写在前头
- 回到单位事情太多了,只能用spring boot凑合着点弄了个后端出来,主要是同数据库和消息队列的交互
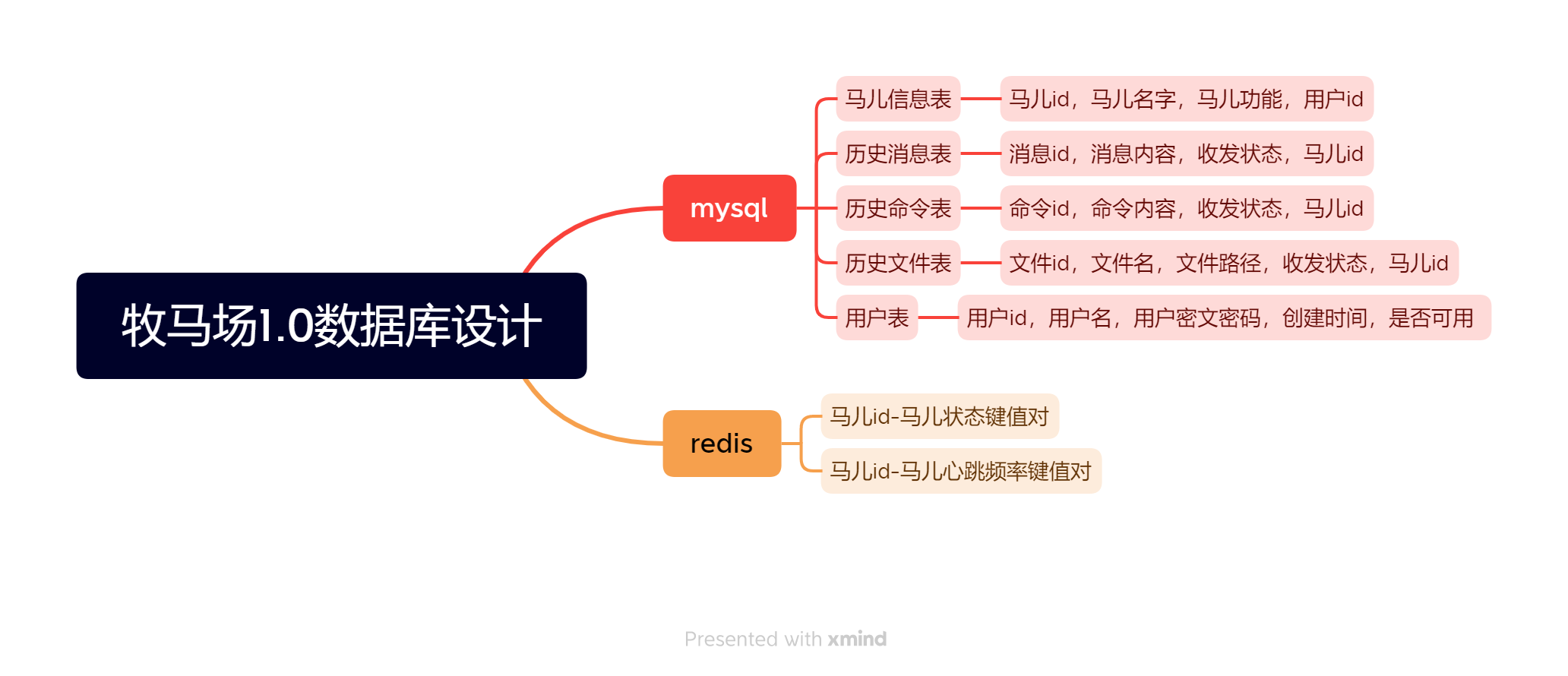
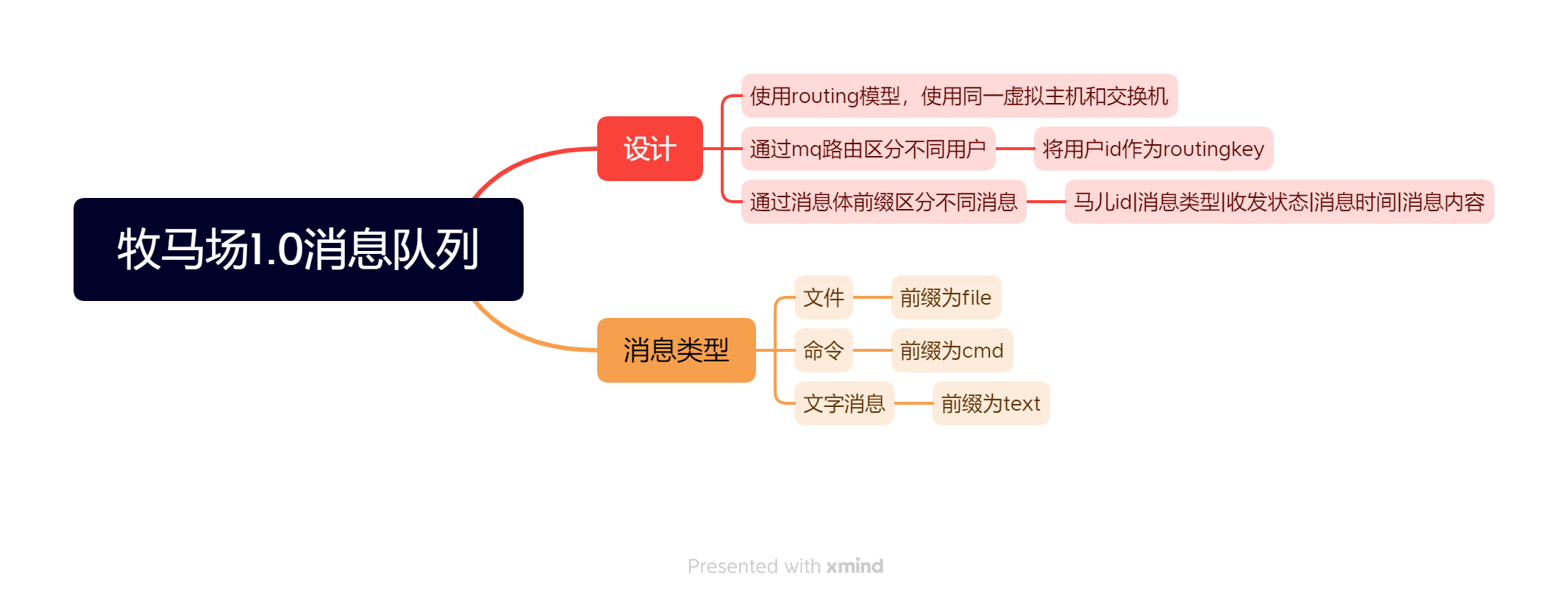
结构设计
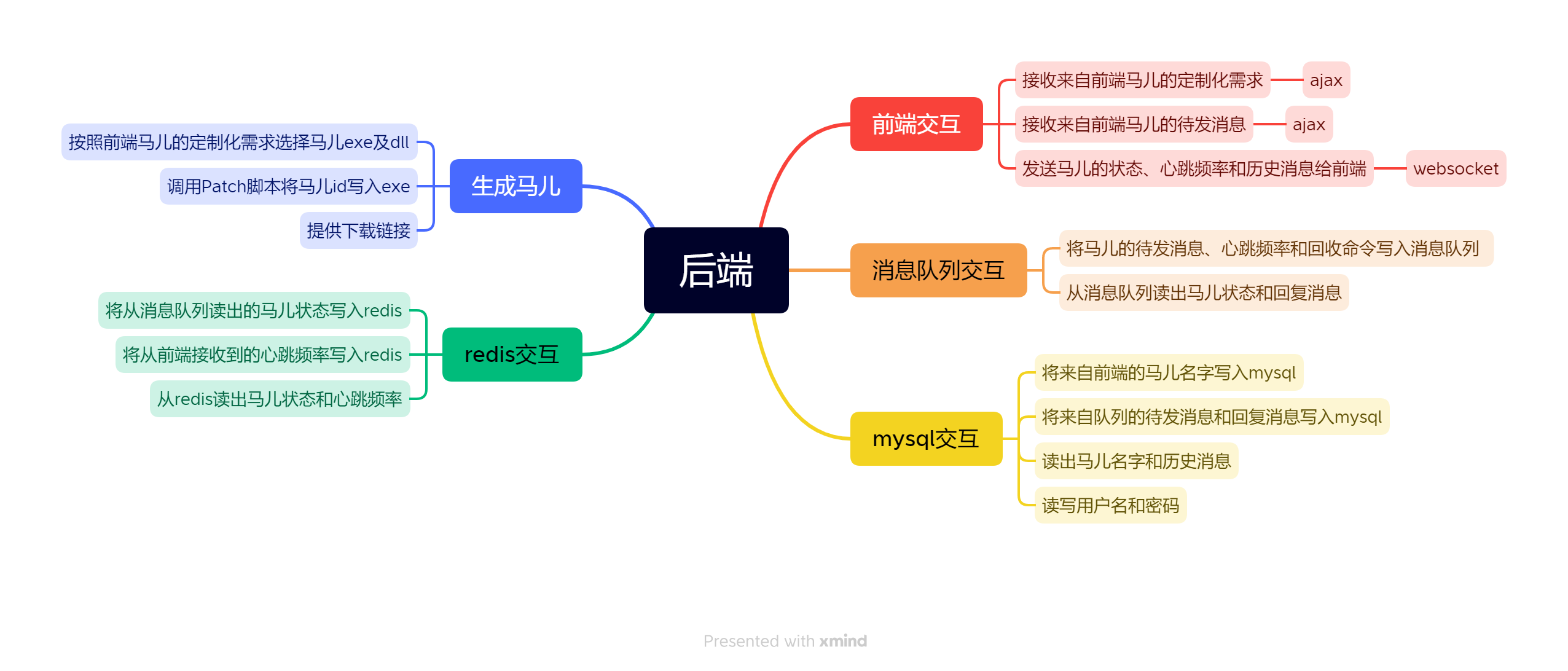
数据库设计
消息队列设计
技术选型
- 开发工具:IDEA
- 运行环境:Jar包内置的Tomcat
- 构建工具:Maven
- java框架:Spring Boot
- 持久层框架:Mybatis
- 数据库连接池:Druid
- 关系型数据库:Mysql
- 缓存型数据库:Redis
- 消息队列:RabbitMQ
- 数据库表设计:PandMan
- 测试工具:PostMan
代码
redis交互
配置
- 需要写个配置类,为redisTemplate增加序列化的配置,使其支持存储java对象
package com.example.horseback.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
objectMapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}
dao层
package com.example.horseback.dao;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.invoke.SerializedLambda;
@Repository
public class RedisUtils {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public boolean set(final String key, Object value){
boolean result = false;
try {
ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
operations.set(key, value);
result = true;
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
public String get(final String key){
Object result = null;
ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
result = operations.get(key);
return result.toString();
}
public void remove(final String key){
if (exists(key)){
redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}
public void remove(final String... keys){
for (String key: keys){
remove(key);
}
}
public boolean exists(final String key){
return redisTemplate.hasKey(key);
}
}
service层
package com.example.horseback.service;
import com.example.horseback.dao.RedisUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class HorseStateService {
@Autowired
private RedisUtils redisUtils;
private String key = "state";
public void setActiveState() {
redisUtils.set(key, 1);
}
public void setDeadState() {
redisUtils.set(key, 0);
}
public String getState() {
return redisUtils.get(key);
}
}
controller层
package com.example.horseback.controller;
import com.example.horseback.service.HorseStateService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HoseStateController {
@Autowired
private HorseStateService horseStateService;
@RequestMapping("/setStateActive")
public void setStateActive(){
horseStateService.setActiveState();
}
@RequestMapping("/setStateDead")
public void setStateDead(){
horseStateService.setDeadState();
}
@RequestMapping("/getState")
public String getState(){
return horseStateService.getState();
}
}
mysql交互
表设计
- 首先在Mysql中增加user_table表,为其添加user_id,user_name和user_pwd三个字段
entity层
- alt+insert自动生成getter和setter以及构造方法
package com.example.horseback.entity;
public class User {
private Integer user_id;
private String user_name;
private String user_pwd;
public User(Integer user_id, String user_name, String user_pwd){
this.user_id = user_id;
this.user_name = user_name;
this.user_pwd = user_pwd;
}
public Integer getUser_id() {
return user_id;
}
public void setUser_id(Integer user_id) {
this.user_id = user_id;
}
public String getUser_name() {
return user_name;
}
public void setUser_name(String user_name) {
this.user_name = user_name;
}
public String getUser_pwd() {
return user_pwd;
}
public void setUser_pwd(String user_pwd) {
this.user_pwd = user_pwd;
}
}
mapper层
- 建议将mybatis-mapper.xml放到resources/mapper目录下,方便其他模块引用
- 如果xml放到resources目录下,需要在application.properties中添加一行
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml,指明引用位置
<mapper namespace="com.example.horseback.dao.UserDao">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.example.horseback.entity.User">
<result column="user_id" property="user_id" />
<result column="user_name" property="user_name" />
<result column="user_pwd" property="user_pwd" />
</resultMap>
<select id="findById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select * from user_table where user_id =
</select>
<select id="findWhenLogIn" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select * from user_table where user_name =
</select>
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="com.example.horseback.entity.User">
insert into user_table (user_name, user_pwd) values (
</insert>
</mapper>
dao层
package com.example.horseback.dao;
import com.example.horseback.entity.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.MappedJdbcTypes;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface UserDao {
User findById(int user_id);
User findWhenLogIn(String user_name, String user_pwd);
Long addUser(String user_name, String user_pwd);
}
service层
package com.example.horseback.service;
import com.example.horseback.dao.UserDao;
import com.example.horseback.entity.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
UserDao userDao;
public User getLoginUser(String userName, String passWord){
return userDao.findWhenLogIn(userName, passWord);
}
public User getUserById(Integer id){
return userDao.findById(id);
}
public long addUser(String userName, String passWord){
return userDao.addUser(userName, passWord);
}
}
controller层
package com.example.horseback.controller;
import com.example.horseback.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String doLogin(String userName, String passWord){
if (userService.getLoginUser(userName, passWord) != null){
return "登录成功!";
}
else {
return "用户名或密码错误!";
}
}
@RequestMapping("/addUser")
public String doAdd(String userName, String passWord){
if(userService.addUser(userName, passWord) == 1){
return "成功插入用户!";
}
else{
return "插入用户失败";
}
}
}
问题
- 在dao层中定义数据库接口方法时,有两种方法让IOC扫描到定义的方法
- 可以在UserDao类上添加@mapper注解,实际调试了很久发现不行
- 在启动类上添加注解
@MapperScan(value = "com.example.horseback.dao"),指明mapper方法的路径,实际调试可行
- 报错提示
sqlSessionFactory or sqlSessionTemplate are required,解决办法
- 网上说是mybatis-starter版本过高,我在pom.xml中试了各种历史版本,还是不行
- 创建一个dao层的基类,在基类中注入sqlSessionFactory,然后让自己的dao去继承这个基类,但是由于我的dao层只是接口,故该方法不行
- 将application.properties改为application.yml,取消自动注入,
@EnableAutoComfiguration(exclude=DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
消息队列交互
- 使用routing模型,如果要设置动态路由,应该用topic模型
- 貌似不能写到controller里,否则在自动注入时会报rabbitTemplate指针为空,要把读写队列的代码写到测试方法里,用SprinBootTest和RunWith注解才行,但在测试方法里我就写不了路由了,有没有大佬有对策?
package com.example.horseback.controller;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
public class MQProcessController {
@Resource
public RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/writeQueue")
public String writeQueueToRouting(String msg, String routingKey) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("directs",routingKey, msg);
return "发送成功";
}
@RequestMapping("/readQueue")
@RabbitListener(bindings = {
@QueueBinding(
value = @Queue,
exchange = @Exchange(value = "directs",type = "direct"),
key = {"test"}
)
})
public void readQueueToRouting(String message){
System.out.println("message1 = " + message);
}
}
配置文件
server.port=8080
redis:
host:
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 8
max-wait: -1
max-idle: 500
min-idle: 0
lettuce:
shutdown-timeout: 30000
spring.rabbitmq.host=localhost
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.password=guest
spring.rabbitmq.username=guest
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.acknowledge-mode=manual
spring.rabbitmq.listener.direct.acknowledge-mode=manual
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.prefetch=1
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/ssm-java1?useSSL=false
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password:
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· Pantheons:用 TypeScript 打造主流大模型对话的一站式集成库