Linux_25 SELinux及systemd新特性
SELinux
SELinux:Secure Enhanced Linux,工作于Linux内核中
DAC:自主访问控制;
MAC:强制访问控制;
SELinux右两种工作级别:
strict:每个进程都受到selinux的控制;
targeted:仅有限个进程收到selinux控制;
只监控容易被入侵的进程;
sanbox
subject operation object
subject:进程
object:进程,文件
文件:open,read,write,close,chown,chmod
subject:domain
object:type
SELinux为每个文件提供了安全标签,也为进程提供了安全标签;
user:role:type
user:SELinux的user;
role:角色;
type:类型
配置SELinux:
SELinux是否启用;
给文件重新打标;
设定某些布尔型特性;
SELinux的状态:
enforcing:强制,每个受限的进程都必然受限;
permissive:启用,每个受限的进程违规操作不会被禁止,但会被记录于审计日志;
disabled:关闭;
相关命令:
getenforce:获取selinux当前状态;
setenforce 0|1
0:设置为permissive
1:设置为enforcing
此设定:重启系统后无效;
配置文件:/etc/sysconfig/selinux,/etc/selinux/config
SELINUX={disabled|enforcing|permissive}
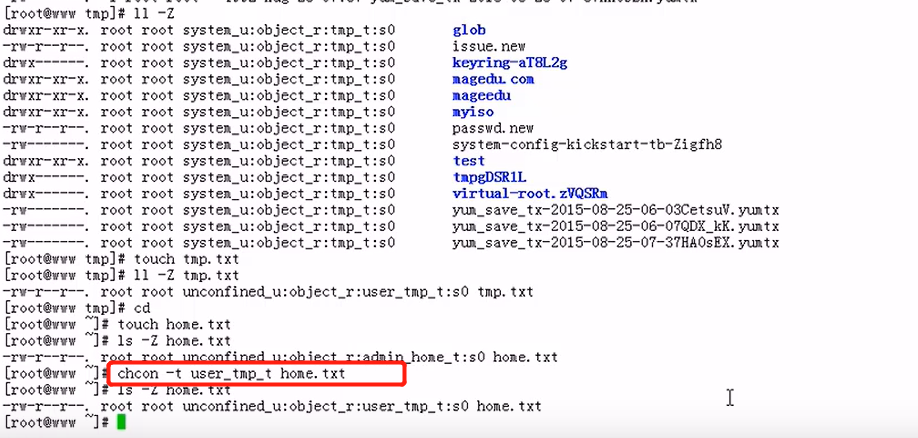
chcon - change file SELinux security context
chcon [OPTION]... CONTEXT FILE...
chcon [OPTION]... [-u USER] [-r ROLE] [-l RANGE] [-t TYPE] FILE...
chcon [OPTION]... --reference=RFILE FILE...
-R:递归打标签:
eg:# 图1
还原文件的默认标签:
restorecon [-R] /path/to/somewhere
布尔型规则:
getsebool
setsebool
getsebool命令:
getsebool命令:
getsebool [-a] [boolean]
setsebool命令:
setsebool [-P] boolean value | bool1=val1 bool2=val2 ...
图1:
Systemd新特性
新特性:
系统引导时实现服务并行启动;
按需激活进程;
系统状态快照;
基于依赖关系定义服务控制逻辑;
核心概念:unit
unit由其相关配置文件进行标识、识别和配置;文件中主要包含了系统服务、监听的socket、保存的快照以及其它与init相关的信息;这些配置文件主要保存在:
/usr/lib/systemd/system
/run/systemd/system
/etc/systemd/system
unit常见类型:
Service unit:文件扩展名为.service,用于定义系统服务;
Target unit:文件扩展为.target,用于模拟实现“运行级别”;
Device unit:.device,用于定义内核识别的设备;
Mount unit:.mount,定义文件系统挂载点;
Socket unit:.socket,用于标识进程间通信用到的socket文件;
Snapshot unit:.snapshot,管理系统快照;
Swap unit:.swap,用于标识swap设备;
Automount unit:.automount,文件系统自动点设备;
Path unit:.path,用于定义文件系统中的一文件或目录;
关键特性:
基于socket的激活机制:socket与程序分离;
基于bus的激活机制;
基于device的激活机制;
基于Path的激活机制;
系统快照:保存个unit的当前状态信息于持久存储设备中;
向后兼容sysv init脚本;
/etc/init.d/
不兼容:
systemctl 的命令是固定不变的;
非由systemd启动的服务,systemctl无法与之通信;
管理系统服务:
CentOS7 :service 类型的unit文件;
systemctl 命令:
-Control the systemd system and service manager
systemctl [OPTIONS...] COMMAND [NAME...]
启动:service NAME start ===>systemctl start NAME.service
停止:service NAME stop ===>systemctl stop NAME.service
重启:service NAME restart ===>systemctl restart NAME.service
状态:service NAME status ===>systemctl status NAME.service
条件式重启:service NAME condrestart ===>systemctl try-restart NAME.service
重载或重启服务:systemctl reload-or-try-restart NAME.service
查看某服务当前激活与否的状态:systemctl is-active NAME.service
查看所有已激活的服务:systemctl list-units --type service
查看所有服务(已激活及未激活):systemctl list-units -t service --all # 或-a
设置服务开机自启:chkconfig NAME on ==>systemctl enable NAME.service
禁止服务开机自启:chkconfig NAME off ==> systemctl disable NAME.service
查看某服务是否能开机自启:chkconfig --list NAME ==>systemctl is-enabled NAME.service
禁止某服务设定为开机自启:systemctl mask NAME.service
取消此禁止:systemctl unmask NAME.service
查看服务的依赖关系:systemctl list-dependencies NAME.service
管理target unit:
运行级别:
0==>runlevel0.target,poweroff.target
1==>runlevel1.target,rescue.target
2==>runlevel2.target,multi-user.target
3==>runlevel3.target,multi-user.target
4==>runlevel4.target,multi-user.target
5==>runlevel5.target,graphical.target
6==>runlevel6.tart,reboot.target
级别切换:init N ==>systemctl isolate NAME.target
查看级别:runlevel ==>systemctl list-units --type target
查看所有级别:systemctl list-units -t target -a
获取默认运行级别:systemctl get-default
修改默认运行级别:systemctl set-default NAME.target
切换至紧急救援模式:systemctl rescue
切换至emergency模式:systemctl emergency
其它常用命令:
关机:systemctl halt,systemctl poweroff
重启:systemctl reboot
挂起:systemctl hibernate
快照并挂起:systemctl hybrid-sleep
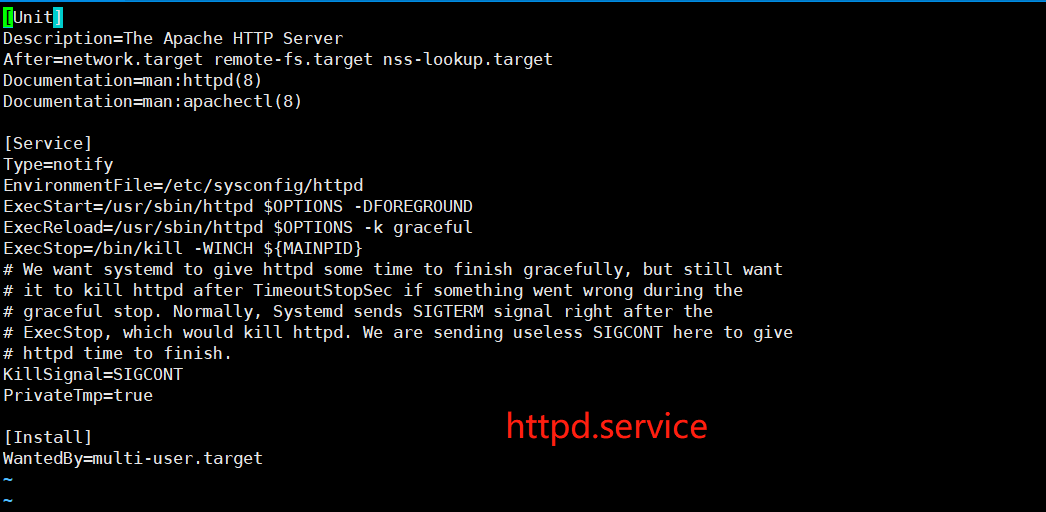
service unit file: # /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service为例
文件通常由三部分组成:
[Unit]:定义与Unit类型无关的通用选项;用于提供unit的描述信息、unit行为及依赖关系等;
[Service]:与特定类型相关的专用选项;此处为Service类型;
[Install]:定义由“systemctl enable”以及"systemctl disable"命令在实现服务启用或禁用时用到的一些选项;
Unit段的常用选项:
Description:描述信息;意义性描述;
After:定义unit的启动次序;表示当前unit应该晚于哪些unit启动;其功能与Before相反;
Requires:依赖到其它units;强依赖,被依赖的units无法激活时,当前unit即无法激活;
Wants:依赖到的其它units;弱依赖;
Conflicts:定义units间的冲突关系;
Service段的常用选项:
Type:用于定义影响ExecStart及相关参数的功能的unit进程启动类型;
类型:
simple:
forking:
oneshot:
dbus:
notify:
idle:
ExecStart:指明启动unit要运行命令或脚本;ExecStartPre,ExecStartPost
ExecStop:指明停止unit要运行的命令或脚本;
Restart:
Install段的常用选项:
Alias:当前unit的别名
RequiredBy:被哪些units所依赖;
WantedBy:被哪些units所依赖;
注意:对于新创建的unit文件或修改了的unit文件,要通知systemd重载此配置文件;
# systemctl daemon-reload

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号