Java数据结构-------Map
常用Map:Hashtable、HashMap、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap
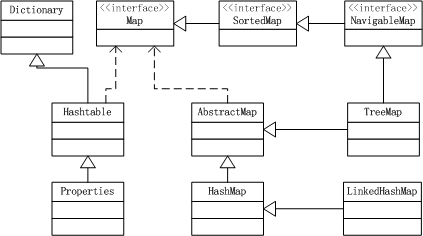
类继承关系:
HashMap
1)无序; 2)访问速度快; 3)key不允许重复(只允许存在一个null Key);
LinkedHashMap
1)有序; 2)HashMap子类;
TreeMap
1)根据key排序(默认为升序); 2)因为要排序,所以key需要实现 Comparable接口,否则会报ClassCastException 异常; 3)根据key的compareTo 方法判断key是否重复。
HashTable
一个遗留类,类似于HashMap,和HashMap的区别如下:
1)Hashtable对绝大多数方法做了同步,是线程安全的,HashMap则不是;
2) Hashtable不允许key和value为null,HashMap则允许;
3)两者对key的hash算法和hash值到内存索引的映射算法不同。
HashMap
HashMap底层通过数组实现,数组中的元素是一个链表,准确的说HashMap是一个数组与链表的结合体。即使用哈希表进行数据存储,并使用链地址法来解决冲突。
HashMap的几个属性:
initialCapacity:初始容量,即数组的大小。实际采用大于等于initialCapacity且是2^N的最小的整数。
loadFactor:负载因子,元素个数/数组大小。衡量数组的填充度,默认为0.75。
threshold:阈值。值为initialCapacity和loadFactor的乘积。当元素个数大于阈值时,进行扩容。
优化点:1、频繁扩容会影响性能。设置合理的初始大小和负载因子可有效减少扩容次数。
2、一个好的hashCode算法,可以尽可能较少冲突,从而提高HashMap的访问速度。
添加元素源代码分析:
public V put(K key, V value) { if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { //判断是否已经初始化,1.7版本新增的延迟初始化:构造函数初始化后table是空数组,没有真正进行初始化,直到使用时在进行真正的初始化 inflateTable(threshold); } if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); int hash = hash(key); //计算key的hash值 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); //根据hash值计算数组索引 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { //如果key已经存在,新值替换旧值,返回旧值 V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; } private void inflateTable(int toSize) { // Find a power of 2 >= toSize int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize); //计算不小于toSize且满足2^n的数,算法很巧妙 threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);//阈值=容量*负载因子,用于判断是否需要扩容,负载因子默认为0.75 table = new Entry[capacity]; //真正的数组初始化 initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity); //初始化hash种子 } private static int roundUpToPowerOf2(int number) { // assert number >= 0 : "number must be non-negative"; return number >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : (number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) : 1; //获取最靠近且大于等于number的2^n: //第一种情况number不是2^n,number的二进制的最高位的高一位变为1且其余位变为0,例如14(0000 1110)-->16(0001 0000)。 // 将number左移1位,相当于最高位的高一位变为1,例如:14(0000 1110)-->28(0001 1100), // 计算最靠近且小于等于上一步得到的数的2^n数,相当于其余位变为0,例如:28(0001 1100)-->16(0001 0000) // //第二种情况number本身就是2^n,按上述步骤计算会得到number*2。例如:16-->32 // number - 1的目的是针对number正好是2^n的特殊处理。做减1处理后,number最高位变为0,次高位变为1,再按第一种情况计算得到number本身。 //由于对本身就是2^n的number的减1处理,当number=1时会出现错误,所以需要对1特殊处理,如果number=1则直接返回1 //最终得到计算最靠近且大于等于number的2^n的方法: (number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) : 1 } //如果一个数是0, 则返回0; //如果是负数, 则返回 -2147483648: //如果是正数, 返回的则是跟它最靠近且小于等于它的2的N次方,例如8->8 17->16 public static int highestOneBit(int i) { // HD, Figure 3-1 i |= (i >> 1); i |= (i >> 2); i |= (i >> 4); i |= (i >> 8); i |= (i >> 16); //对正数来说,移位完之后为最高位之后都变为1,移5次是因为int为32位,例如:0010010 ---> 0011111 return i - (i >>> 1); //结果为最高位为1,其他位为0,例如0010000,从而得到最靠近且小于等于它的2的N次方。 } //单独处理key为null的情况,放在数组索引位置为0的链表 private V putForNullKey(V value) { for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == null) { //如果已经存在key为null的元素,用新值替换调旧值,返回旧值。 V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(0, null, value, 0);//如果不存在key为null的元素,在0位置新增key为null的元素,返回null。 return null; } //计算key的hash值 final int hash(Object k) { int h = hashSeed; //hash种子,1.7版本引入,获取更好的hash值,减少hash冲突;当等于0时禁止调备用hash函数 if (0 != h && k instanceof String) { return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k); } h ^= k.hashCode(); // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by // constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded // number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor). h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12); return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4); } //根据hash值计算数组索引 static int indexFor(int h, int length) { // assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2"; return h & (length-1); //首先想到的应该是取模运算,h(hash值)%length(数组长度),考虑到取模运算效率较低,JDK采用另一种方法。 //数组长度length总是2的N次方且h为非负数,此时h & (length-1)就等价于h % length,但&运算比%运算效率高的多。 //当数组长度为2的n次幂的时候,不同的key算得得index相同的几率较小。可以这么理解,2^4-1为0000 1111和0000 1110对比,或者的最后一位为0,经过&运算,1101和1100会映射到同一个数组索引。 //length-1即2^N-1,二进制表示为00...0011...11,h & (length-1)的计算结果就是0~length-1之间的值, //如果h的小于length,h & (length-1) = h;如果h大于length,h & (length-1) = h的后n位 } //在指定的数组索引添加Entry void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { //当元素个数>=threshold且指定索引元素不为null时,进行扩容 resize(2 * table.length); //扩容,数组长度增加一倍 hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; //重新计算hash值 bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); //重新根据hash值计算数组索引 } createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); // } //如果e==null(bucketIndex位置没有元素),数组中存放新Entry,新Entry的next为null; //如果e!=null(bucketIndex位置已有元素),数组中存放新Entry,新Entry的next为e; void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++; } //扩容 void resize(int newCapacity) { Entry[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); //重新初始化hash种子 table = newTable; threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); } //从oldTable转移到newTable void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { while(null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); //重新计算hash值 } int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); //重新根据hash值计算数组索引 e.next = newTable[i]; //如果e为第一个元素,e.next = null,否则,e.next = 前一个元素。经过扩容,链表上的多个元素的顺序会反转。 newTable[i] = e; //在指定数组索引赋值e e = next; //赋值为下一个元素,进入下一个循环 } } }
获取元素源代码分析:
public V get(Object key) { if (key == null) return getForNullKey(); //key=null,特殊处理 Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key); return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue(); } final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { if (size == 0) { return null; } int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key); //计算key的hash值 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; //计算数组索引 e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //遍历链表,查找hash值相等且key相等的元素 return e; } return null; } private V getForNullKey() { if (size == 0) { return null; } for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == null) return e.value; } return null; }
Java8的HashMap
HashMap结构:数组+链表+红黑树
在Java8中,当链表的长度大于8时,有可能转化为红黑树。因为长度为n的链表,查找操作的时间复杂度为O(n),当链表长度过长时,查找元素的效率大大降低。红黑树具有以下特点:插入、查找、删除的时间复杂度为O(log n)。红黑树的性质:从根到叶子的最长的可能路径不多于最短的可能路径的两倍长。这样最坏情况也可以是高效的。所以当链表长度较长时,转换为红黑树结构有利于提高操作效率。
put
首先判断是否初始化,如果没有,先进行初始化。懒加载--直到只有时才初始化。
通过计算key的hash值对应的table下标,找到该位置(桶)的第一个节点,有以下情况:
1)如果为null,创建新的Node作为该桶的第一个元素;
2)如果为红黑树节点TreeNode,则向红黑树插入此节点;
3)如果为链表,将该节点插入链表尾部(java7中是在链表头部插入,缺点为在并发的情况下因为插入而进行扩容时可能会出现链表环而发生死循环,当然HashMap本身就不支持并发访问)。如果链表长度超过8,则进行红黑树转化。

1 public V put(K key, V value) { 2 return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); 3 } 4 5 final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, 6 boolean evict) { 7 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; 8 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) 9 //初始化哈希表。懒加载(lazy-load ),当首次使用时才初始化。 10 n = (tab = resize()).length; 11 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) 12 //通过哈希值找到对应的位置,如果该位置还没有元素存在,直接插入 13 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 14 else { 15 Node<K,V> e; K k; 16 if (p.hash == hash && 17 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 18 //如果该位置的元素的 key 与之相等,则直接到后面重新赋值 19 e = p; 20 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) 21 //如果当前节点为树节点,则将元素插入红黑树中 22 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); 23 else { 24 //否则一步步遍历链表 25 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { 26 if ((e = p.next) == null) { 27 //插入元素到链尾 28 p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 29 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st 30 //元素个数大于等于 8,改造为红黑树 31 treeifyBin(tab, hash); 32 break; 33 } 34 //如果该位置的元素的 key 与之相等,则重新赋值 35 if (e.hash == hash && 36 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 37 break; 38 p = e; 39 } 40 } 41 //前面当哈希表中存在当前key时对e进行了赋值,这里统一对该key重新赋值更新 42 if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key 43 V oldValue = e.value; 44 if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) 45 e.value = value; 46 afterNodeAccess(e); 47 return oldValue; 48 } 49 } 50 ++modCount; 51 //检查是否超出 threshold 限制,是则进行扩容 52 if (++size > threshold) 53 resize(); 54 afterNodeInsertion(evict); 55 return null; 56 }
红黑树转发方法为treeifyBin。
如果哈希表为null或者元素数量小于MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(64),只进行扩容不进行树化。这么做为了避免在哈希表创建初期,多个键值对恰好被放入了同一个链表中而导致不必要的转化。

1 final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) { 2 int n, index; Node<K,V> e; 3 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) 4 //如果哈希表为null或者元素数量小于MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(64),只进行扩容不进行树化。 5 //这么做为了避免在哈希表创建初期,多个键值对恰好被放入了同一个链表中而导致不必要的转化。 6 resize(); 7 else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 8 TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null; 9 do { 10 TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null); 11 if (tl == null) 12 hd = p; 13 else { 14 p.prev = tl; 15 tl.next = p; 16 } 17 tl = p; 18 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 19 if ((tab[index] = hd) != null) 20 hd.treeify(tab); 21 } 22 }
扩容的方法为resize
我们都知道数组是无法自动扩容的,所以我们需要重新计算新的容量,创建新的数组,并将所有元素拷贝到新数组中,并释放旧数组的数据。
Java8中每次扩容都为之前的两倍,也正是因为如此,每个元素在数组中的新的索引位置只可能是两种情况,一种为不变,一种为原位置 + 扩容长度(即偏移值为扩容长度大小);反观 Java8 之前,每次扩容需要重新计算每个值在数组中的索引位置,增加了性能消耗。
通过下标找到桶上的节点,对老的table进行赋值null防止内存泄漏。
1)如果是单节点,直接复制到新的桶上;
2)如果是红黑树节点TreeNode,则对树进行分离(split);
3)如果是链表,则复制链表到新的table。同样会对节点重新hash后决定分配到原来的还是新的位置。

1 final Node<K,V>[] resize() { 2 Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; 3 int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; 4 int oldThr = threshold; 5 int newCap, newThr = 0; 6 if (oldCap > 0) { 7 if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { 8 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 9 return oldTab; 10 } 11 else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && 12 oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) 13 newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold 14 } 15 else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold 16 newCap = oldThr; 17 else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults 18 newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; 19 newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); 20 } 21 if (newThr == 0) { 22 float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; 23 newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? 24 (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); 25 } 26 threshold = newThr; 27 @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) 28 Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; 29 table = newTab; 30 if (oldTab != null) { 31 for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { 32 Node<K,V> e; 33 if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { 34 oldTab[j] = null; 35 if (e.next == null) 36 newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; 37 else if (e instanceof TreeNode) 38 ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); 39 else { // preserve order 40 Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; 41 Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; 42 Node<K,V> next; 43 do { 44 next = e.next; 45 if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { 46 if (loTail == null) 47 loHead = e; 48 else 49 loTail.next = e; 50 loTail = e; 51 } 52 else { 53 if (hiTail == null) 54 hiHead = e; 55 else 56 hiTail.next = e; 57 hiTail = e; 58 } 59 } while ((e = next) != null); 60 if (loTail != null) { 61 loTail.next = null; 62 newTab[j] = loHead; 63 } 64 if (hiTail != null) { 65 hiTail.next = null; 66 newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; 67 } 68 } 69 } 70 } 71 } 72 return newTab; 73 }
get
通过key的hash值找到对应的桶,找到该桶的第一个元素;
1)如果正好是第一个元素,直接返回;
2)判断是否是红黑树节点,如果是,则在红黑树中查找目标节点;
3)如果不是红黑树节点,遍历链表,寻找目标节点。

1 public V get(Object key) { 2 Node<K,V> e; 3 return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; 4 } 5 6 final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { 7 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; 8 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && 9 (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 10 //检查当前位置的第一个元素,如果正好是该元素,则直接返回 11 if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node 12 ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 13 return first; 14 if ((e = first.next) != null) { 15 //否则检查是否为树节点,则调用 getTreeNode 方法获取树节点 16 if (first instanceof TreeNode) 17 return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); 18 //遍历整个链表,寻找目标元素 19 do { 20 if (e.hash == hash && 21 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 22 return e; 23 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 24 } 25 } 26 return null; 27 }
链表和红黑树转换的思考
HashMap在jdk1.8之后引入了红黑树的概念,表示若桶中链表元素超过8时,会自动转化成红黑树;若桶中元素小于等于6时,树结构还原成链表形式。
1、为什么选择当链表长度为8时转换为红黑树?为啥不是6、10?
1)存储成本
普通节点
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
}
红黑树节点
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
}
其中LinkedHashMap.Entry继承了普通节点Node<K,V>
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
可以看出红黑树节点比普通节点占用的空间要大的多,大约是普通节点的两倍。所以我们只在容器中包含足够多的节点时才使用红黑树。
根据泊松分布可以计算出桶中元素个数和概率的对照表:
* 0: 0.60653066
* 1: 0.30326533
* 2: 0.07581633
* 3: 0.01263606
* 4: 0.00157952
* 5: 0.00015795
* 6: 0.00001316
* 7: 0.00000094
* 8: 0.00000006
* more: less than 1 in ten million
可以看到链表中元素个数为8时的概率已经非常小,再多的就更少了,所以原作者在选择链表元素个数时选择了8,是根据概率统计而选择的。
2)查询和更新成本
采用红黑树和链表进行查询时的平均查找长度对比如下:
当长度为8时,log(n)=3 8/2=4
当长度为7时,log(n)=2.80 7/2=3.5
当长度为6时,log(n)=2.58 6/2=3
当长度为5时,log(n)=2.32 5/2=2.5
当长度为4时,log(n)=2 4/2=2
红黑树的平均查找长度是log(n),长度为8,查找长度为log(8)=3,链表的平均查找长度为n/2,当长度为8时,平均查找长度为8/2=4,这才有转换成树的必要;链表长度如果是小于等于6,6/2=3,虽然速度也很快的,但是转化为树结构和生成树的时间并不会太短。
2、当执行remove,红黑树中的元素小于8时会不会转换回链表?为什么?
选择6时转换会链表的考虑:
中间有个差值7可以防止链表和树之间频繁的转换。假设一下,如果设计成链表个数超过8则链表转换成树结构,链表个数小于8则树结构转换成链表,如果一个HashMap不停的插入、删除元素,链表个数在8左右徘徊,就会频繁的发生树转链表、链表转树,效率会很低。
LinkedHashMap----有序的HashMap
简单来说,HashMap+双向链表=LinkedHashMap。
HashMap是无序的,即添加的顺序和遍历元素的顺序具有不确定性。LinkedHashMap是HashMap的子类,是一种特殊的HashMap。
LinkedHashMap通过维护一个额外的双向链表(在Entry中加入 before, after属性记录该元素的前驱和后继),将所有的Entry节点链入一个双向链表,从而实现有序性。通过迭代器遍历元素是有序的。
两种排序方式:
1)元素插入顺序:accessOrder=false,默认为false;
2)最近访问顺序:accessOrder=true。此情况下,不能使用迭代器遍历集合,因为get()方法会修改Map,在迭代器模式中修改集合会报ConcurrentModificationException。可以用来实现LRU(最近最少使用)算法。
TreeMap
TreeMap实现了SortedMap,可以根据key对元素进行排序,还提供了接口对有序的key集合进行筛选。
内部基于红黑树实现,红黑树是一种平衡查找树,它的统计性能要优于平衡二叉树。可以在O(logN) 时间内做查找、插入和删除,性能较好。
如果确实需要将排序功能加入HashMap,应该使用TreeMap,而不应该自己去实现排序。
HashMap的线程安全问题&并发Map
1、多线程并发扩容可能导致死循环,如果扩容前相邻的两个Entry在扩容后还是分配到相同的table位置上,就可能会出现死循环的BUG(即出现循环链表);
2、在多线程环境下,一个线程在扩容时,其他线程可能也正在执行put操作,如果hash值相同,可能出现同时在同一数组下用链表表示,造成闭环,导致在get操作时出现死循环。
Collections.synchronizedMap(hashMap);
ConcurrentHashMap
参考资料:
Map 综述(二):彻头彻尾理解 LinkedHashMap



