【Spring源码解析】Bean循环依赖
1.什么是循环依赖
....
2.Spring Bean循环依赖
2.1 不能解决:构造器注入循环依赖;
根本原因:Spring解决循环依赖依靠的是Bean的“中间态”这个概念,而这个中间态指的是已经实例化,但还没初始化的状态。
而构造器是完成实例化的东东,所以构造器的循环依赖无法解决~~~
加入singletonFactories三级缓存的前提是执行了构造器,所以构造器的循环依赖没法解决
2.2 prototype模式field属性注入循环依赖
2.3 能解决:singleton模式field属性注入(或setter方法注入)循环依赖
3.测试demo
3.1 spring-bean-circular-references.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="a" class="spring.circularreferences.A">
<property name="b" ref="b" />
</bean>
<bean id="b" class="spring.circularreferences.B">
<property name="a" ref="a" />
</bean>
</beans>
3.2 CircularReferencesTest.java
public class CircularReferencesTest {
@Test
public void test01() {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("spring-bean-circular-references.xml");
DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
A a = (A)factory.getBean("a");
B b = (B)factory.getBean("b");
Assert.assertEquals(a,b.getA());
Assert.assertEquals(b,a.getB());
}
}
- 源码部分解析
4.1 三级缓存,参考DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java
/** 一级缓存:存放完全实例化属性赋值完成的Bean,直接可以使用 **/
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
/** 三级缓存:singletonFactories,三级缓存,存放实例化完成的Bean工厂 **/
/** Cache of singleton factories: bean name --> ObjectFactory */
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16);
/** 二级缓存:earlySingletonObjects,存放早期Bean的引用,尚未属性装配的Bean **/
/** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<>(16);
4.2 流程
- getBean(...); // AbstractBeanFactory类 198行
- doGetBean(...) // AbstractBeanFactory类 239行
- getSingleton(beanName) // AbstractBeanFactory类 246行
- getSingleton(beanName,()->{...})// AbstractBeanFactory类 315行
- singletonFactory.getObject();// AbstractBeanFactory类 222行
- createBean();// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类 456行
- doCreateBean()// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类 526行
- addSingletonFactory()// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类 566行
- populateBean()// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类 572行
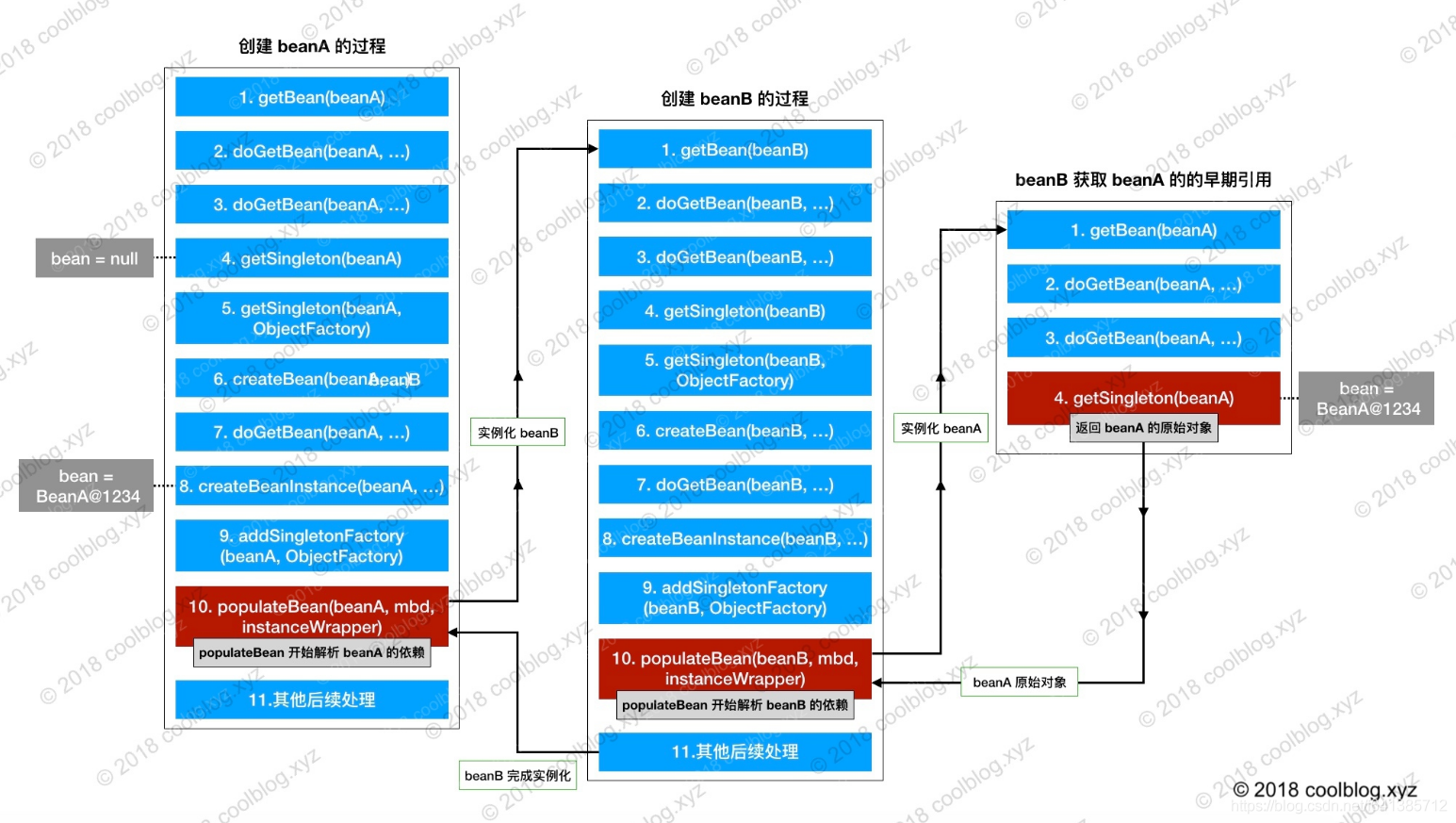
4.3 实例化Bean
// Create bean instance. 实例化Bean
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
4.4 getSingleton 获取实例对象
/**
* Return the (raw) singleton object registered under the given name.
* <p>Checks already instantiated singletons and also allows for an early
* reference to a currently created singleton (resolving a circular reference).
* @param beanName the name of the bean to look for
* @param allowEarlyReference whether early references should be created or not
* @return the registered singleton object, or {@code null} if none found
*/
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
//先从一级缓存中获取已经实例化属性赋值完成的Bean
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
//一级缓存不存在,并且Bean正处于创建的过程中
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
//从二级缓存中查询,获取Bean的早期引用,实例化完成但是未赋值完成的Bean
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
//二级缓存中不存在,并且允许创建早期引用(二级缓存中添加)
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
//从三级缓存中查询,实例化完成,属性未装配完成
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
//二级缓存中添加
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
//从三级缓存中移除
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
4.5 addSingletonFactory
/**
* Add the given singleton factory for building the specified singleton
* if necessary.
* <p>To be called for eager registration of singletons, e.g. to be able to
* resolve circular references.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonFactory the factory for the singleton object
*/
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}
- 参考




