9.最短路径
实验9 最短路径
实验目的
- 掌握图的存储结构
- 掌握迪杰斯特拉和弗洛伊德算法寻求最短路径算法及实现
实验内容
- 从文件中读入有向图(网)并以邻接矩阵存储
- 利用杰斯特拉算法寻求最短路径(弗洛伊德算法及实现自学完成)
代码
tu.txt (教程P171 图6.22)
6 8
a b c d e f
a f 100
a c 10
a e 30
b c 5
c d 50
e d 20
e f 60
d f 10
dijkstra.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
#define ERROR 0
#define MaxInt 32767 //表示极大值,即∞
#define MVNum 10 //最大顶点数
typedef char VerTexType; //假设顶点的数据类型为字符型
typedef int ArcType; //假设边的权值类型为整型
int *D = new int[MVNum]; //用于记录最短路的长度
bool *S = new bool[MVNum]{}; //标记顶点是否进入S集合
int *Path = new int[MVNum]; //用于记录最短路顶点的前驱
//------------图的邻接矩阵-----------------
struct AMGraph
{
VerTexType vexs[MVNum]; //顶点表
ArcType arcs[MVNum][MVNum]; //邻接矩阵
int vexnum, arcnum; //图的当前点数和边数
};
int LocateVex(AMGraph &G, VerTexType v)
{
//确定点v在G中的位置
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i)
if (G.vexs[i] == v)
return i;
return -1;
} //LocateVex
// 采用邻接矩阵表示法,创建无向网G
void CreateUDN(AMGraph &G)
{
int i, j, k;
fstream file;
file.open("tu.txt"); //数据文件要按教材 P171 图 6.22 自行编辑产生
if (!file)
{
cout << "没有找到图文件!" << endl;
exit(ERROR);
}
file >> G.vexnum >> G.arcnum; //输入总顶点数,总边数
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i)
file >> G.vexs[i];
// 初始化邻接矩阵,边的权值均置为极大值MaxInt
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i)
for (j = 0; j < G.vexnum; ++j)
G.arcs[i][j] = MaxInt;
// 构造邻接矩阵
for (k = 0; k < G.arcnum; ++k)
{
VerTexType v1, v2;
ArcType w;
file >> v1 >> v2 >> w;
i = LocateVex(G, v1);
j = LocateVex(G, v2); //确定v1和v2在G中的位置,即顶点数组的下标
G.arcs[i][j] = w;
}
file.close();
}
// 用Dijkstra算法求有向网G的v0顶点到其余顶点的最短路径
void ShortestPath_DIJ(AMGraph &G, int start)
{
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i)
{
D[i] = G.arcs[start][i]; //将v0到各个终点的最短路径长度初始化为弧上的权值
if (D[i] != MaxInt)
Path[i] = start; //如果v0和v之间有弧,则将v的前驱置为v0
else
Path[i] = -1; //如果v0和v之间无弧,则将v的前驱置为-1
}
S[start] = true; //将v0加入S
D[start] = 0; //源点到源点的距离为0
/*―初始化结束,开始主循环,每次求得v0到某个顶点v的最短路径,将v加到S集―*/
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i)
{ //对其余n-1个顶点,依次进行计算
int min = MaxInt;
int min_index = -1;
for (int w = 0; w < G.vexnum; ++w)
{
if (!S[w] && D[w] < min)
{ //选择一条当前的最短路径,终点为v
min_index = w;
min = D[w];
}
}
S[min_index] = true; //将v加入S
for (int k = 0; k < G.vexnum; ++k) //更新从v0出发到集合V?S上所有顶点的最短路径长度
{
if (!S[k] && (D[k] + G.arcs[min_index][k]))
{
D[k] = D[min_index] + G.arcs[min_index][k]; //更新D[w]
Path[k] = min_index; //更改w的前驱为v
} //if
}
} //for
} //ShortestPath_DIJ
// 显示最短路径
void DisplayPath(AMGraph &G, int begin, int temp)
{
if (Path[temp] != -1)
{
DisplayPath(G, begin, Path[temp]);
cout << G.vexs[Path[temp]] << "-->";
}
}
// 显示图的邻接矩阵
void DisplayGraph(AMGraph &G)
{
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < G.vexnum; j++)
if (G.arcs[i][j] != MaxInt)
cout << G.arcs[i][j] << '\t';
else
cout << "∞" << '\t';
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
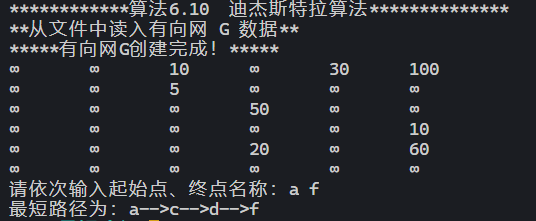
cout << "************算法6.10 迪杰斯特拉算法**************" << endl;
AMGraph G;
int i, j, num_start, num_destination;
VerTexType start, destination;
cout << "**从文件中读入有向网 G 数据**" << endl;
CreateUDN(G);
cout << "*****有向网G创建完成!*****" << endl;
DisplayGraph(G);
cout << "请依次输入起始点、终点名称:";
cin >> start >> destination;
num_start = LocateVex(G, start);
num_destination = LocateVex(G, destination);
ShortestPath_DIJ(G, num_start);
cout << "最短路径为:";
DisplayPath(G, num_start, num_destination);
cout << G.vexs[num_destination] << endl;
}
截图
其它
dijkstra.py (Python版)
from math import inf as M
nodes = ['v0', 'v1', 'v2', 'v3', 'v4']
nodes_num = len(nodes)
graph = [
[0, 10, M, M, 5],
[M, 0, 1, M, 2],
[M, M, 0, 4, M],
[7, M, 6, 0, M],
[M, 3, 9, 2, 0]
]
# 初始化
visited = [False] * nodes_num
distance = [M] * nodes_num
path = [-1] * nodes_num
start = 2
visited[start] = True
for i in range(nodes_num):
distance[i] = graph[start][i]
if i != start and distance[i] != M: # start的邻接结点的path为start
path[i] = start
# 迪杰斯特拉
while not all(visited): # 如果没有全部访问完成
# 选择一个没有访问过且路径最短的结点
choice_vex = -1
tmp_dist = M
for i in range(nodes_num):
if visited[i]: # 访问过的不管
continue
if distance[i] < tmp_dist: # 记录距离更小结点的下标
tmp_dist = distance[i]
choice_vex = i
# 得到了没有访问过且路径最短的结点, 开始处理它
visited[choice_vex] = True
# 更新与其相邻的未访问过的结点的distance
for adjvex in range(nodes_num):
# 访问过的结点, 不相邻的结点不管
if visited[adjvex]:
continue
if graph[choice_vex][adjvex] == M:
continue
new_dist = distance[choice_vex] + graph[choice_vex][adjvex]
if new_dist < distance[adjvex]: # 如果距离更短,更新邻接点的信息
distance[adjvex] = new_dist
path[adjvex] = choice_vex
# 输出路径
for i in range(nodes_num):
if i == start:
continue
print(f"{nodes[start]} -> {nodes[i]} 最短距离: {distance[i]}, 路线: ", end='')
stack = []
stack.append(i)
parent_vex = path[i]
while parent_vex != -1:
stack.append(parent_vex)
parent_vex = path[parent_vex]
route = [nodes[i] for i in reversed(stack)]
print(' -> '.join(route))
floyd.py (弗洛伊德算法)
from math import inf as M
nodes = ['v0', 'v1', 'v2', 'v3', 'v4']
nodes_num = len(nodes)
A = [
[0, M, 1, M, 10],
[M, 0, M, 1, 5],
[M, 1, 0, M, 7],
[M, M, M, 0, 1],
[M, M, M, M, 0]
]
path = [[-1] * nodes_num for i in range(nodes_num)]
# Floyd
for k in range(nodes_num): # k 为中转结点
# 遍历整个矩阵, i 为行号, j为列号
for i in range(nodes_num):
for j in range(nodes_num):
dist = A[i][k] + A[k][j]
if dist < A[i][j]:
A[i][j] = dist
path[i][j] = k
result = []
def get_path(start, end):
k = path[start][end]
if k == -1:
if start not in result:
result.append(start)
if end not in result:
result.append(end)
else:
get_path(start, k)
get_path(k, end)
get_path(2, 4)
print(" -> ".join(nodes[i] for i in result))



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 为什么说在企业级应用开发中,后端往往是效率杀手?
· 用 C# 插值字符串处理器写一个 sscanf
· Java 中堆内存和栈内存上的数据分布和特点
· 开发中对象命名的一点思考
· .NET Core内存结构体系(Windows环境)底层原理浅谈
· 为什么说在企业级应用开发中,后端往往是效率杀手?
· DeepSeek 解答了困扰我五年的技术问题。时代确实变了!
· 本地部署DeepSeek后,没有好看的交互界面怎么行!
· 趁着过年的时候手搓了一个低代码框架
· 推荐一个DeepSeek 大模型的免费 API 项目!兼容OpenAI接口!