.getKey(); 84 85 Integer value = next.getValue(); 86 87 System.out.println(key + "\t"+value); 88 89 } 90 91 } 92 93 94 95 // 使用keyset方式进行遍历 96 97 public static void methodLoop1(Map<String, Integer>map){ 98 99 100 101 //1.获取到所有的key的Set集合, 使用keySet方法 102 103 Set<String> set = map.keySet(); 104 105 106 107 //2.获取到迭代器 108 109 Iterator<String> iter = set.iterator(); 110 111 112 113 //3.遍历迭代器 114 115 while(iter.hasNext()){ 116 117 String key = iter.next();// 获取到key 118 119 Integer value = map.get(key);// 获取到value 120 121 122 123 System.out.println(key + "\t" + value); 124 125 } 126 127 128 129 } 130 131 } 132
*③ LinkedHashMap是Map集合的一个实现类, 继承自HashMap;
* 特点:
* 1. 符合Map接口的特点(除了无序之外的特点都有)
* 2. 有序, 存取的顺序一致
* 3. 双向链表和哈希表
* 4. 线程不安全,效率高
public class Demo06LinkedHashMap { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建Linkedhashmap对象 Map<Cat, Integer>map = new LinkedHashMap<Cat, Integer>(); //添加元素 map.put(new Cat("Tom"), 100); map.put(new Cat("Jack"), 200); map.put(new Cat("Rose"), 300); //使用增强for遍历出来 Set<Cat> set = map.keySet(); for (Cat cat : set) { Integer value = map.get(cat); System.out.println(cat + "\t" + value); } } }
* 为什么使用Map集合存储对象的时候key不能重复.
* key依赖了: hashCode和equals方法
*
* 因为JDK中的String类已经覆盖了Object中的 equals方法和hashCode
* 如果自定义的对象,需要通过内容去判断对象是否是同一个对象,也需要覆盖Object中的equals方法和hashCode方法
*④ Properties类是Map集合的实现类, 继承自HashTable;
* HashTable是JDK1.0的一个集合,线程安全,目前已经弃用;
*
* 但是他的子类Properties依然活跃在开发舞台;
* Properties特点:
* 1. 拥有Map集合的特点
* 2. 类中并没有在创建对象的时候指定泛型, 默认的泛型是String
* 3. 可以配合IO流, 来读取或者存储文件的内容到集合.
* 4. 以后的时候场景: 主要是读取配置文件中的信息到集合中
*
* 提供了常用的成员方法:
1. public String getProperty(String key);// 通过key获取值
2. public Object setProperty(String key, String value);// 设置键值,返回被替换的元素
3. public Set<String> stringPropertyNames();// 获取所有键的集合
4. public void load(InputStream is);// 使用字节流读取文件内容集合
5. public void load(Reader reader);// 使用字符流读取文件内容到集合
package cn.itcast.demo01; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Reader; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; /* * 将文件中的内容读取到集合中Properties * public void load(Reader reader);// 使用字符流读取文件内容到集合 */ public class Demo09LoadFileToProperties { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建Properties对象 Properties p = new Properties(); //2.调用load方法加载IO的内容到集合中 Reader r = new FileReader("abc.properties"); p.load(r); //3.遍历集合, stringPropertyName();获取到所有键的Set集合 Set<String> set = p.stringPropertyNames(); for (String key : set) { // 通过key获取到value String value = p.getProperty(key); System.out.println(key + "\t" + value); } //关闭流释放资源 r.close(); } }
package cn.itcast.demo01; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Writer; import java.util.Properties; /* * 将集合Properties中的内容,存储到文件中; * public void store(Writer writer, String comments); * writer: 表示需要传入一个字符输出流 * comments: 就是一个描述信息 */ public class Demo10StorePropertiesToFile { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建Properties对象 Properties p = new Properties(); //2.添加元素 p.setProperty("name", "Tom"); p.setProperty("age", "13"); p.setProperty("address", "BeiJing"); //3.将集合中的内容存储到文件中 Writer w = new FileWriter("abc2.properties"); p.store(w, "welcome to Here"); //4.关闭流,释放资源 w.close(); } }
* 可变参数: 写在方法参数当中的类型, 本质上就是一额数组
package cn.itcast.demo01;
/*
*
* 特点:
* 1. 格式: 数据类型 ... 变量名;// 必须是三个点,
* 2. 使用的使用, 传入的是同种数据类型的多个元素, 可以是0-n个
* 3. 作用: 就是对数组的简化使用
*
* 注意点:
* 1. 不能在同一个方法中写两个可变参数
* 2. 如果有多个参数需要传递, 那么可变参数需要写在最后面
*/
public class Demo11VariablePara { public static void main(String[] args) { // 可以传入0-n个数字 //method(); //method(10); method(10,20,30); //method2(10,20,30); method3(10,20,30); int[]array = {1,2,3,4}; method3(100,array); } public static void method(int...a){// 等价于 int[]a for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.println(a[i]); } } // 1. 不能在同一个方法中写两个可变参数 //public static void method2(int...a, int ...b){ //} //2. 如果有多个参数需要传递, 那么可变参数需要写在最后面 public static void method3(int a,int...array){ } }
* Collections类
package cn.itcast.demo01; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.List; /* * Collections类, 工具类, 构造方法已经被私有化了 * 所以提供了一些常见的静态方法: * public static void shuffle(List<?> list);// 将List集合乱序 * public static void sort(List<T> list);// 排序List集合, 默认升序, 使用的是ASCII/Unicode * * 补充如何降序: * 需要使用方法: public static void sort(List<?>list, Comparator c); * */ public class Demo12Collections { public static void main(String[] args) { //methodShuffle(); //methodSort(); methodDesSort(); } // 扩展降序: ort(List<?>list, Comparator c); public static void methodDesSort() { // 1.定义List集合 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); // 2.添加元素 list.add("BBB"); list.add("AAA"); list.add("DDD"); list.add("CCC"); //3.降序 Comparator<String> c = new Comparator<String>() { @Override public int compare(String o1, String o2) { return o2.compareTo(o1); } }; Collections.sort(list, c); System.out.println(list); } // sort(List<T> list);// 排序List集合, 默认升序 public static void methodSort() { // 1.定义List集合 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); // 2.添加元素 list.add("BBB"); list.add("AAA"); list.add("DDD"); list.add("CCC"); Collections.sort(list); System.out.println(list); } //shuffle(List<?> list);// 将List集合乱序 public static void methodShuffle(){ //1.定义List集合 List<String>list = new ArrayList<String>(); //2.添加元素 list.add("AAA"); list.add("BBB"); list.add("CCC"); list.add("DDD"); System.out.println(list);//[AAA, BBB, CCC, DDD] Collections.shuffle(list);// 打乱顺序 System.out.println(list);//[AAA, BBB, DDD, CCC] } }




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步