python django初识ajax
什么是json
json是轻量级文本数据交互格式
json独立语言
符合的json对象
["one", "two", "three"] { "one": 1, "two": 2, "three": 3 } {"names": ["张三", "李四"] } [ { "name": "张三"}, {"name": "李四"} ]
不合格的json对象
{ name: "张三", 'age': 32 } // 属性名必须使用双引号
[32, 64, 128, 0xFFF] // 不能使用十六进制值
{ "name": "张三", "age": undefined } // 不能使用undefined
{ "name": "张三",
"birthday": new Date('Fri, 26 Aug 2011 07:13:10 GMT'),
"getName": function() {return this.name;} // 不能使用函数和日期对象
}
json支持的7种数据格式
| Python | JSON |
| dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str, unicode | string |
| int, long, float | number |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
javaScript中关于json对象和字符串转换的2种方法
JSON.parse(): 用于将一个 JSON 字符串转换为 JavaScript 对象
JSON.parse('{"name":"Q1mi"}'); JSON.parse('{name:"Q1mi"}') ; // 错误 JSON.parse('[18,undefined]') ; // 错误
JSON.stringify(): 用于将 JavaScript 值转换为 JSON 字符串。
JSON.stringify({"name":"Q1mi"})
Ajax简介
- 同步交互:客户端发出一个请求后,需要等待服务器响应结束后,才能发出第二个请求;
- 异步交互:客户端发出一个请求后,无需等待服务器响应结束,就可以发出第二个请求。
除了异步特点外,还有一个就是浏览器页面局部刷新
from django.db import models # Create your models here. class User(models.Model): username=models.CharField(max_length=32) password=models.CharField(max_length=32)
发请求给服务器的途径
1. 地址栏:get
2. form表单,支持get和post
3. 超链接 <a href="/path/">click</a> 这种是get方式
4. Ajax请求: 可以指定get和post
发Ajax请求一般返回httpResponse()
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse from app01 import models import json from django.http import JsonResponse def index(request): return render(request, 'index.html') def login(request): user = request.POST.get("user") pwd = request.POST.get("pwd") #根据表单的用户名和密码到数据库中匹配 user_obj = models.User.objects.filter(username=user, password=pwd).first() print(user_obj) #一般请求下,需要定义一个字典。msg是约定成俗的名字,用来做提示的 response = {"user":None,"msg":None} if user_obj: # 判断有返回结果的请求下 response["user"] = user_obj.username # 修改字典的用户名 print(user_obj.username) else: response["msg"] = "用户名或者密码不一致" # 修改提示信息 #返回json格式数据,默认序列化时,对中文默认使用的ascii编码。 # ensure_ascii=False表示显示真正的中文 # return HttpResponse(json.dumps(response, ensure_ascii=False)) return JsonResponse(response)
前端配置文件
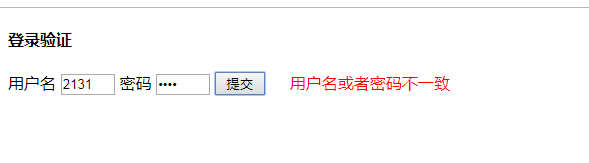
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.min.js"></script> <style type="text/css"> input { width: 50px; } </style> </head> <body> {% csrf_token %} <h4>登录验证</h4> <form> <lable>用户名</lable> <input type="text" id="user"> <lable>密码</lable> <input type="password" id="pwd"> <input type="button" value="提交" id="login_btn"> {#显示错误信息#} <span class="error"></span> </form> {% csrf_token %} <script> $("#login_btn").click(function () { var csrf = $("[name=csrfmiddlewaretoken]").val(); //发送ajax请求 $.ajax({ url: "/login/", //请求的url type: "post", //默认get data: { user: $("#user").val(), pwd: $("#pwd").val(), csrfmiddlewaretoken: csrf, }, success: function (data) { //data接收响应体,必须要有 console.log(data); //打印响应体 console.log(typeof data); //打印数据类型 {#var data = JSON.parse(data); //反序列化数据#} if (data.user) { // 登陆成功 //window.location.href表示跳转页面 alert("登录成功"); window.location.href = "/index/"; } else { // 登陆失败 //修改span标签,显示失败的返回值,并显示红色,左间距20px $(".error").text(data.msg).css({"color": "red", "margin-left": "20px"}) //设置定时器,2秒后清空提示信息 setTimeout(function () { $(".error").text("") //清空提示信息 }, 2000) } } }) }); </script> </body> </html>
文件上传
请求头 contentType
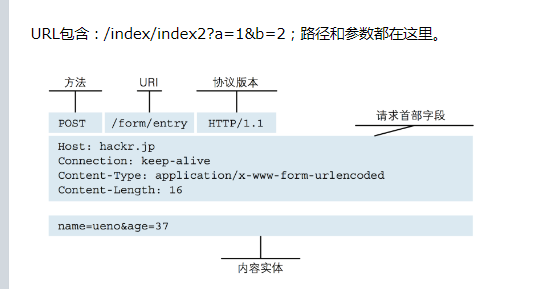

1. application/x-www-form-urlencoded
最常见的Post提交数据方式,原生的from表单,如果不设置enctype属性,那么默认就是 application/x-www-form-urlencoded
2.multipart/form-data
这又是一个常见post数据提交的方式,我们使用表单上传文件时,必须让 <form> 表单的 enctype 等于 multipart/form-data
<form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
</form>
3.application/json
form 提交上传文件
因为django对于文件,单独做了一个属性request.FILES
ajax和form默认都是application/x-www-form-urlencoded;
urlencoded的数据格式是a=1&b=2这种格式
def file_put(request): if request.method=='POST': print(request.POST)#打印post信息 # < QueryDict: {'csrfmiddlewaretoken': ['TyrJMwNy8VTYHUjKYooMsEhce8kcS1fiKUT4nlAgEkxCgnTp1NzOtig0m1XHtLV7'], # 'user': ['']} > # < MultiValueDict: {'img': [ < InMemoryUploadedFile: 自定制web框架的流程.png(image / png) >]} > print(request.FILES)#打印文件信息 file_obj=request.FILES.get("img")#获取img print(type(file_obj))#<class 'django.core.files.uploadedfile.InMemoryUploadedFile'> print(file_obj.__dict__)# 打印img对象属性 print(file_obj.name)#打印文件名 with open("static/img/"+file_obj.name,'wb') as f: for line in file_obj: f.write(line)#写入文件 return render(request,"file_put.html")#渲染file_put.html
file_put.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h3>form表单文件上传</h3> <form action=""method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> {% csrf_token %} <input type="text" name="user"> <input type="file" name="img"> <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>
ajax指定ContentType
请求头ContentType有3种类型,最常用的是第1,3这两种类型。
那么ajax如果要发送json,需要声明ContentType类型
index.html修改
{% load static %} <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static "bootstrap/css/bootstrap.css" %}"> </head> <body> <button class="btn2">click</button> <script src="{% static "js/jquery.js" %}"></script> <script> $.ajax({ url:"/ajax_handle/",//发送url type:"post", contentType:"json",//申明json类型 data:JSON.stringify({//序列号jison a:1, b:2, }), success:function (data) {//接收相应体 console.log(data)//打印相应体 } }) </script> </body> </html>
注意:form表单不能发送json数据,只能由ajax发送!
那么application/json的数据,在哪里呢?在request.body里面!
查看Pycharm控制台输出:
<QueryDict: {}>
为什么django视图函数,接收的POST数据是空的呢?明明发过来了啊!
因为wsgi接收数据时,它会对ContentType做if判断。当ContentType为application/x-www-form-urlencoded时,并且请求方式为POST时,将数据给request.POST封装成一个字典!
那么application/json的数据,在哪里呢?在request.body里面!
views.py
def ajax_handle(request): print(request.POST) print(request.body)
#由于是一个bytes类型,需要解码,再用json反序列才行 data=json.loads(request.body.decode('utf-8')) print(data)#打印json print(data["a"])#取key为a的值 return HttpResponse('ok')
<QueryDict: {}>
b'{"a":1,"b":2}'
{'a': 1, 'b': 2}
1
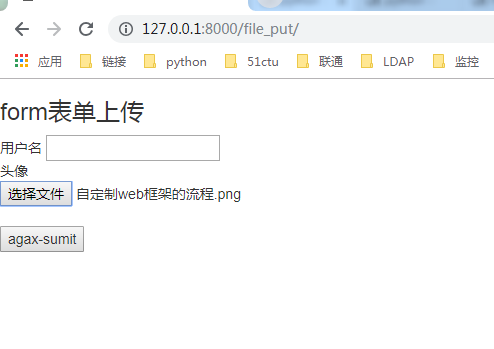
基于ajax的文件上传
利用ajax和FormData实现页面无刷新的文件上传效果,主要用到了jQuery的ajax()方法和XMLHttpRequest Level 2的FormData接口
def file_put(request): if request.method == 'POST': print(request.POST) # 打印post信息 print(request.FILES) # 打印文件信息 file_obj = request.FILES.get("img") print(type(file_obj)) print(file_obj.__dict__) # 打印img对象属性 print(file_obj.name) # 打印文件名 response = {"state": False} with open("statics/img/" + file_obj.name, 'wb') as f: for line in file_obj: ret = f.write(line) # 写入文件 print(ret) # 返回写入 if ret: # 判断返回值 response["state"] = True return HttpResponse(json.dumps(response)) return render(request, "file_put.html") # 渲染file_put.html
file_put.html 文件
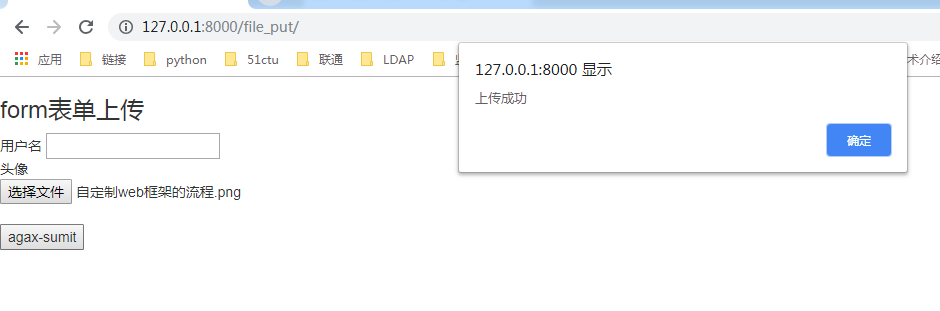
{% load static %} <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static "bootstrap/css/bootstrap.css" %}"> </head> <body> {% csrf_token %} <h3>form表单上传</h3> <form action=""> 用户名 <input type="text" id="user"><br> 头像 <input type="file" id="avatar"><br> <input type="button" id="agax-sumit" value="agax-sumit"> </form> <script src="{% static "js/jquery.js" %}"></script> <script> $("#agax-sumit").click(function(){ var csrf = $("[name=csrfmiddlewaretoken]").val(); //csrf var formdata=new FormData(); //实例化了一个空的FormData对象 formdata.append("csrfmiddlewaretoken",csrf); //给当前FormData对象添加一个键/值对. formdata.append("user",$("#user").val()); formdata.append("img",$("#avatar")[0].files[0]); $.ajax({ url:"", //表示为当前url type:"post", data:formdata, //发送一个FormData对象 processData: false , // 不处理数据 contentType: false, // 不设置内容类型 success:function(data){ var data = JSON.parse(data); //反序列化数据 console.log(data); if (data.state){ //判断返回值 //弹出提示框,并刷新整个页面 alert('上传成功');window.location.href="/file_put/"; }else { alert('上传失败'); } } }) }) </script> </body> </html>