RNN(cell)总结和实践
一、RNNCell:
1、使用实例 hello--ohlol
图示:
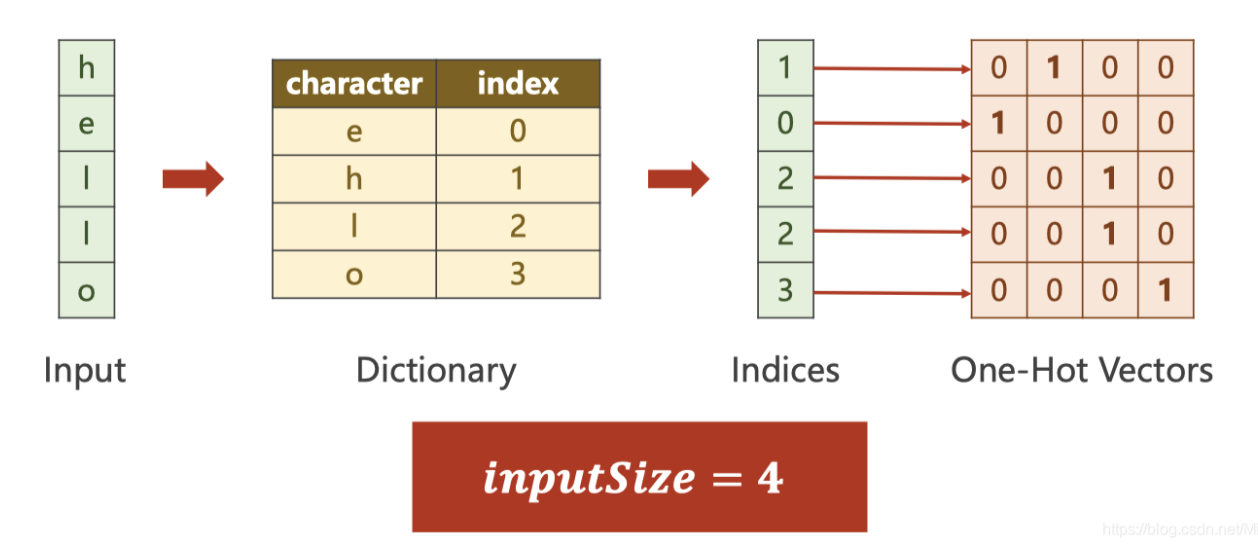
要注意inputSize
1 #载入数据 2 3 import torch 4 input_size = 4 5 hidden_size = 4 6 batch_size = 1 7 8 idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o'] 9 x_data = [1, 0, 2, 3, 3] # hello中各个字符的下标 10 y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2] # ohlol中各个字符的下标 11 12 one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0], 13 [0, 1, 0, 0], 14 [0, 0, 1, 0], 15 [0, 0, 0, 1]] 16 x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data] # (seqLen, inputSize) 17 18 inputs = torch.Tensor(x_one_hot).view(-1, batch_size, input_size) 19 labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data).view(-1, 1) 20 # torch.Tensor默认是torch.FloatTensor是32位浮点类型数据,torch.LongTensor是64位整型
1 inputs.shape 2 labels.shape 3 #torch.Size([5, 1, 4]);torch.Size([5, 1]
1 inputs.shape2 labels.shape3 #torch.Size([5, 1, 4]);torch.Size([5, 1])
1 #构建模型 2 3 import torch.nn as nn 4 5 class Model(nn.Module): 6 def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size): 7 super(Model, self).__init__() 8 self.batch_size = batch_size 9 self.input_size = input_size 10 self.hidden_size = hidden_size 11 self.rnncell = nn.RNNCell(input_size=self.input_size, hidden_size=self.hidden_size) 12 13 def forward(self, inputs, hidden): 14 hidden = self.rnncell(inputs, hidden) # (batch_size, hidden_size) 15 return hidden 16 17 def init_hidden(self): 18 return torch.zeros(self.batch_size, self.hidden_size) 19 20 net = Model(input_size, hidden_size, batch_size) 21 22 criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 23 optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.1)
1 #模型训练 2 3 epochs = 15 4 5 for epoch in range(epochs): 6 loss = 0 7 optimizer.zero_grad() 8 hidden = net.init_hidden() 9 print('Predicted string:', end='') 10 for input, label in zip(inputs, labels): 11 hidden = net(input, hidden) 12 # 注意交叉熵在计算loss的时候维度关系,这里的hidden是([1, 4]), label是 ([1]) 13 loss += criterion(hidden, label) 14 _, idx = hidden.max(dim = 1) 15 print(idx2char[idx.item()], end='') 16 loss.backward() 17 optimizer.step() 18 print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss=%.4f' % (epoch+1, loss.item()))
##结果 Predicted string:helhh, Epoch [1/15] loss=6.4109 Predicted string:ohloo, Epoch [2/15] loss=5.3787 Predicted string:ohloo, Epoch [3/15] loss=4.7781 Predicted string:ohloo, Epoch [4/15] loss=4.2434 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [5/15] loss=3.7612 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [6/15] loss=3.3989 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [7/15] loss=3.1192 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [8/15] loss=2.8756 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [9/15] loss=2.6559 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [10/15] loss=2.4753 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [11/15] loss=2.3358 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [12/15] loss=2.2265 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [13/15] loss=2.1403 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [14/15] loss=2.0739 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [15/15] loss=2.0232
2、使用cell时要注意:
(1)、输入和输出维度
(2)、序列长度
(3)、批处理大小
二、RNN
1、实例代码展示
1 #基础数据 2 import torch 3 input_size = 4 4 hidden_size = 4 5 batch_size = 1 6 seq_len = 5 7 num_layers = 1 8 9 idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o'] 10 x_data = [1, 0, 2, 3, 3] # hello中各个字符的下标 11 y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2] # ohlol中各个字符的下标 12 13 one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0], 14 [0, 1, 0, 0], 15 [0, 0, 1, 0], 16 [0, 0, 0, 1]] 17 x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data] # (seqLen, inputSize) 18 19 inputs = torch.Tensor(x_one_hot).view(seq_len, batch_size, input_size) 20 labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data) 21 print(inputs.shape, labels.shape)
#输出torch.Size([5, 1, 4]) torch.Size([5])
1 #构建model 2 import torch.nn as nn 3 4 class Model(nn.Module): 5 def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size, num_layers=1): 6 super(Model, self).__init__() 7 self.num_layers = num_layers 8 self.batch_size = batch_size 9 self.input_size = input_size 10 self.hidden_size = hidden_size 11 self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=self.input_size, hidden_size=self.hidden_size, ) 12 13 def forward(self, inputs): 14 hidden = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, self.batch_size, self.hidden_size) 15 out, _ = self.rnn(inputs, hidden) # 注意维度是(seqLen, batch_size, hidden_size) 16 return out.view(-1, self.hidden_size) # 为了容易计算交叉熵这里调整维度为(seqLen * batch_size, hidden_size) 17 18 net = Model(input_size, hidden_size, batch_size) 19 20 criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 21 optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.1)
1 ##训练 2 epochs = 15 3 4 for epoch in range(epochs): 5 optimizer.zero_grad() 6 outputs = net(inputs) 7 # print(outputs.shape, labels.shape) 8 # 这里的outputs维度是([seqLen * batch_size, hidden]), labels维度是([seqLen]) 9 loss = criterion(outputs, labels) 10 loss.backward() 11 optimizer.step() 12 13 _, idx = outputs.max(dim=1) 14 idx = idx.data.numpy() 15 print('Predicted: ', ''.join([idx2char[x] for x in idx]), end='') 16 print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss = %.3f' % (epoch + 1, loss.item()))
##输出 Predicted: ololl, Epoch [1/15] loss = 1.189 Predicted: ollll, Epoch [2/15] loss = 1.070 Predicted: ollll, Epoch [3/15] loss = 0.976 Predicted: ohlll, Epoch [4/15] loss = 0.883 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [5/15] loss = 0.788 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [6/15] loss = 0.715 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [7/15] loss = 0.652 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [8/15] loss = 0.603 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [9/15] loss = 0.570 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [10/15] loss = 0.548 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [11/15] loss = 0.530 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [12/15] loss = 0.511 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [13/15] loss = 0.488 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [14/15] loss = 0.462 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [15/15] loss = 0.439
2、注意要点:
(1)inputs维度是: (seqLen, batch_size, input_size)
(2)lables维度是: (seqLen * batch_size)
(2)outputs维度是: (seqLen, batch_size, hidden_size)
为了能和labels做交叉熵,需要reshape一下: outputs.view(-1, hidden_size)
3、注释
input_size和hidden_size: 输入维度和隐层维度
batch_size: 批处理大小
seq_len: 序列长度
num_layers: 隐层数目






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· DeepSeek在M芯片Mac上本地化部署