![]()
没有多态时
1 package cn.xlf.polymorphism;
2
3 public class Test {
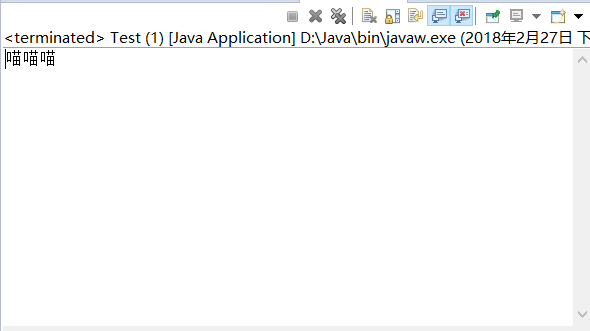
4 public static void textAnimalVoice(Cat c){
5 c.voice();
6 }
7 public static void textAnimalVoice(Dog c){
8 c.voice();
9 }
10
11 public static void main(String[] args){
12 Cat c = new Cat();
13 textAnimalVoice(c);
14 }
15
16 }
![]()
多态
1 package cn.xlf.polymorphism;
2
3 public class Animal {
4 public void voice(){
5 System.out.println("普通动物叫声!");
6
7 }
8 }
9 class Cat extends Animal{
10 public void voice(){
11 System.out.println("喵喵喵");
12 }
13 public void catchMouse(){
14 System.out.println("抓老鼠");
15 }
16 }
17 class Dog extends Animal{
18 public void voice(){
19 System.out.println("汪汪汪");
20 }
21 public void seeDoor(){
22 System.out.println("看门狗");
23 }
24 }
1 package cn.xlf.polymorphism;
2
3
4 public class test02 {
5 public static void textAnimalVoice(Animal c){//Animal 里面包含了Cat Dog
6 c.voice();
7 if(c instanceof Cat){// c是 Cat 的实例对象
8 ((Cat) c).catchMouse();
9 }
10 }
11
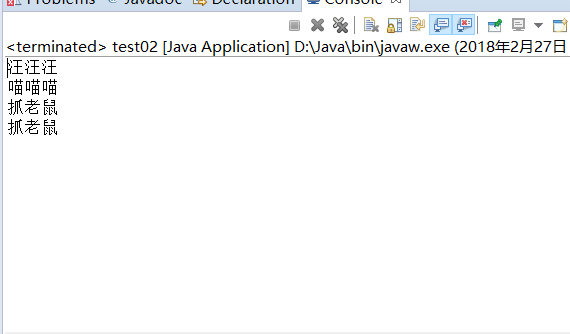
12 public static void main(String[] args){
13 Animal c = new Cat();
14 Animal a = new Dog();
15 textAnimalVoice(a);
16 textAnimalVoice(c);
17
18 Cat a2 = (Cat)c;//强制转换 c 为 Cat
19 a2.catchMouse();;
20
21
22 }
23
24
25
26 }
![]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号