委托
internal delegate void Feedback(int i);
internal class Feedback : System.MulticastDelegate { //构造器 public Feedback(object @object, IntPtr method); //这个方法的原型和源代码指定的一样 public virtual void Invoke(int i); //以下方法实现对回调方法的异步回调 public virtual IAsyncResult BeginInvoke(int i, AsyncCallback callback, object @object); public virtual void EndInvoke(IAsyncResult result); }
1,委托基础
①System.MulticastDelegate派生自System.Delegate,后者派生自System.Object。由于历史原因造成两个委托类(MulticastDelegate、Delegate)。即使创建的所有委托类型都将MulticastDelegate作为基类,个别情况下还是会使用到Delegate类型,例如Delegate类的两个静态方法(Combine、Remove)需要传递Delegate类型参数
②委托是类,所以凡是能够定义类的地方,都能定义委托
③MulticastDelegate
|
字段 |
类型 |
说明 |
|
_target |
System.object |
委托对象包含一个静态方法:为null; 委托对象包含一个实例方法:这个字段引用的是回调方法要操作的对象 |
|
_methedPtr |
System.IntPtr |
一个内部的整数值,CLR用它标识要回调的方法 |
|
_invocationList |
System.Object |
该字段通常为null,构造委托链时它引用一个委托数组 |
Feedback fbStatic = new Feedback(Program.FeedbackToConsole); Feedback fbInstance = new Feedback(new Program.FeedbackToFile());
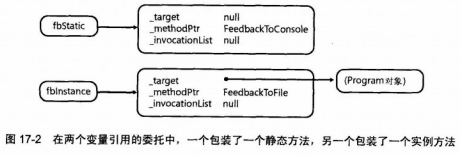
由于Feedback委托要获取一个int参数并返回void,所以编译器生成的Invoke方法也要获取一个int并返回void
2,用委托回调多个方法(委托链)
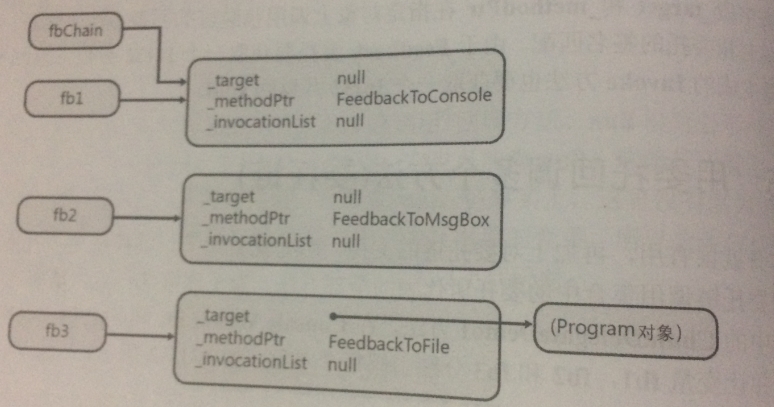
①
Feedback fbChain=null;
fbChain = (Feedback) Delegate.Combine(fbChain, fb1);
fbChain为null,fb1不为null,Combine发现视图合并的是null和fb1,在内部会直接返回fb1
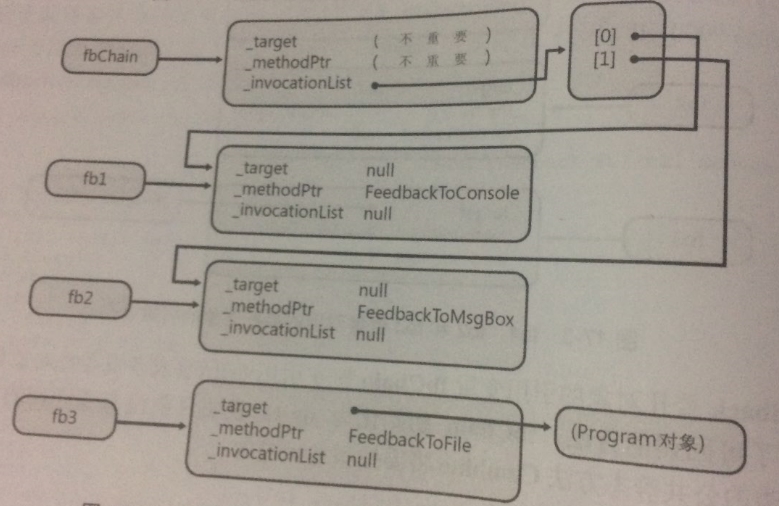
②
Feedback fbChain=null;
fbChain = (Feedback) Delegate.Combine(fbChain, fb1);
fbChain = (Feedback) Delegate.Combine(fbChain, fb2);
Combine发现fbChain和fb2都不为null,会构造一个新的委托对象(_target和_methedPtr不重要)。_invocationList会初始化一个委托对象数组,索引0处被初始化为fb1,索引2处被初始化为fb2
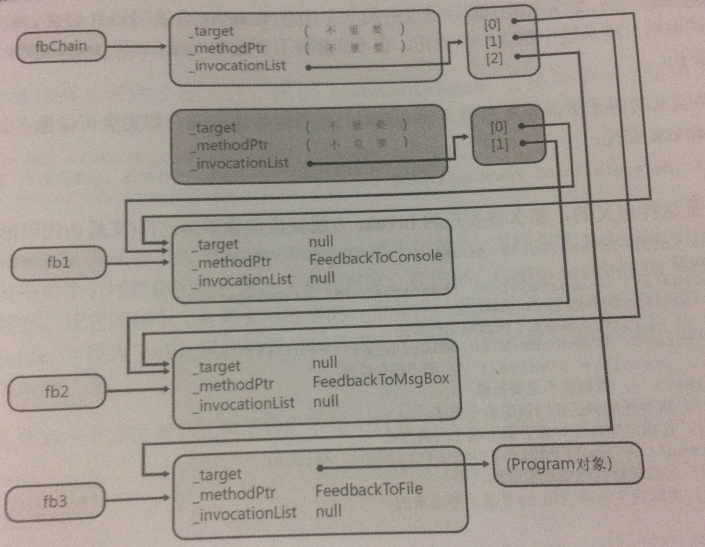
③
Feedback fbChain=null; fbChain = (Feedback) Delegate.Combine(fbChain, fb1); fbChain = (Feedback) Delegate.Combine(fbChain, fb2); fbChain = (Feedback) Delegate.Combine(fbChain, fb3);
Combine发现fbChain和fb3都不为null。会如②一样创建一个新的对象。之前新建的委托对象以其_invocationList字段引用的数据现在可以进行垃圾回收
④在fbChain引用的委托上调用Invoke时,该委托发现私有字段_invocationList不为null,所以会执行一个循环来遍历数组中的所有元素,并依次调用每个委托包装的方法
//伪代码Invoke的实现 public void Invoke(int value) { Delegate[] delegateSet= _invocationList as Delegate[]; if (delegateSet != null) { //这个委托数组指定了应该调用的委托 foreach (Feedback d in delegateSet) { d(value); } } else { //该委托标识了要回调的单个方法 //在指定的目标对象上调用这个回调方法 _methedPtr.Invoke(_target, value); } }
如果委托有返回值(internal delegate int Feedback(int i)),则只返回最后一个委托的结果(前面的返回值会被丢弃)
3,删除委托
fbChain = (Feedback) Delegate.Remove(fbChain, fb3);
①链中只有一个委托,Remove之后会返回null
②链中只有两个委托,Remove之后会返回剩余的那个数据项
③链中有两个以上,Remove之后会新建一个委托对象(初始化_invocationList数组将引用原始数组中的所有数据项,被删除的除外)
④每次Remove方法调用只能从链中删除一个委托
4,取得对委托链调用的更多控制
public abstract class MulticastDelegate { //创建一个委托数组,其中每个元素都引用链中的一个委托 public sealed override Delegate[] GetInvocationList(); }
5,c#为委托提供的简化语法
语法糖:越是高级的语言,提供的简化语法越多,以方便写程序
①不需要构造委托对象
public void SomeAysncTask(object o){} public void aa() { //QueueUserWorkItem方法的第一参数要求的是一个委托对象, //可以直接传入签名相同的方法 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(SomeAysncTask, 1); }
②不需要定义回调方法(lambda表达式)
class Class1 { public void aa() { ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(r => Console.WriteLine(r), 1); } }
编译器看到lambda表达式后,会在当前类(Class1)中自定义一个新的私有方法(匿名函数)。由编译器生成,可以使用ILDasm.exe查看方法名称。每次编译都可能为方法生成一个不同的名称。(注意:C#编译器向方法引用了System.Runtime.CompilerServices.CompilerGeneratedAttribute特性,指出该方法由编译器生成,而非程序员写的)
匿名方法是否是static取决于方法内部有没有访问任何实例成员,如果方法内部没有访问任何实例成员,则匿名方式标记为static
③局部变量不需要手动包装到类中即可回调方法
回调代码引用存在于定义方法中的局部参数(numToDo)或变量(squares)
internal sealed class AClass { public static void UsingLocalVariablesInTheCallbackCode(int numToDo) { //一些局部变量 int[] squares = new int[numToDo]; AutoResetEvent done = new AutoResetEvent(false); for (int i = 0; i < squares.Length; i++) { ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(obj => { int num = (int) obj; squares[num] = num*num;//该任务通常更耗时 //如果是最后一个任务,就让主线程继续运行 if (Interlocked.Decrement(ref numToDo) == 0) done.Set(); }, i); } //等待其他所有线程结束运行 done.WaitOne(); //显示结果 for (int i = 0; i < squares.Length; i++) { Console.WriteLine(squares[i]); } } }
c#编译器重写了以上的代码
internal sealed class AClass { public static void UsingLocalVariablesInTheCallbackCode(int numToDo) { //一些局部变量 WaitCallback callback1 = null; <>c_DisplayClass2 class1=new <>c_DisplayClass2(); class1.numToDo = numToDo; class1.squares = new int[numToDo]; class1.done = new AutoResetEvent(false); for (int i = 0; i < class1.squares.Length; i++) { if(callback1 == null) //新建的委托对象绑定到辅助对象及其匿名实例方法 callback1=new WaitCallback(class1.< UsingLocalVariablesInTheCallbackCode > b_0); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(callback1, i); } //等待其他所有线程结束运行 class1.done.WaitOne(); //显示结果 for (int i = 0; i < class1.squares.Length; i++) { Console.WriteLine(class1.squares[i]); } } } private sealed class <>c_DisplayClass2:object { //回调代码要使用的每个变量都有一个对应的公共字段 public int[] squares; public int numToDo; public AutoResetEvent done; //公共无参构造器 public <>c_DisplayClass2{} //包含回调代码的公共实例方法 public void <UsingLocalVariablesInTheCallbackCode>b_0(object obj) { int num = (int) obj; squares[num] = num*num; if (Interlocked.Decrement(ref numToDo) == 0) done.Set(); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号