Leetcode 单词的压缩编码(字典树)
题目描述:
给定一个单词列表,我们将这个列表编码成一个索引字符串 S 与一个索引列表 A。例如,如果这个列表是 ["time", "me", "bell"],我们就可以将其表示为 S = "time#bell#" 和 indexes = [0, 2, 5]。
对于每一个索引,我们可以通过从字符串 S 中索引的位置开始读取字符串,直到 "#" 结束,来恢复我们之前的单词列表。那么成功对给定单词列表进行编码的最小字符串长度是多少呢?
题解:
分析题目可知能够进行压缩的字符串的特征--为其他字符串的后缀。考虑建立一个字典树,为了确定不同的单词具有相同的后缀,我们可以将其反序之后插入字典树中。例如,我们有 "time" 和 "me",可以将 "emit" 和 "em" 插入字典树中。图示如下:
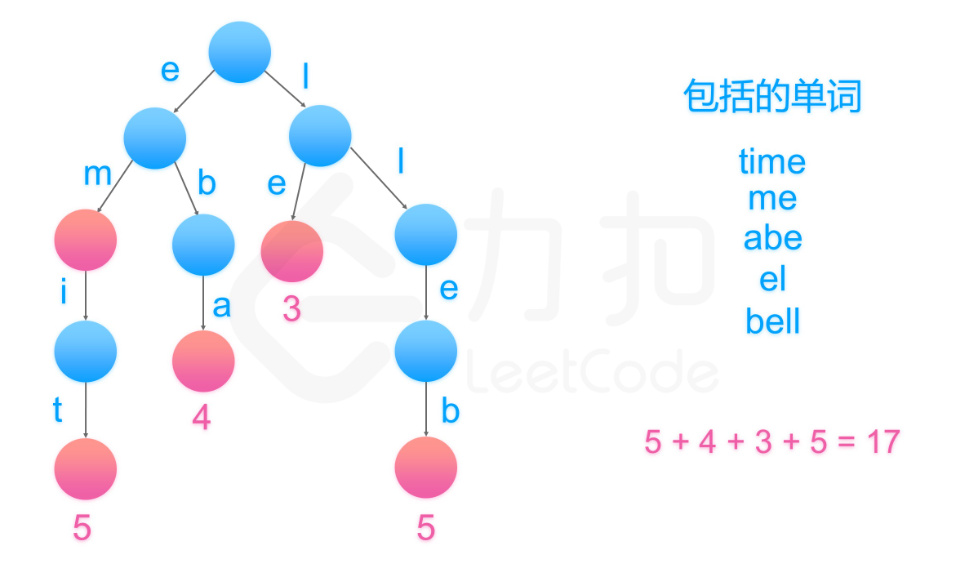
然后,字典树的叶子节点(没有孩子的节点)就代表没有后缀的单词,统计叶子节点代表的单词长度加一的和即为我们要的答案。(参考自:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/short-encoding-of-words/solution/dan-ci-de-ya-suo-bian-ma-by-leetcode-solution/)
AC代码:
class TrieNode{ TrieNode* child[26]; public: int count; // 是否为叶子节点 TrieNode() { for(int i=0;i<26;i++) child[i] = NULL; count = 0; } TrieNode* get(char c) // 或许字符c对应的child节点 { if(child[c-'a'] == NULL) { child[c-'a'] = new TrieNode(); count++; } return child[c-'a']; } }; class Solution { public: TrieNode* insert(TrieNode* root,string s) { int Len = s.size(); // 倒插 for(int i=Len-1;i>=0;i--) { root = root->get(s[i]); } return root; } int minimumLengthEncoding(vector<string>& words) { int Len = words.size(); TrieNode* trie = new TrieNode(); node.clear(); for(int i=0;i<Len;i++) { string word = words[i]; TrieNode* leaf = insert(trie,word); node[leaf] = i; } int ans = 0; // map 的遍历方式 for(auto [node,idx]:node) { if(node->count == 0) ans += (words[idx].size()+1); } return ans; } private: unordered_map<TrieNode*,int> node; };





