tensorflow张量限幅
本篇内容有clip_by_value、clip_by_norm、gradient clipping
1.tf.clip_by_value
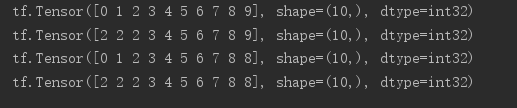
a = tf.range(10) print(a) # if x<a res=a,else x=x print(tf.maximum(a,2)) # if x>a,res=a,else x=x print(tf.minimum(a,8)) # 综合maximum和minimum两个函数的功能,指定上下限 print(tf.clip_by_value(a,2,8))
2.tf.clip_by_norm
# 随机生成一个2行2列的tensor a = tf.random.normal([2,2],mean=10) # 打印二范数 print(tf.norm(a)) # 根据新的norm进行放缩 print(tf.clip_by_norm(a,15)) print(tf.norm(tf.clip_by_norm(a,15)))

3.tf.clip_by_global_norm
# gradient clipping为解决梯度下降和梯度消失问题 # 可保证整体向量同时缩放(等倍数) for g in grads: grads,_ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(grads,15)
实测:
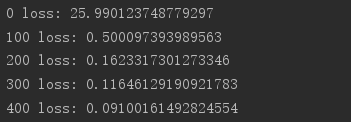
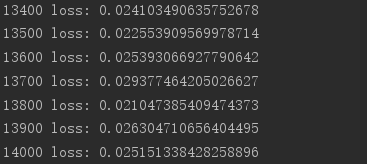
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow import keras from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, optimizers import os os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2' print(tf.__version__) (x, y), _ = datasets.mnist.load_data() x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 50. y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y) y = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10) print('x:', x.shape, 'y:', y.shape) train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x,y)).batch(128).repeat(30) x,y = next(iter(train_db)) print('sample:', x.shape, y.shape) # print(x[0], y[0]) def main(): # 784 => 512 w1, b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([784, 512], stddev=0.1)), tf.Variable(tf.zeros([512])) # 512 => 256 w2, b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([512, 256], stddev=0.1)), tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256])) # 256 => 10 w3, b3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([256, 10], stddev=0.1)), tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) optimizer = optimizers.SGD(lr=0.01) for step, (x,y) in enumerate(train_db): # [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784] x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 784)) with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # layer1. h1 = x @ w1 + b1 h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1) # layer2 h2 = h1 @ w2 + b2 h2 = tf.nn.relu(h2) # output out = h2 @ w3 + b3 # out = tf.nn.relu(out) # compute loss # [b, 10] - [b, 10] loss = tf.square(y-out) # [b, 10] => [b] loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss, axis=1) # [b] => scalar loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss) # compute gradient grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3]) # print('==before==') # for g in grads: # print(tf.norm(g)) grads, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(grads, 15) # print('==after==') # for g in grads: # print(tf.norm(g)) # update w' = w - lr*grad optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3])) if step % 100 == 0: print(step, 'loss:', float(loss)) if __name__ == '__main__': main()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号