Spring Security学习小记
本文中用到的Spring Security版本为 5.3.4.RELEASE 。
以下多数内容为阅读官方文档(https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.3.4.RELEASE/reference/html5)的总结。
1 What
Spring Security provides comprehensive support for authentication, authorization, and protection against common exploits. It also provides integration with other libraries to simplify its usage. 即提供认证、授权、漏洞保护(如CSRF、XSS漏洞预防、密码保存策略等)。
认证(Authentication)和授权(Authorization):
Authentication is how we verify the identity of who is trying to access a particular resource. A common way to authenticate users is by requiring the user to enter a username and password. Once authentication is performed we know the identity and can perform authorization.
注:SpringSecurity依赖于Servlet,并不依赖于SpringMVC。
2 主要功能
功能
Spring Security主要提供authenticate、authorize两个功能:
前者通常用于根据前端传的principal、crendential信息(通常是username、password)去校验该用户是否存在。若存在则将针对该用户的授权信息GrandAuthority返回给调用者;
后者通常是根据前端传的GrandAuthority信息(在前者认证通过后得到)判断该用户是否有权访问某种资源,如某个接口、某个图片等。授权实际上包括三个方面的内容(具体见后面的 Expression-Based Access Control 一节):
who (Authentication):谁能访问,也就是校验访问者是否能访问某个URL,称为Web Request Security。通常是要求用户已登录并校验token是否有效,若有效则提取出Authentication信息,也即该用户的角色等相关信息。
where (MethodInvocation):能访问哪个方法,该方法通常是与某个URL对应的handler方法。称为Method Invocation Security。
what (SomeDomainObject):能访问什么数据,称为Domain Object Security或Access Controll List(ACL),如学生是否能查询某个课程。在我们之前的实践中通常who、where的授权用框架功能实现,而what由开发者在handler方法内部自己实现。
总结而言,包括功能权限(可访问哪些接口)和数据权限(可访问哪些数据)的控制。
异常处理
Authenticate出异常抛AuthenticationException:如用户名或密码未传、密码不正确等。
Authorize异常抛AccessDeniedException:如当前用户认证了,但没有访问某个接口所需的角色,从而没有访问权限。
对于这两种异常,用户可以自己在onFailureHanlder中处理。实际上,它们也都会在ExceptionTranslationFilter中被translate,因此可以在ExceptionTranslationFilter中做一些文章(如对返回的异常进行统一处理)。需要注意的是,ExceptionTranslationFilter不会处理这两种异常之外的异常。相关源码:

public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req; HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res; try { chain.doFilter(request, response); logger.debug("Chain processed normally"); } catch (IOException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Exception ex) { // Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex); RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer .getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain); if (ase == null) { ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType( AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain); } if (ase != null) { if (response.isCommitted()) { throw new ServletException("Unable to handle the Spring Security Exception because the response is already committed.", ex); } handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase); } else { // Rethrow ServletExceptions and RuntimeExceptions as-is if (ex instanceof ServletException) { throw (ServletException) ex; } else if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) ex; } // Wrap other Exceptions. This shouldn't actually happen // as we've already covered all the possibilities for doFilter throw new RuntimeException(ex); } } } private void handleSpringSecurityException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, RuntimeException exception) throws IOException, ServletException { if (exception instanceof AuthenticationException) { logger.debug( "Authentication exception occurred; redirecting to authentication entry point", exception); sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain, (AuthenticationException) exception); } else if (exception instanceof AccessDeniedException) { Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication(); if (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) || authenticationTrustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication)) { logger.debug( "Access is denied (user is " + (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) ? "anonymous" : "not fully authenticated") + "); redirecting to authentication entry point", exception); sendStartAuthentication( request, response, chain, new InsufficientAuthenticationException( messages.getMessage( "ExceptionTranslationFilter.insufficientAuthentication", "Full authentication is required to access this resource"))); } else { logger.debug( "Access is denied (user is not anonymous); delegating to AccessDeniedHandler", exception); accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response, (AccessDeniedException) exception); } } }
实现
Authentication基于servlet filter实现;Authorization基于Spring Intercepter实现。
Integrations
参阅:https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.3.4.RELEASE/reference/html5/#integrations
Spring Security与很多现有Servlet或Spring Framework 的功能(具体如下图所示的)无缝集成。包括:
这里介绍其中几种:
Servlet API Integration
Servlet 2.5+ :(实现类为 org.springframework.security.web.servletapi.SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestWrapper)
HttpServletRequest.getRemoteUser() will return the result of SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getName()
HttpServletRequest.getUserPrincipal() will return the result of SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()
HttpServletRequest.isUserInRole(String) will return the result of SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getAuthorities() ,这个用得较多。
Servlet 3+ :(实现类为 org.springframework.security.web.servletapi.HttpServlet3RequestFactory)
HttpServletRequest.authenticate(HttpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse) :used to ensure that a user is authenticated. If they are not authenticated, the configured AuthenticationEntryPoint will be used to request the user to authenticate (i.e. redirect to the login page).
HttpServletRequest.login(String,String) :used to authenticate the user with the current AuthenticationManager
HttpServletRequest.logout() :used to log the current user out. Typically this means that the SecurityContextHolder will be cleared out, the HttpSession will be invalidated, any "Remember Me" authentication will be cleaned up, etc.
HttpServletRequest.startAsync() :Puts this request into asynchronous mode, and initializes its AsyncContext with the original (unwrapped) ServletRequest and ServletResponse objects.
Servlet 3.1 :
HttpServletRequest.changeSessionId()
Spring MVC Integration
@AuthenticationPrincipal:通过该注解可以自动将值注入方法参数,等价于 SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal()
示例:通过@AuthenticationPrincipal直接向Handler方法注入Security信息

@RequestMapping("/messages/inbox")
public ModelAndView findMessagesForUser(@AuthenticationPrincipal CustomUser customUser) {
// .. find messages for this user and return them ...
}
上例等价于通过SecurityContext来获取:
CustomerUser customUser = (CustomerUser)SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
3 原理
参阅官方文档:https://spring.io/projects/spring-security#learn、https://spring.io/guides/topicals/spring-security-architecture
3.1 Spring Security Filter
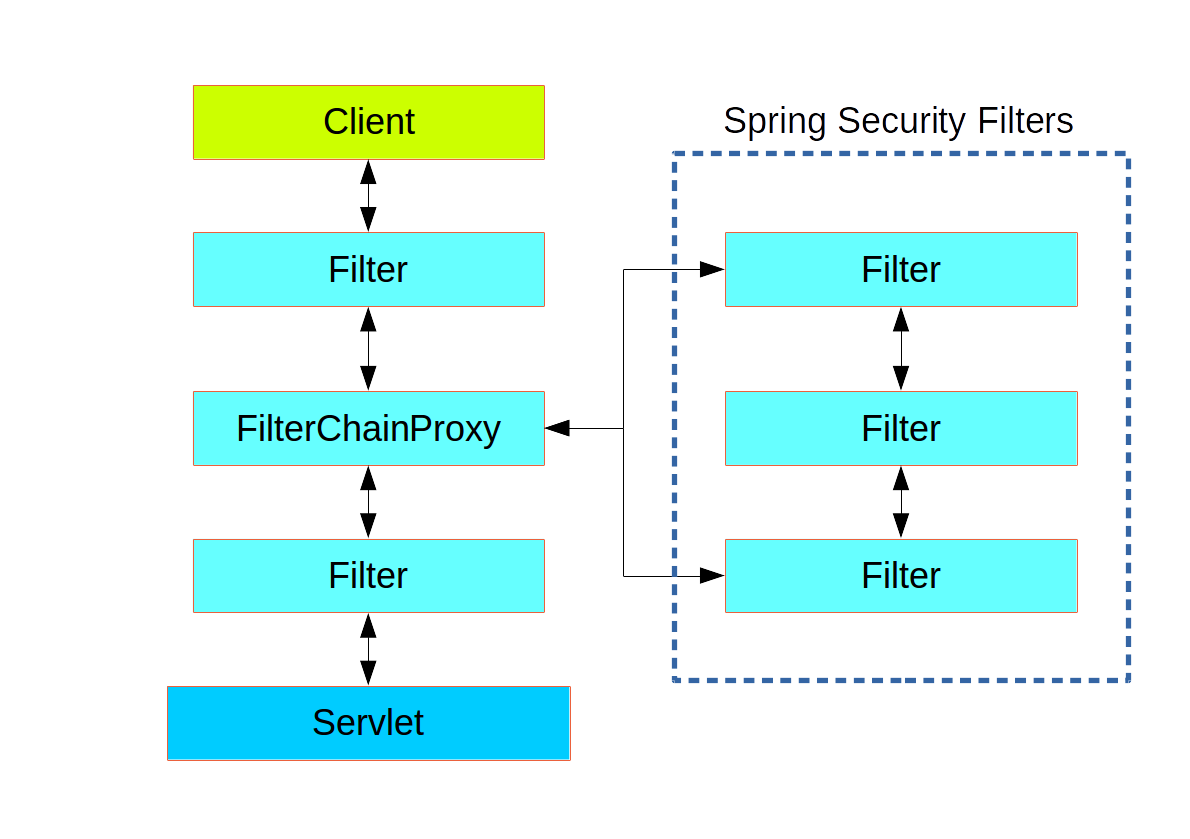
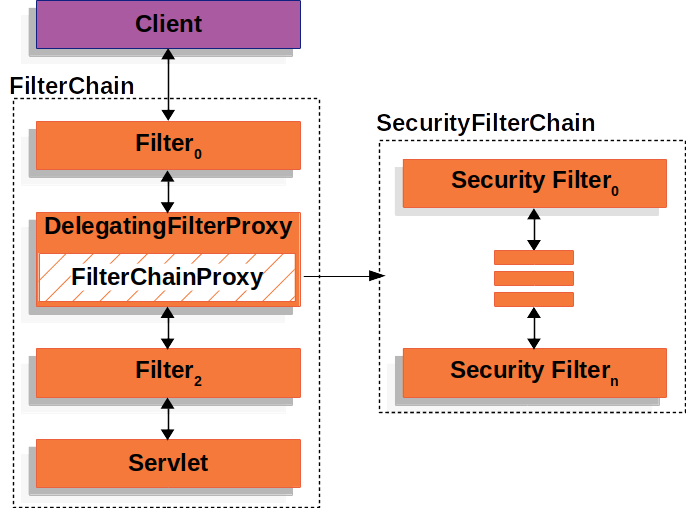
如图,实际上只会有一个filter(Spring Security中称为FilterChainProxy)被真正加入到Servlet Container的filter chain中。使用SpringSecurity时指定的各种业务filter(如authentication filter、authorization filter)并不会成为真正的Servlet filter,而是作为逻辑filter组成一个filter chain(即FilterChainProxy#VirtualFilterChain),这个chain会被FilterChainProxy.doFilter调用。
FilterChainProxy:注册到Servlet Container的filter chain,实际上还被DelegatingFilterProxy wrap。如上图左边所示。
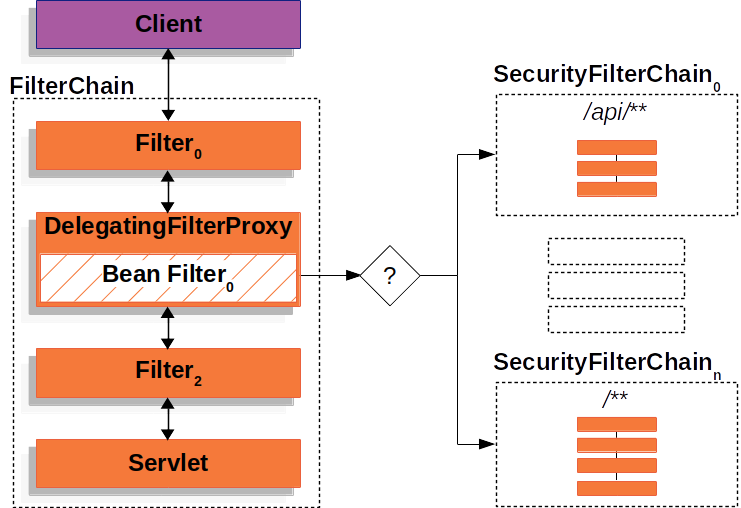
SecurityFilterChain:SpringSecurity中用户添加的各种filter组成逻辑filter,包装成SecurityFilterChain保存在FilterChainProxy对象中,可以有多个SecurityFilterChain(List<SecurityChain> filterChains)。如上图右边所示。用户可以添加自定义的SecurityFilterChain,未自定义则默认初始化DefaultSecurityFilterChain。
FilterChainProxy#VirtualFilterChain:请求到来时FilterChainProxy.doFilter方法从DefaultSecurityFilterChain获取match当前request的filter列表并包装成VirtualFilterChain,通过VirtualFilterChain依次调用各filter。
可以看出,与普通的filter一样,Spring Security Filter是在DispatcherServlet之前起作用的。
相关源码:

1 /* 2 * Copyright 2004, 2005, 2006 Acegi Technology Pty Limited 3 * 4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at 7 * 8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 9 * 10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 14 * limitations under the License. 15 */ 16 17 package org.springframework.security.web; 18 19 import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; 20 import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; 21 import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder; 22 import org.springframework.security.web.firewall.FirewalledRequest; 23 import org.springframework.security.web.firewall.HttpFirewall; 24 import org.springframework.security.web.firewall.StrictHttpFirewall; 25 import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.RequestMatcher; 26 import org.springframework.security.web.util.UrlUtils; 27 import org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy; 28 import org.springframework.web.filter.GenericFilterBean; 29 30 import javax.servlet.Filter; 31 import javax.servlet.FilterChain; 32 import javax.servlet.ServletException; 33 import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; 34 import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; 35 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 36 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; 37 import java.io.IOException; 38 import java.util.*; 39 40 /** 41 * Delegates {@code Filter} requests to a list of Spring-managed filter beans. As of 42 * version 2.0, you shouldn't need to explicitly configure a {@code FilterChainProxy} bean 43 * in your application context unless you need very fine control over the filter chain 44 * contents. Most cases should be adequately covered by the default 45 * {@code <security:http />} namespace configuration options. 46 * <p> 47 * The {@code FilterChainProxy} is linked into the servlet container filter chain by 48 * adding a standard Spring {@link DelegatingFilterProxy} declaration in the application 49 * {@code web.xml} file. 50 * 51 * <h2>Configuration</h2> 52 * <p> 53 * As of version 3.1, {@code FilterChainProxy} is configured using a list of 54 * {@link SecurityFilterChain} instances, each of which contains a {@link RequestMatcher} 55 * and a list of filters which should be applied to matching requests. Most applications 56 * will only contain a single filter chain, and if you are using the namespace, you don't 57 * have to set the chains explicitly. If you require finer-grained control, you can make 58 * use of the {@code <filter-chain>} namespace element. This defines a URI pattern 59 * and the list of filters (as comma-separated bean names) which should be applied to 60 * requests which match the pattern. An example configuration might look like this: 61 * 62 * <pre> 63 * <bean id="myfilterChainProxy" class="org.springframework.security.util.FilterChainProxy"> 64 * <constructor-arg> 65 * <util:list> 66 * <security:filter-chain pattern="/do/not/filter*" filters="none"/> 67 * <security:filter-chain pattern="/**" filters="filter1,filter2,filter3"/> 68 * </util:list> 69 * </constructor-arg> 70 * </bean> 71 * </pre> 72 * 73 * The names "filter1", "filter2", "filter3" should be the bean names of {@code Filter} 74 * instances defined in the application context. The order of the names defines the order 75 * in which the filters will be applied. As shown above, use of the value "none" for the 76 * "filters" can be used to exclude a request pattern from the security filter chain 77 * entirely. Please consult the security namespace schema file for a full list of 78 * available configuration options. 79 * 80 * <h2>Request Handling</h2> 81 * <p> 82 * Each possible pattern that the {@code FilterChainProxy} should service must be entered. 83 * The first match for a given request will be used to define all of the {@code Filter}s 84 * that apply to that request. This means you must put most specific matches at the top of 85 * the list, and ensure all {@code Filter}s that should apply for a given matcher are 86 * entered against the respective entry. The {@code FilterChainProxy} will not iterate 87 * through the remainder of the map entries to locate additional {@code Filter}s. 88 * <p> 89 * {@code FilterChainProxy} respects normal handling of {@code Filter}s that elect not to 90 * call 91 * {@link javax.servlet.Filter#doFilter(javax.servlet.ServletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse, javax.servlet.FilterChain)} 92 * , in that the remainder of the original or {@code FilterChainProxy}-declared filter 93 * chain will not be called. 94 * 95 * <h3>Request Firewalling</h3> 96 * 97 * An {@link HttpFirewall} instance is used to validate incoming requests and create a 98 * wrapped request which provides consistent path values for matching against. See 99 * {@link StrictHttpFirewall}, for more information on the type of attacks which the 100 * default implementation protects against. A custom implementation can be injected to 101 * provide stricter control over the request contents or if an application needs to 102 * support certain types of request which are rejected by default. 103 * <p> 104 * Note that this means that you must use the Spring Security filters in combination with 105 * a {@code FilterChainProxy} if you want this protection. Don't define them explicitly in 106 * your {@code web.xml} file. 107 * <p> 108 * {@code FilterChainProxy} will use the firewall instance to obtain both request and 109 * response objects which will be fed down the filter chain, so it is also possible to use 110 * this functionality to control the functionality of the response. When the request has 111 * passed through the security filter chain, the {@code reset} method will be called. With 112 * the default implementation this means that the original values of {@code servletPath} 113 * and {@code pathInfo} will be returned thereafter, instead of the modified ones used for 114 * security pattern matching. 115 * <p> 116 * Since this additional wrapping functionality is performed by the 117 * {@code FilterChainProxy}, we don't recommend that you use multiple instances in the 118 * same filter chain. It shouldn't be considered purely as a utility for wrapping filter 119 * beans in a single {@code Filter} instance. 120 * 121 * <h2>Filter Lifecycle</h2> 122 * <p> 123 * Note the {@code Filter} lifecycle mismatch between the servlet container and IoC 124 * container. As described in the {@link DelegatingFilterProxy} Javadocs, we recommend you 125 * allow the IoC container to manage the lifecycle instead of the servlet container. 126 * {@code FilterChainProxy} does not invoke the standard filter lifecycle methods on any 127 * filter beans that you add to the application context. 128 * 129 * @author Carlos Sanchez 130 * @author Ben Alex 131 * @author Luke Taylor 132 * @author Rob Winch 133 */ 134 public class FilterChainProxy extends GenericFilterBean { 135 // ~ Static fields/initializers 136 // ===================================================================================== 137 138 private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(FilterChainProxy.class); 139 140 // ~ Instance fields 141 // ================================================================================================ 142 143 private final static String FILTER_APPLIED = FilterChainProxy.class.getName().concat( 144 ".APPLIED"); 145 146 private List<SecurityFilterChain> filterChains; 147 148 private FilterChainValidator filterChainValidator = new NullFilterChainValidator(); 149 150 private HttpFirewall firewall = new StrictHttpFirewall(); 151 152 // ~ Methods 153 // ======================================================================================================== 154 155 public FilterChainProxy() { 156 } 157 158 public FilterChainProxy(SecurityFilterChain chain) { 159 this(Arrays.asList(chain)); 160 } 161 162 public FilterChainProxy(List<SecurityFilterChain> filterChains) { 163 this.filterChains = filterChains; 164 } 165 166 @Override 167 public void afterPropertiesSet() { 168 filterChainValidator.validate(this); 169 } 170 171 @Override 172 public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, 173 FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { 174 boolean clearContext = request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) == null; 175 if (clearContext) { 176 try { 177 request.setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE); 178 doFilterInternal(request, response, chain); 179 } 180 finally { 181 SecurityContextHolder.clearContext(); 182 request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED); 183 } 184 } 185 else { 186 doFilterInternal(request, response, chain); 187 } 188 } 189 190 private void doFilterInternal(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, 191 FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { 192 193 FirewalledRequest fwRequest = firewall 194 .getFirewalledRequest((HttpServletRequest) request); 195 HttpServletResponse fwResponse = firewall 196 .getFirewalledResponse((HttpServletResponse) response); 197 198 List<Filter> filters = getFilters(fwRequest); 199 200 if (filters == null || filters.size() == 0) { 201 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 202 logger.debug(UrlUtils.buildRequestUrl(fwRequest) 203 + (filters == null ? " has no matching filters" 204 : " has an empty filter list")); 205 } 206 207 fwRequest.reset(); 208 209 chain.doFilter(fwRequest, fwResponse); 210 211 return; 212 } 213 214 VirtualFilterChain vfc = new VirtualFilterChain(fwRequest, chain, filters); 215 vfc.doFilter(fwRequest, fwResponse); 216 } 217 218 /** 219 * Returns the first filter chain matching the supplied URL. 220 * 221 * @param request the request to match 222 * @return an ordered array of Filters defining the filter chain 223 */ 224 private List<Filter> getFilters(HttpServletRequest request) { 225 for (SecurityFilterChain chain : filterChains) { 226 if (chain.matches(request)) { 227 return chain.getFilters(); 228 } 229 } 230 231 return null; 232 } 233 234 /** 235 * Convenience method, mainly for testing. 236 * 237 * @param url the URL 238 * @return matching filter list 239 */ 240 public List<Filter> getFilters(String url) { 241 return getFilters(firewall.getFirewalledRequest((new FilterInvocation(url, null) 242 .getRequest()))); 243 } 244 245 /** 246 * @return the list of {@code SecurityFilterChain}s which will be matched against and 247 * applied to incoming requests. 248 */ 249 public List<SecurityFilterChain> getFilterChains() { 250 return Collections.unmodifiableList(filterChains); 251 } 252 253 /** 254 * Used (internally) to specify a validation strategy for the filters in each 255 * configured chain. 256 * 257 * @param filterChainValidator the validator instance which will be invoked on during 258 * initialization to check the {@code FilterChainProxy} instance. 259 */ 260 public void setFilterChainValidator(FilterChainValidator filterChainValidator) { 261 this.filterChainValidator = filterChainValidator; 262 } 263 264 /** 265 * Sets the "firewall" implementation which will be used to validate and wrap (or 266 * potentially reject) the incoming requests. The default implementation should be 267 * satisfactory for most requirements. 268 * 269 * @param firewall 270 */ 271 public void setFirewall(HttpFirewall firewall) { 272 this.firewall = firewall; 273 } 274 275 @Override 276 public String toString() { 277 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 278 sb.append("FilterChainProxy["); 279 sb.append("Filter Chains: "); 280 sb.append(filterChains); 281 sb.append("]"); 282 283 return sb.toString(); 284 } 285 286 // ~ Inner Classes 287 // ================================================================================================== 288 289 /** 290 * Internal {@code FilterChain} implementation that is used to pass a request through 291 * the additional internal list of filters which match the request. 292 */ 293 private static class VirtualFilterChain implements FilterChain { 294 private final FilterChain originalChain; 295 private final List<Filter> additionalFilters; 296 private final FirewalledRequest firewalledRequest; 297 private final int size; 298 private int currentPosition = 0; 299 300 private VirtualFilterChain(FirewalledRequest firewalledRequest, 301 FilterChain chain, List<Filter> additionalFilters) { 302 this.originalChain = chain; 303 this.additionalFilters = additionalFilters; 304 this.size = additionalFilters.size(); 305 this.firewalledRequest = firewalledRequest; 306 } 307 308 @Override 309 public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) 310 throws IOException, ServletException { 311 if (currentPosition == size) { 312 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 313 logger.debug(UrlUtils.buildRequestUrl(firewalledRequest) 314 + " reached end of additional filter chain; proceeding with original chain"); 315 } 316 317 // Deactivate path stripping as we exit the security filter chain 318 this.firewalledRequest.reset(); 319 320 originalChain.doFilter(request, response); 321 } 322 else { 323 currentPosition++; 324 325 Filter nextFilter = additionalFilters.get(currentPosition - 1); 326 327 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 328 logger.debug(UrlUtils.buildRequestUrl(firewalledRequest) 329 + " at position " + currentPosition + " of " + size 330 + " in additional filter chain; firing Filter: '" 331 + nextFilter.getClass().getSimpleName() + "'"); 332 } 333 334 nextFilter.doFilter(request, response, this); 335 } 336 } 337 } 338 339 public interface FilterChainValidator { 340 void validate(FilterChainProxy filterChainProxy); 341 } 342 343 private static class NullFilterChainValidator implements FilterChainValidator { 344 @Override 345 public void validate(FilterChainProxy filterChainProxy) { 346 } 347 } 348 349 }
 、
、
默认的Spring Security Filter顺序(参阅:https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.3.4.RELEASE/reference/html5/#servlet-security-filters):

ChannelProcessingFilter
ConcurrentSessionFilter
WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
HeaderWriterFilter
CorsFilter
CsrfFilter
LogoutFilter
OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter
Saml2WebSsoAuthenticationRequestFilter
X509AuthenticationFilter
AbstractPreAuthenticatedProcessingFilter
CasAuthenticationFilter
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter
Saml2WebSsoAuthenticationFilter
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
ConcurrentSessionFilter
OpenIDAuthenticationFilter
DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter
DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter
DigestAuthenticationFilter
BearerTokenAuthenticationFilter
BasicAuthenticationFilter
RequestCacheAwareFilter
SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter
JaasApiIntegrationFilter
RememberMeAuthenticationFilter
AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
OAuth2AuthorizationCodeGrantFilter
SessionManagementFilter
ExceptionTranslationFilter
FilterSecurityInterceptor
SwitchUserFilter
3.2 Authentication
The Authentication serves two main purposes within Spring Security:
An input to AuthenticationManager to provide the credentials a user has provided to authenticate. When used in this scenario, isAuthenticated() returns false.
Represents the currently authenticated user. The current Authentication can be obtained from the SecurityContext.
The Authentication contains:
principal - identifies the user. When authenticating with a username/password this is often an instance of UserDetails.
credentials - Often a password. In many cases this will be cleared after the user is authenticated to ensure it is not leaked.
authorities - the GrantedAuthoritys are high level permissions the user is granted. A few examples are roles or scopes.
主要执行流程:
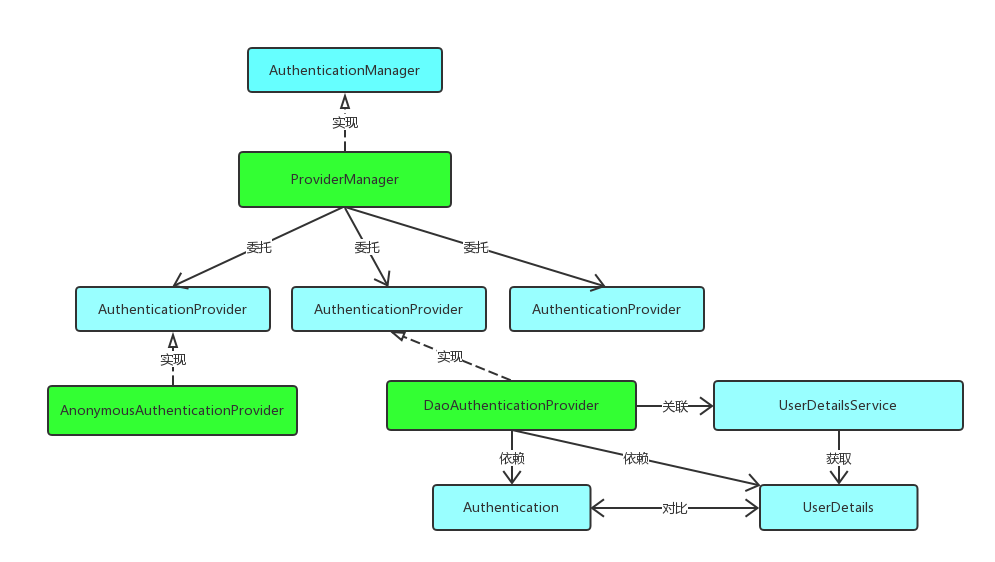
先由ProcessingFilter预处理,处理通过则交由AuthenticationManager进一步处理;
AuthenticationManager的具体实现为ProviderManager,其内部包含若干AuthenticationProvider,会依次调用这些AuthenticationProvider进行authenticate操作;
若authenticate成功则交由AuthenticationSuccessHanlder进一步处理;
上述过程中出错则交由AuthenticationFailureHanlder处理。
示意图:(from https://www.cnkirito.moe/categories/Spring-Security/ )
 、
、 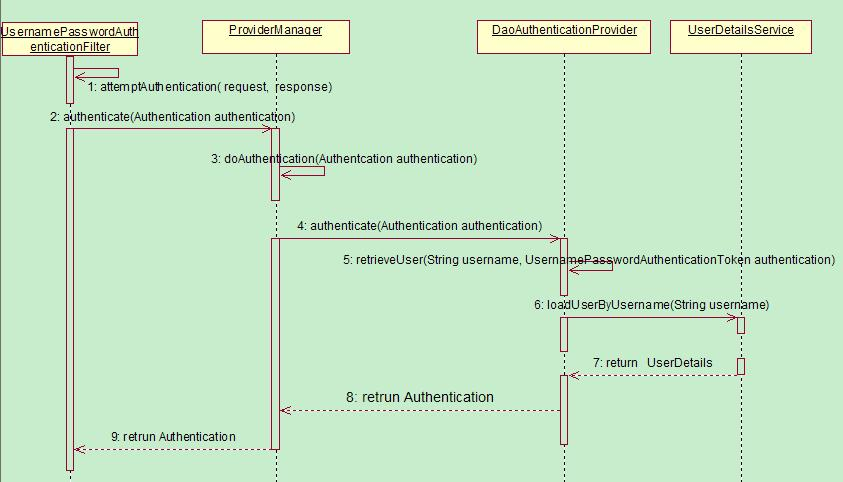
相关代码:
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
ProviderManager
AuthenticationProcider
3.3 Authorization
Authorization是通过Spring 拦截器来实现的。
3.3.0 启用/配置(GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration)
参阅:https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.3.4.RELEASE/reference/html5/#ns-global-method
通过 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 来启用authorize功能,该注解会去加载 GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration 配置类,后者会进行包括但不限于如下内容的配置:
GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration
afterInvocationManager
authenticationManager
methodSecurityMetadataSource
runAsManager
MethodSecurityExpressionHandler
PermissionEvaluator
RoleHierarchy
源码:

1 /* 2 * Copyright 2002-2016 the original author or authors. 3 * 4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at 7 * 8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 9 * 10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 14 * limitations under the License. 15 */ 16 package org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration; 17 18 import java.util.ArrayList; 19 import java.util.List; 20 import java.util.Map; 21 22 import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor; 23 import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; 24 import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; 25 26 import org.springframework.beans.factory.SmartInitializingSingleton; 27 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 28 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 29 import org.springframework.context.annotation.AdviceMode; 30 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; 31 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; 32 import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportAware; 33 import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAttributes; 34 import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils; 35 import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata; 36 import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDecisionManager; 37 import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDecisionVoter; 38 import org.springframework.security.access.AfterInvocationProvider; 39 import org.springframework.security.access.PermissionEvaluator; 40 import org.springframework.security.access.annotation.Jsr250MethodSecurityMetadataSource; 41 import org.springframework.security.access.annotation.Jsr250Voter; 42 import org.springframework.security.access.annotation.SecuredAnnotationSecurityMetadataSource; 43 import org.springframework.security.access.expression.method.DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler; 44 import org.springframework.security.access.expression.method.ExpressionBasedAnnotationAttributeFactory; 45 import org.springframework.security.access.expression.method.ExpressionBasedPostInvocationAdvice; 46 import org.springframework.security.access.expression.method.ExpressionBasedPreInvocationAdvice; 47 import org.springframework.security.access.expression.method.MethodSecurityExpressionHandler; 48 import org.springframework.security.access.hierarchicalroles.RoleHierarchy; 49 import org.springframework.security.access.intercept.AfterInvocationManager; 50 import org.springframework.security.access.intercept.AfterInvocationProviderManager; 51 import org.springframework.security.access.intercept.RunAsManager; 52 import org.springframework.security.access.intercept.aopalliance.MethodSecurityInterceptor; 53 import org.springframework.security.access.intercept.aspectj.AspectJMethodSecurityInterceptor; 54 import org.springframework.security.access.method.DelegatingMethodSecurityMetadataSource; 55 import org.springframework.security.access.method.MethodSecurityMetadataSource; 56 import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PostInvocationAdviceProvider; 57 import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreInvocationAuthorizationAdvice; 58 import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreInvocationAuthorizationAdviceVoter; 59 import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PrePostAnnotationSecurityMetadataSource; 60 import org.springframework.security.access.vote.AffirmativeBased; 61 import org.springframework.security.access.vote.AuthenticatedVoter; 62 import org.springframework.security.access.vote.RoleVoter; 63 import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager; 64 import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationTrustResolver; 65 import org.springframework.security.authentication.DefaultAuthenticationEventPublisher; 66 import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.ObjectPostProcessor; 67 import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder; 68 import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.configuration.AuthenticationConfiguration; 69 import org.springframework.security.config.core.GrantedAuthorityDefaults; 70 import org.springframework.util.Assert; 71 72 /** 73 * Base {@link Configuration} for enabling global method security. Classes may extend this 74 * class to customize the defaults, but must be sure to specify the 75 * {@link EnableGlobalMethodSecurity} annotation on the subclass. 76 * 77 * @author Rob Winch 78 * @author Eddú Meléndez 79 * @since 3.2 80 * @see EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 81 */ 82 @Configuration 83 public class GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration 84 implements ImportAware, SmartInitializingSingleton { 85 private static final Log logger = LogFactory 86 .getLog(GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration.class); 87 private ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor = new ObjectPostProcessor<Object>() { 88 public <T> T postProcess(T object) { 89 throw new IllegalStateException(ObjectPostProcessor.class.getName() 90 + " is a required bean. Ensure you have used @" 91 + EnableGlobalMethodSecurity.class.getName()); 92 } 93 }; 94 private DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler defaultMethodExpressionHandler = new DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler(); 95 private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager; 96 private AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth; 97 private boolean disableAuthenticationRegistry; 98 private AnnotationAttributes enableMethodSecurity; 99 private ApplicationContext context; 100 private MethodSecurityExpressionHandler expressionHandler; 101 private Jsr250MethodSecurityMetadataSource jsr250MethodSecurityMetadataSource; 102 private MethodSecurityInterceptor methodSecurityInterceptor; 103 104 /** 105 * Creates the default MethodInterceptor which is a MethodSecurityInterceptor using 106 * the following methods to construct it. 107 * <ul> 108 * <li>{@link #accessDecisionManager()}</li> 109 * <li>{@link #afterInvocationManager()}</li> 110 * <li>{@link #authenticationManager()}</li> 111 * <li>{@link #methodSecurityMetadataSource()}</li> 112 * <li>{@link #runAsManager()}</li> 113 * 114 * </ul> 115 * 116 * <p> 117 * Subclasses can override this method to provide a different 118 * {@link MethodInterceptor}. 119 * </p> 120 * 121 * @return 122 * @throws Exception 123 */ 124 @Bean 125 public MethodInterceptor methodSecurityInterceptor() throws Exception { 126 this.methodSecurityInterceptor = isAspectJ() 127 ? new AspectJMethodSecurityInterceptor() 128 : new MethodSecurityInterceptor(); 129 methodSecurityInterceptor.setAccessDecisionManager(accessDecisionManager()); 130 methodSecurityInterceptor.setAfterInvocationManager(afterInvocationManager()); 131 methodSecurityInterceptor 132 .setSecurityMetadataSource(methodSecurityMetadataSource()); 133 RunAsManager runAsManager = runAsManager(); 134 if (runAsManager != null) { 135 methodSecurityInterceptor.setRunAsManager(runAsManager); 136 } 137 138 return this.methodSecurityInterceptor; 139 } 140 141 /* 142 * (non-Javadoc) 143 * 144 * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.SmartInitializingSingleton# 145 * afterSingletonsInstantiated() 146 */ 147 @Override 148 public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() { 149 try { 150 initializeMethodSecurityInterceptor(); 151 } 152 catch (Exception e) { 153 throw new RuntimeException(e); 154 } 155 156 PermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator = getSingleBeanOrNull( 157 PermissionEvaluator.class); 158 if (permissionEvaluator != null) { 159 this.defaultMethodExpressionHandler 160 .setPermissionEvaluator(permissionEvaluator); 161 } 162 163 RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy = getSingleBeanOrNull(RoleHierarchy.class); 164 if (roleHierarchy != null) { 165 this.defaultMethodExpressionHandler.setRoleHierarchy(roleHierarchy); 166 } 167 168 AuthenticationTrustResolver trustResolver = getSingleBeanOrNull( 169 AuthenticationTrustResolver.class); 170 if (trustResolver != null) { 171 this.defaultMethodExpressionHandler.setTrustResolver(trustResolver); 172 } 173 174 GrantedAuthorityDefaults grantedAuthorityDefaults = getSingleBeanOrNull( 175 GrantedAuthorityDefaults.class); 176 if (grantedAuthorityDefaults != null) { 177 this.defaultMethodExpressionHandler.setDefaultRolePrefix( 178 grantedAuthorityDefaults.getRolePrefix()); 179 } 180 } 181 182 private <T> T getSingleBeanOrNull(Class<T> type) { 183 String[] beanNamesForType = this.context.getBeanNamesForType(type); 184 if (beanNamesForType == null || beanNamesForType.length != 1) { 185 return null; 186 } 187 return this.context.getBean(beanNamesForType[0], type); 188 } 189 190 private void initializeMethodSecurityInterceptor() throws Exception { 191 if(this.methodSecurityInterceptor == null) { 192 return; 193 } 194 this.methodSecurityInterceptor.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager()); 195 } 196 197 /** 198 * Provide a custom {@link AfterInvocationManager} for the default implementation of 199 * {@link #methodSecurityInterceptor()}. The default is null if pre post is not 200 * enabled. Otherwise, it returns a {@link AfterInvocationProviderManager}. 201 * 202 * <p> 203 * Subclasses should override this method to provide a custom 204 * {@link AfterInvocationManager} 205 * </p> 206 * 207 * @return 208 */ 209 protected AfterInvocationManager afterInvocationManager() { 210 if (prePostEnabled()) { 211 AfterInvocationProviderManager invocationProviderManager = new AfterInvocationProviderManager(); 212 ExpressionBasedPostInvocationAdvice postAdvice = new ExpressionBasedPostInvocationAdvice( 213 getExpressionHandler()); 214 PostInvocationAdviceProvider postInvocationAdviceProvider = new PostInvocationAdviceProvider( 215 postAdvice); 216 List<AfterInvocationProvider> afterInvocationProviders = new ArrayList<>(); 217 afterInvocationProviders.add(postInvocationAdviceProvider); 218 invocationProviderManager.setProviders(afterInvocationProviders); 219 return invocationProviderManager; 220 } 221 return null; 222 } 223 224 /** 225 * Provide a custom {@link RunAsManager} for the default implementation of 226 * {@link #methodSecurityInterceptor()}. The default is null. 227 * 228 * @return 229 */ 230 protected RunAsManager runAsManager() { 231 return null; 232 } 233 234 /** 235 * Allows subclasses to provide a custom {@link AccessDecisionManager}. The default is 236 * a {@link AffirmativeBased} with the following voters: 237 * 238 * <ul> 239 * <li>{@link PreInvocationAuthorizationAdviceVoter}</li> 240 * <li>{@link RoleVoter}</li> 241 * <li>{@link AuthenticatedVoter}</li> 242 * </ul> 243 * 244 * @return 245 */ 246 protected AccessDecisionManager accessDecisionManager() { 247 List<AccessDecisionVoter<? extends Object>> decisionVoters = new ArrayList<AccessDecisionVoter<? extends Object>>(); 248 ExpressionBasedPreInvocationAdvice expressionAdvice = new ExpressionBasedPreInvocationAdvice(); 249 expressionAdvice.setExpressionHandler(getExpressionHandler()); 250 if (prePostEnabled()) { 251 decisionVoters 252 .add(new PreInvocationAuthorizationAdviceVoter(expressionAdvice)); 253 } 254 if (jsr250Enabled()) { 255 decisionVoters.add(new Jsr250Voter()); 256 } 257 decisionVoters.add(new RoleVoter()); 258 decisionVoters.add(new AuthenticatedVoter()); 259 return new AffirmativeBased(decisionVoters); 260 } 261 262 /** 263 * Provide a {@link MethodSecurityExpressionHandler} that is registered with the 264 * {@link ExpressionBasedPreInvocationAdvice}. The default is 265 * {@link DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler} which optionally will Autowire an 266 * {@link AuthenticationTrustResolver}. 267 * 268 * <p> 269 * Subclasses may override this method to provide a custom 270 * {@link MethodSecurityExpressionHandler} 271 * </p> 272 * 273 * @return 274 */ 275 protected MethodSecurityExpressionHandler createExpressionHandler() { 276 return defaultMethodExpressionHandler; 277 } 278 279 /** 280 * Gets the {@link MethodSecurityExpressionHandler} or creates it using 281 * {@link #expressionHandler}. 282 * 283 * @return a non {@code null} {@link MethodSecurityExpressionHandler} 284 */ 285 protected final MethodSecurityExpressionHandler getExpressionHandler() { 286 if (expressionHandler == null) { 287 expressionHandler = createExpressionHandler(); 288 } 289 return expressionHandler; 290 } 291 292 /** 293 * Provides a custom {@link MethodSecurityMetadataSource} that is registered with the 294 * {@link #methodSecurityMetadataSource()}. Default is null. 295 * 296 * @return a custom {@link MethodSecurityMetadataSource} that is registered with the 297 * {@link #methodSecurityMetadataSource()} 298 */ 299 protected MethodSecurityMetadataSource customMethodSecurityMetadataSource() { 300 return null; 301 } 302 303 /** 304 * Allows providing a custom {@link AuthenticationManager}. The default is to use any 305 * authentication mechanisms registered by 306 * {@link #configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder)}. If 307 * {@link #configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder)} was not overridden, then an 308 * {@link AuthenticationManager} is attempted to be autowired by type. 309 * 310 * @return 311 */ 312 protected AuthenticationManager authenticationManager() throws Exception { 313 if (authenticationManager == null) { 314 DefaultAuthenticationEventPublisher eventPublisher = objectPostProcessor 315 .postProcess(new DefaultAuthenticationEventPublisher()); 316 auth = new AuthenticationManagerBuilder(objectPostProcessor); 317 auth.authenticationEventPublisher(eventPublisher); 318 configure(auth); 319 if (disableAuthenticationRegistry) { 320 authenticationManager = getAuthenticationConfiguration() 321 .getAuthenticationManager(); 322 } 323 else { 324 authenticationManager = auth.build(); 325 } 326 } 327 return authenticationManager; 328 } 329 330 /** 331 * Sub classes can override this method to register different types of authentication. 332 * If not overridden, {@link #configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder)} will attempt to 333 * autowire by type. 334 * 335 * @param auth the {@link AuthenticationManagerBuilder} used to register different 336 * authentication mechanisms for the global method security. 337 * @throws Exception 338 */ 339 protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { 340 this.disableAuthenticationRegistry = true; 341 } 342 343 /** 344 * Provides the default {@link MethodSecurityMetadataSource} that will be used. It 345 * creates a {@link DelegatingMethodSecurityMetadataSource} based upon 346 * {@link #customMethodSecurityMetadataSource()} and the attributes on 347 * {@link EnableGlobalMethodSecurity}. 348 * 349 * @return 350 */ 351 @Bean 352 public MethodSecurityMetadataSource methodSecurityMetadataSource() { 353 List<MethodSecurityMetadataSource> sources = new ArrayList<>(); 354 ExpressionBasedAnnotationAttributeFactory attributeFactory = new ExpressionBasedAnnotationAttributeFactory( 355 getExpressionHandler()); 356 MethodSecurityMetadataSource customMethodSecurityMetadataSource = customMethodSecurityMetadataSource(); 357 if (customMethodSecurityMetadataSource != null) { 358 sources.add(customMethodSecurityMetadataSource); 359 } 360 if (prePostEnabled()) { 361 sources.add(new PrePostAnnotationSecurityMetadataSource(attributeFactory)); 362 } 363 if (securedEnabled()) { 364 sources.add(new SecuredAnnotationSecurityMetadataSource()); 365 } 366 if (jsr250Enabled()) { 367 GrantedAuthorityDefaults grantedAuthorityDefaults = 368 getSingleBeanOrNull(GrantedAuthorityDefaults.class); 369 if (grantedAuthorityDefaults != null) { 370 this.jsr250MethodSecurityMetadataSource.setDefaultRolePrefix( 371 grantedAuthorityDefaults.getRolePrefix()); 372 } 373 sources.add(jsr250MethodSecurityMetadataSource); 374 } 375 return new DelegatingMethodSecurityMetadataSource(sources); 376 } 377 378 /** 379 * Creates the {@link PreInvocationAuthorizationAdvice} to be used. The default is 380 * {@link ExpressionBasedPreInvocationAdvice}. 381 * 382 * @return 383 */ 384 @Bean 385 public PreInvocationAuthorizationAdvice preInvocationAuthorizationAdvice() { 386 ExpressionBasedPreInvocationAdvice preInvocationAdvice = new ExpressionBasedPreInvocationAdvice(); 387 preInvocationAdvice.setExpressionHandler(getExpressionHandler()); 388 return preInvocationAdvice; 389 } 390 391 /** 392 * Obtains the attributes from {@link EnableGlobalMethodSecurity} if this class was 393 * imported using the {@link EnableGlobalMethodSecurity} annotation. 394 */ 395 public final void setImportMetadata(AnnotationMetadata importMetadata) { 396 Map<String, Object> annotationAttributes = importMetadata 397 .getAnnotationAttributes(EnableGlobalMethodSecurity.class.getName()); 398 enableMethodSecurity = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(annotationAttributes); 399 } 400 401 @Autowired(required = false) 402 public void setObjectPostProcessor(ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor) { 403 this.objectPostProcessor = objectPostProcessor; 404 this.defaultMethodExpressionHandler = objectPostProcessor 405 .postProcess(defaultMethodExpressionHandler); 406 } 407 408 @Autowired(required = false) 409 public void setJsr250MethodSecurityMetadataSource( 410 Jsr250MethodSecurityMetadataSource jsr250MethodSecurityMetadataSource) { 411 this.jsr250MethodSecurityMetadataSource = jsr250MethodSecurityMetadataSource; 412 } 413 414 @Autowired(required = false) 415 public void setMethodSecurityExpressionHandler( 416 List<MethodSecurityExpressionHandler> handlers) { 417 if (handlers.size() != 1) { 418 logger.debug("Not autowiring MethodSecurityExpressionHandler since size != 1. Got " 419 + handlers); 420 return; 421 } 422 this.expressionHandler = handlers.get(0); 423 } 424 425 @Autowired 426 public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) { 427 this.context = context; 428 } 429 430 private AuthenticationConfiguration getAuthenticationConfiguration() { 431 return context.getBean(AuthenticationConfiguration.class); 432 } 433 434 private boolean prePostEnabled() { 435 return enableMethodSecurity().getBoolean("prePostEnabled"); 436 } 437 438 private boolean securedEnabled() { 439 return enableMethodSecurity().getBoolean("securedEnabled"); 440 } 441 442 private boolean jsr250Enabled() { 443 return enableMethodSecurity().getBoolean("jsr250Enabled"); 444 } 445 446 private int order() { 447 return (Integer) enableMethodSecurity().get("order"); 448 } 449 450 private boolean isAspectJ() { 451 return enableMethodSecurity().getEnum("mode") == AdviceMode.ASPECTJ; 452 } 453 454 private AnnotationAttributes enableMethodSecurity() { 455 if (enableMethodSecurity == null) { 456 // if it is null look at this instance (i.e. a subclass was used) 457 EnableGlobalMethodSecurity methodSecurityAnnotation = AnnotationUtils 458 .findAnnotation(getClass(), EnableGlobalMethodSecurity.class); 459 Assert.notNull(methodSecurityAnnotation, 460 EnableGlobalMethodSecurity.class.getName() + " is required"); 461 Map<String, Object> methodSecurityAttrs = AnnotationUtils 462 .getAnnotationAttributes(methodSecurityAnnotation); 463 this.enableMethodSecurity = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(methodSecurityAttrs); 464 } 465 return this.enableMethodSecurity; 466 } 467 }
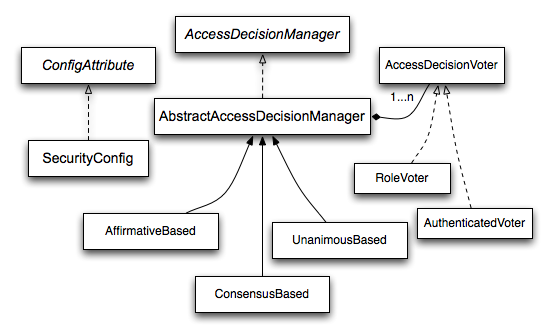
3.3.1 Pre-Invocation Handling
Spring Security provides interceptors which control access to secure objects such as method invocations or web requests. A pre-invocation decision on whether the invocation is allowed to proceed is made by the AccessDecisionManager.
即在目标handler方法被调用前的处理,如校验当前用户角色是否有权访问目标handler方法。
相关代码类及依次的调用关系:
AbstractSecurityInterceptor#beforeInvocation,源码:

1 /* 2 * Copyright 2004, 2005, 2006 Acegi Technology Pty Limited 3 * 4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at 7 * 8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 9 * 10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 14 * limitations under the License. 15 */ 16 17 package org.springframework.security.access.intercept; 18 19 import java.util.Collection; 20 import java.util.HashSet; 21 import java.util.Set; 22 23 import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; 24 import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; 25 import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; 26 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; 27 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher; 28 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware; 29 import org.springframework.context.MessageSource; 30 import org.springframework.context.MessageSourceAware; 31 import org.springframework.context.support.MessageSourceAccessor; 32 import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDecisionManager; 33 import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException; 34 import org.springframework.security.access.ConfigAttribute; 35 import org.springframework.security.access.SecurityMetadataSource; 36 import org.springframework.security.access.event.AuthenticationCredentialsNotFoundEvent; 37 import org.springframework.security.access.event.AuthorizationFailureEvent; 38 import org.springframework.security.access.event.AuthorizedEvent; 39 import org.springframework.security.access.event.PublicInvocationEvent; 40 import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationCredentialsNotFoundException; 41 import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager; 42 import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationServiceException; 43 import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication; 44 import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException; 45 import org.springframework.security.core.SpringSecurityMessageSource; 46 import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext; 47 import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder; 48 import org.springframework.util.Assert; 49 50 /** 51 * Abstract class that implements security interception for secure objects. 52 * <p> 53 * The <code>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</code> will ensure the proper startup 54 * configuration of the security interceptor. It will also implement the proper handling 55 * of secure object invocations, namely: 56 * <ol> 57 * <li>Obtain the {@link Authentication} object from the {@link SecurityContextHolder}.</li> 58 * <li>Determine if the request relates to a secured or public invocation by looking up 59 * the secure object request against the {@link SecurityMetadataSource}.</li> 60 * <li>For an invocation that is secured (there is a list of <code>ConfigAttribute</code>s 61 * for the secure object invocation): 62 * <ol type="a"> 63 * <li>If either the 64 * {@link org.springframework.security.core.Authentication#isAuthenticated()} returns 65 * <code>false</code>, or the {@link #alwaysReauthenticate} is <code>true</code>, 66 * authenticate the request against the configured {@link AuthenticationManager}. When 67 * authenticated, replace the <code>Authentication</code> object on the 68 * <code>SecurityContextHolder</code> with the returned value.</li> 69 * <li>Authorize the request against the configured {@link AccessDecisionManager}.</li> 70 * <li>Perform any run-as replacement via the configured {@link RunAsManager}.</li> 71 * <li>Pass control back to the concrete subclass, which will actually proceed with 72 * executing the object. A {@link InterceptorStatusToken} is returned so that after the 73 * subclass has finished proceeding with execution of the object, its finally clause can 74 * ensure the <code>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</code> is re-called and tidies up 75 * correctly using {@link #finallyInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken)}.</li> 76 * <li>The concrete subclass will re-call the <code>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</code> via 77 * the {@link #afterInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken, Object)} method.</li> 78 * <li>If the <code>RunAsManager</code> replaced the <code>Authentication</code> object, 79 * return the <code>SecurityContextHolder</code> to the object that existed after the call 80 * to <code>AuthenticationManager</code>.</li> 81 * <li>If an <code>AfterInvocationManager</code> is defined, invoke the invocation manager 82 * and allow it to replace the object due to be returned to the caller.</li> 83 * </ol> 84 * </li> 85 * <li>For an invocation that is public (there are no <code>ConfigAttribute</code>s for 86 * the secure object invocation): 87 * <ol type="a"> 88 * <li>As described above, the concrete subclass will be returned an 89 * <code>InterceptorStatusToken</code> which is subsequently re-presented to the 90 * <code>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</code> after the secure object has been executed. The 91 * <code>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</code> will take no further action when its 92 * {@link #afterInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken, Object)} is called.</li> 93 * </ol> 94 * </li> 95 * <li>Control again returns to the concrete subclass, along with the <code>Object</code> 96 * that should be returned to the caller. The subclass will then return that result or 97 * exception to the original caller.</li> 98 * </ol> 99 * 100 * @author Ben Alex 101 * @author Rob Winch 102 */ 103 public abstract class AbstractSecurityInterceptor implements InitializingBean, 104 ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware { 105 // ~ Static fields/initializers 106 // ===================================================================================== 107 108 protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); 109 110 // ~ Instance fields 111 // ================================================================================================ 112 113 protected MessageSourceAccessor messages = SpringSecurityMessageSource.getAccessor(); 114 private ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher; 115 private AccessDecisionManager accessDecisionManager; 116 private AfterInvocationManager afterInvocationManager; 117 private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager = new NoOpAuthenticationManager(); 118 private RunAsManager runAsManager = new NullRunAsManager(); 119 120 private boolean alwaysReauthenticate = false; 121 private boolean rejectPublicInvocations = false; 122 private boolean validateConfigAttributes = true; 123 private boolean publishAuthorizationSuccess = false; 124 125 // ~ Methods 126 // ======================================================================================================== 127 128 public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { 129 Assert.notNull(getSecureObjectClass(), 130 "Subclass must provide a non-null response to getSecureObjectClass()"); 131 Assert.notNull(this.messages, "A message source must be set"); 132 Assert.notNull(this.authenticationManager, "An AuthenticationManager is required"); 133 Assert.notNull(this.accessDecisionManager, "An AccessDecisionManager is required"); 134 Assert.notNull(this.runAsManager, "A RunAsManager is required"); 135 Assert.notNull(this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource(), 136 "An SecurityMetadataSource is required"); 137 Assert.isTrue(this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource() 138 .supports(getSecureObjectClass()), 139 "SecurityMetadataSource does not support secure object class: " 140 + getSecureObjectClass()); 141 Assert.isTrue(this.runAsManager.supports(getSecureObjectClass()), 142 "RunAsManager does not support secure object class: " 143 + getSecureObjectClass()); 144 Assert.isTrue(this.accessDecisionManager.supports(getSecureObjectClass()), 145 "AccessDecisionManager does not support secure object class: " 146 + getSecureObjectClass()); 147 148 if (this.afterInvocationManager != null) { 149 Assert.isTrue(this.afterInvocationManager.supports(getSecureObjectClass()), 150 "AfterInvocationManager does not support secure object class: " 151 + getSecureObjectClass()); 152 } 153 154 if (this.validateConfigAttributes) { 155 Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributeDefs = this 156 .obtainSecurityMetadataSource().getAllConfigAttributes(); 157 158 if (attributeDefs == null) { 159 logger.warn("Could not validate configuration attributes as the SecurityMetadataSource did not return " 160 + "any attributes from getAllConfigAttributes()"); 161 return; 162 } 163 164 Set<ConfigAttribute> unsupportedAttrs = new HashSet<>(); 165 166 for (ConfigAttribute attr : attributeDefs) { 167 if (!this.runAsManager.supports(attr) 168 && !this.accessDecisionManager.supports(attr) 169 && ((this.afterInvocationManager == null) || !this.afterInvocationManager 170 .supports(attr))) { 171 unsupportedAttrs.add(attr); 172 } 173 } 174 175 if (unsupportedAttrs.size() != 0) { 176 throw new IllegalArgumentException( 177 "Unsupported configuration attributes: " + unsupportedAttrs); 178 } 179 180 logger.debug("Validated configuration attributes"); 181 } 182 } 183 184 protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) { 185 Assert.notNull(object, "Object was null"); 186 final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled(); 187 188 if (!getSecureObjectClass().isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) { 189 throw new IllegalArgumentException( 190 "Security invocation attempted for object " 191 + object.getClass().getName() 192 + " but AbstractSecurityInterceptor only configured to support secure objects of type: " 193 + getSecureObjectClass()); 194 } 195 196 Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource() 197 .getAttributes(object); 198 199 if (attributes == null || attributes.isEmpty()) { 200 if (rejectPublicInvocations) { 201 throw new IllegalArgumentException( 202 "Secure object invocation " 203 + object 204 + " was denied as public invocations are not allowed via this interceptor. " 205 + "This indicates a configuration error because the " 206 + "rejectPublicInvocations property is set to 'true'"); 207 } 208 209 if (debug) { 210 logger.debug("Public object - authentication not attempted"); 211 } 212 213 publishEvent(new PublicInvocationEvent(object)); 214 215 return null; // no further work post-invocation 216 } 217 218 if (debug) { 219 logger.debug("Secure object: " + object + "; Attributes: " + attributes); 220 } 221 222 if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) { 223 credentialsNotFound(messages.getMessage( 224 "AbstractSecurityInterceptor.authenticationNotFound", 225 "An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext"), 226 object, attributes); 227 } 228 229 Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired(); 230 231 // Attempt authorization 232 try { 233 this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes); 234 } 235 catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) { 236 publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated, 237 accessDeniedException)); 238 239 throw accessDeniedException; 240 } 241 242 if (debug) { 243 logger.debug("Authorization successful"); 244 } 245 246 if (publishAuthorizationSuccess) { 247 publishEvent(new AuthorizedEvent(object, attributes, authenticated)); 248 } 249 250 // Attempt to run as a different user 251 Authentication runAs = this.runAsManager.buildRunAs(authenticated, object, 252 attributes); 253 254 if (runAs == null) { 255 if (debug) { 256 logger.debug("RunAsManager did not change Authentication object"); 257 } 258 259 // no further work post-invocation 260 return new InterceptorStatusToken(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(), false, 261 attributes, object); 262 } 263 else { 264 if (debug) { 265 logger.debug("Switching to RunAs Authentication: " + runAs); 266 } 267 268 SecurityContext origCtx = SecurityContextHolder.getContext(); 269 SecurityContextHolder.setContext(SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext()); 270 SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(runAs); 271 272 // need to revert to token.Authenticated post-invocation 273 return new InterceptorStatusToken(origCtx, true, attributes, object); 274 } 275 } 276 277 /** 278 * Cleans up the work of the <tt>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</tt> after the secure 279 * object invocation has been completed. This method should be invoked after the 280 * secure object invocation and before afterInvocation regardless of the secure object 281 * invocation returning successfully (i.e. it should be done in a finally block). 282 * 283 * @param token as returned by the {@link #beforeInvocation(Object)} method 284 */ 285 protected void finallyInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken token) { 286 if (token != null && token.isContextHolderRefreshRequired()) { 287 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 288 logger.debug("Reverting to original Authentication: " 289 + token.getSecurityContext().getAuthentication()); 290 } 291 292 SecurityContextHolder.setContext(token.getSecurityContext()); 293 } 294 } 295 296 /** 297 * Completes the work of the <tt>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</tt> after the secure 298 * object invocation has been completed. 299 * 300 * @param token as returned by the {@link #beforeInvocation(Object)} method 301 * @param returnedObject any object returned from the secure object invocation (may be 302 * <tt>null</tt>) 303 * @return the object the secure object invocation should ultimately return to its 304 * caller (may be <tt>null</tt>) 305 */ 306 protected Object afterInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken token, Object returnedObject) { 307 if (token == null) { 308 // public object 309 return returnedObject; 310 } 311 312 finallyInvocation(token); // continue to clean in this method for passivity 313 314 if (afterInvocationManager != null) { 315 // Attempt after invocation handling 316 try { 317 returnedObject = afterInvocationManager.decide(token.getSecurityContext() 318 .getAuthentication(), token.getSecureObject(), token 319 .getAttributes(), returnedObject); 320 } 321 catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) { 322 AuthorizationFailureEvent event = new AuthorizationFailureEvent( 323 token.getSecureObject(), token.getAttributes(), token 324 .getSecurityContext().getAuthentication(), 325 accessDeniedException); 326 publishEvent(event); 327 328 throw accessDeniedException; 329 } 330 } 331 332 return returnedObject; 333 } 334 335 /** 336 * Checks the current authentication token and passes it to the AuthenticationManager 337 * if {@link org.springframework.security.core.Authentication#isAuthenticated()} 338 * returns false or the property <tt>alwaysReauthenticate</tt> has been set to true. 339 * 340 * @return an authenticated <tt>Authentication</tt> object. 341 */ 342 private Authentication authenticateIfRequired() { 343 Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext() 344 .getAuthentication(); 345 346 if (authentication.isAuthenticated() && !alwaysReauthenticate) { 347 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 348 logger.debug("Previously Authenticated: " + authentication); 349 } 350 351 return authentication; 352 } 353 354 authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(authentication); 355 356 // We don't authenticated.setAuthentication(true), because each provider should do 357 // that 358 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 359 logger.debug("Successfully Authenticated: " + authentication); 360 } 361 362 SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication); 363 364 return authentication; 365 } 366 367 /** 368 * Helper method which generates an exception containing the passed reason, and 369 * publishes an event to the application context. 370 * <p> 371 * Always throws an exception. 372 * 373 * @param reason to be provided in the exception detail 374 * @param secureObject that was being called 375 * @param configAttribs that were defined for the secureObject 376 */ 377 private void credentialsNotFound(String reason, Object secureObject, 378 Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttribs) { 379 AuthenticationCredentialsNotFoundException exception = new AuthenticationCredentialsNotFoundException( 380 reason); 381 382 AuthenticationCredentialsNotFoundEvent event = new AuthenticationCredentialsNotFoundEvent( 383 secureObject, configAttribs, exception); 384 publishEvent(event); 385 386 throw exception; 387 } 388 389 public AccessDecisionManager getAccessDecisionManager() { 390 return accessDecisionManager; 391 } 392 393 public AfterInvocationManager getAfterInvocationManager() { 394 return afterInvocationManager; 395 } 396 397 public AuthenticationManager getAuthenticationManager() { 398 return this.authenticationManager; 399 } 400 401 public RunAsManager getRunAsManager() { 402 return runAsManager; 403 } 404 405 /** 406 * Indicates the type of secure objects the subclass will be presenting to the 407 * abstract parent for processing. This is used to ensure collaborators wired to the 408 * {@code AbstractSecurityInterceptor} all support the indicated secure object class. 409 * 410 * @return the type of secure object the subclass provides services for 411 */ 412 public abstract Class<?> getSecureObjectClass(); 413 414 public boolean isAlwaysReauthenticate() { 415 return alwaysReauthenticate; 416 } 417 418 public boolean isRejectPublicInvocations() { 419 return rejectPublicInvocations; 420 } 421 422 public boolean isValidateConfigAttributes() { 423 return validateConfigAttributes; 424 } 425 426 public abstract SecurityMetadataSource obtainSecurityMetadataSource(); 427 428 public void setAccessDecisionManager(AccessDecisionManager accessDecisionManager) { 429 this.accessDecisionManager = accessDecisionManager; 430 } 431 432 public void setAfterInvocationManager(AfterInvocationManager afterInvocationManager) { 433 this.afterInvocationManager = afterInvocationManager; 434 } 435 436 /** 437 * Indicates whether the <code>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</code> should ignore the 438 * {@link Authentication#isAuthenticated()} property. Defaults to <code>false</code>, 439 * meaning by default the <code>Authentication.isAuthenticated()</code> property is 440 * trusted and re-authentication will not occur if the principal has already been 441 * authenticated. 442 * 443 * @param alwaysReauthenticate <code>true</code> to force 444 * <code>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</code> to disregard the value of 445 * <code>Authentication.isAuthenticated()</code> and always re-authenticate the 446 * request (defaults to <code>false</code>). 447 */ 448 public void setAlwaysReauthenticate(boolean alwaysReauthenticate) { 449 this.alwaysReauthenticate = alwaysReauthenticate; 450 } 451 452 public void setApplicationEventPublisher( 453 ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) { 454 this.eventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher; 455 } 456 457 public void setAuthenticationManager(AuthenticationManager newManager) { 458 this.authenticationManager = newManager; 459 } 460 461 public void setMessageSource(MessageSource messageSource) { 462 this.messages = new MessageSourceAccessor(messageSource); 463 } 464 465 /** 466 * Only {@code AuthorizationFailureEvent} will be published. If you set this property 467 * to {@code true}, {@code AuthorizedEvent}s will also be published. 468 * 469 * @param publishAuthorizationSuccess default value is {@code false} 470 */ 471 public void setPublishAuthorizationSuccess(boolean publishAuthorizationSuccess) { 472 this.publishAuthorizationSuccess = publishAuthorizationSuccess; 473 } 474 475 /** 476 * By rejecting public invocations (and setting this property to <tt>true</tt>), 477 * essentially you are ensuring that every secure object invocation advised by 478 * <code>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</code> has a configuration attribute defined. 479 * This is useful to ensure a "fail safe" mode where undeclared secure objects will be 480 * rejected and configuration omissions detected early. An 481 * <tt>IllegalArgumentException</tt> will be thrown by the 482 * <tt>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</tt> if you set this property to <tt>true</tt> and 483 * an attempt is made to invoke a secure object that has no configuration attributes. 484 * 485 * @param rejectPublicInvocations set to <code>true</code> to reject invocations of 486 * secure objects that have no configuration attributes (by default it is 487 * <code>false</code> which treats undeclared secure objects as "public" or 488 * unauthorized). 489 */ 490 public void setRejectPublicInvocations(boolean rejectPublicInvocations) { 491 this.rejectPublicInvocations = rejectPublicInvocations; 492 } 493 494 public void setRunAsManager(RunAsManager runAsManager) { 495 this.runAsManager = runAsManager; 496 } 497 498 public void setValidateConfigAttributes(boolean validateConfigAttributes) { 499 this.validateConfigAttributes = validateConfigAttributes; 500 } 501 502 private void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { 503 if (this.eventPublisher != null) { 504 this.eventPublisher.publishEvent(event); 505 } 506 } 507 508 private static class NoOpAuthenticationManager implements AuthenticationManager { 509 510 public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) 511 throws AuthenticationException { 512 throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Cannot authenticate " 513 + authentication); 514 } 515 } 516 }
默认有两种实现:MethodSecurityInterceptor、AspectJSecurityInterceptor,前者用得最多,两者的区别:It would not be uncommon to use both types of security interceptors in the same application, with AspectJSecurityInterceptor being used for domain object instance security and the AOP Alliance MethodSecurityInterceptor being used for services layer security.
AccessDecisionManager#decide,类似于Authentication中的ProviderManager。decision有同意、拒绝、弃权三状态,该类的具体实现有:
AffirmativeBased(有1个同意则算同意),默认用这个
ConsensusBased(同意的比拒绝的多则算同意)
UnanimousBased(没有一个拒绝则算同意)
AccessDecisionVoter#vote,类似于Authentication中的AuthenticationProvider。具体实现主要有:
WebExpressionVoter
RoleVoter,实现如 RoleHierarchyVoter。Authorize时校验用户当前角色的用户是否有权访问接口时就是此Voter起作用的,若框架发现用户的authority值以"ROLE_"开头则会用此Voter,相关源码:

1 public class RoleVoter implements AccessDecisionVoter<Object> { 2 // ~ Instance fields 3 // ================================================================================================ 4 5 private String rolePrefix = "ROLE_"; 6 7 // ~ Methods 8 // ======================================================================================================== 9 10 public String getRolePrefix() { 11 return rolePrefix; 12 } 13 14 /** 15 * Allows the default role prefix of <code>ROLE_</code> to be overridden. May be set 16 * to an empty value, although this is usually not desirable. 17 * 18 * @param rolePrefix the new prefix 19 */ 20 public void setRolePrefix(String rolePrefix) { 21 this.rolePrefix = rolePrefix; 22 } 23 24 public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute) { 25 if ((attribute.getAttribute() != null) 26 && attribute.getAttribute().startsWith(getRolePrefix())) { 27 return true; 28 } 29 else { 30 return false; 31 } 32 } 33 34 /** 35 * This implementation supports any type of class, because it does not query the 36 * presented secure object. 37 * 38 * @param clazz the secure object 39 * 40 * @return always <code>true</code> 41 */ 42 public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) { 43 return true; 44 } 45 46 public int vote(Authentication authentication, Object object, 47 Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes) { 48 if(authentication == null) { 49 return ACCESS_DENIED; 50 } 51 int result = ACCESS_ABSTAIN; 52 Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = extractAuthorities(authentication); 53 54 for (ConfigAttribute attribute : attributes) { 55 if (this.supports(attribute)) { 56 result = ACCESS_DENIED; 57 58 // Attempt to find a matching granted authority 59 for (GrantedAuthority authority : authorities) { 60 if (attribute.getAttribute().equals(authority.getAuthority())) { 61 return ACCESS_GRANTED; 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 67 return result; 68 } 69 70 Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> extractAuthorities( 71 Authentication authentication) { 72 return authentication.getAuthorities(); 73 } 74 }
PreInvocationAuthorizationAdviceVoter、ExpressionBasedPreInvocationAdvice:handler方法上的 PreAuthorize("hasRole( "TEACHER" )") 就是由此完成自动校验的。这里所支持的SpringEL表达式见 org.springframwork.security. ore.authentication.SecurityExpressionOperations。将在后文Expression-Based Access Controller一节细说。
相关类及其间关系示意图:
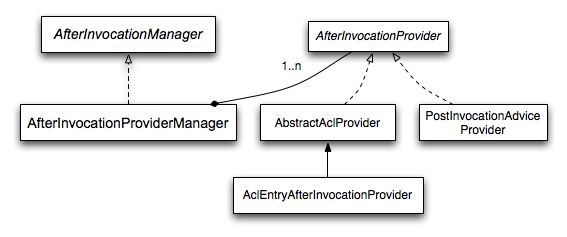
3.3.2 After-Invocation Handling
Whilst the AccessDecisionManager is called by the AbstractSecurityInterceptor before proceeding with the secure object invocation, some applications need a way of modifying the object actually returned by the secure object invocation. Whilst you could easily implement your own AOP concern to achieve this, Spring Security provides a convenient hook that has several concrete implementations that integrate with its ACL capabilities.
即在目标handler方法被调用后且返回给调用者前的处理,如对方法返回的数据进行过滤。
相关类及其间关系示意图:
3.3.3 Hierarchical Roles
允许定义多个角色间的优先级关系,这样高优先级的角色自动包含低优先级的角色。
如当定义了ADMIN 包含 STUDENT角色时,对于要求有"STUDENT"角色才能访问的接口,拥有"ADMIN"角色的用户也能访问。
定义示例可参阅 RoleHierarchyImpl 类,示例:

1 <bean id="roleVoter" class="org.springframework.security.access.vote.RoleHierarchyVoter"> 2 <constructor-arg ref="roleHierarchy" /> 3 </bean> 4 <bean id="roleHierarchy" 5 class="org.springframework.security.access.hierarchicalroles.RoleHierarchyImpl"> 6 <property name="hierarchy"> 7 <value> 8 ROLE_ADMIN > ROLE_STAFF 9 ROLE_STAFF > ROLE_USER 10 ROLE_USER > ROLE_GUEST 11 </value> 12 </property> 13 </bean>
3.3.4 Expression-Based Access Control
(参阅:https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.3.4.RELEASE/reference/html5/#el-access)
Spring Security 3.0 introduced the ability to use Spring EL expressions as an authorization mechanism in addition to the simple use of configuration attributes and access-decision voters which have seen before. Expression-based access control is built on the same architecture but allows complicated Boolean logic to be encapsulated in a single expression.
即提供了诸如 @PreAuthorize(" hasRole('ADMIN') ") 这种authorization方式,注解中的参数支持Spring EL表达式,默认提供的表达式(包括 hasRole、hasAuthority、hasPermission等)定义见SecurityExpressionOperations接口。
相关接口或类:
interface SecurityExpressionOperations:定义支持的操作,这些操作作为Spring EL表达式。定义见源码:

1 /* 2 * Copyright 2002-2016 the original author or authors. 3 * 4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at 7 * 8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 9 * 10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 14 * limitations under the License. 15 */ 16 package org.springframework.security.access.expression; 17 18 import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication; 19 20 /** 21 * Standard interface for expression root objects used with expression-based security. 22 * 23 * @author Andrei Stefan 24 * @author Luke Taylor 25 * @since 3.1.1 26 */ 27 public interface SecurityExpressionOperations { 28 29 /** 30 * Gets the {@link Authentication} used for evaluating the expressions 31 * @return the {@link Authentication} for evaluating the expressions 32 */ 33 Authentication getAuthentication(); 34 35 /** 36 * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has a particular authority within 37 * {@link Authentication#getAuthorities()}. 38 * @param authority the authority to test (i.e. "ROLE_USER") 39 * @return true if the authority is found, else false 40 */ 41 boolean hasAuthority(String authority); 42 43 /** 44 * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has any of the specified authorities 45 * within {@link Authentication#getAuthorities()}. 46 * @param authorities the authorities to test (i.e. "ROLE_USER", "ROLE_ADMIN") 47 * @return true if any of the authorities is found, else false 48 */ 49 boolean hasAnyAuthority(String... authorities); 50 51 /** 52 * <p> 53 * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has a particular authority within 54 * {@link Authentication#getAuthorities()}. 55 * </p> 56 * <p> 57 * This is similar to {@link #hasAuthority(String)} except that this method implies 58 * that the String passed in is a role. For example, if "USER" is passed in the 59 * implementation may convert it to use "ROLE_USER" instead. The way in which the role 60 * is converted may depend on the implementation settings. 61 * </p> 62 * 63 * @param role the authority to test (i.e. "USER") 64 * @return true if the authority is found, else false 65 */ 66 boolean hasRole(String role); 67 68 /** 69 * <p> 70 * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has any of the specified authorities 71 * within {@link Authentication#getAuthorities()}. 72 * </p> 73 * <p> 74 * This is a similar to hasAnyAuthority except that this method implies 75 * that the String passed in is a role. For example, if "USER" is passed in the 76 * implementation may convert it to use "ROLE_USER" instead. The way in which the role 77 * is converted may depend on the implementation settings. 78 * </p> 79 * 80 * @param roles the authorities to test (i.e. "USER", "ADMIN") 81 * @return true if any of the authorities is found, else false 82 */ 83 boolean hasAnyRole(String... roles); 84 85 /** 86 * Always grants access. 87 * @return true 88 */ 89 boolean permitAll(); 90 91 /** 92 * Always denies access 93 * @return false 94 */ 95 boolean denyAll(); 96 97 /** 98 * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} is anonymous 99 * @return true if the user is anonymous, else false 100 */ 101 boolean isAnonymous(); 102 103 /** 104 * Determines ifthe {@link #getAuthentication()} is authenticated 105 * @return true if the {@link #getAuthentication()} is authenticated, else false 106 */ 107 boolean isAuthenticated(); 108 109 /** 110 * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} was authenticated using remember me 111 * @return true if the {@link #getAuthentication()} authenticated using remember me, 112 * else false 113 */ 114 boolean isRememberMe(); 115 116 /** 117 * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} authenticated without the use of 118 * remember me 119 * @return true if the {@link #getAuthentication()} authenticated without the use of 120 * remember me, else false 121 */ 122 boolean isFullyAuthenticated(); 123 124 /** 125 * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has permission to access the target 126 * given the permission 127 * @param target the target domain object to check permission on 128 * @param permission the permission to check on the domain object (i.e. "read", 129 * "write", etc). 130 * @return true if permission is granted to the {@link #getAuthentication()}, else 131 * false 132 */ 133 boolean hasPermission(Object target, Object permission); 134 135 /** 136 * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has permission to access the domain 137 * object with a given id, type, and permission. 138 * @param targetId the identifier of the domain object to determine access 139 * @param targetType the type (i.e. com.example.domain.Message) 140 * @param permission the perission to check on the domain object (i.e. "read", 141 * "write", etc) 142 * @return true if permission is granted to the {@link #getAuthentication()}, else 143 * false 144 */ 145 boolean hasPermission(Object targetId, String targetType, Object permission); 146 147 }
其中,hasPermission的实现中用到了PermissionEvaluator,后者需要用户自己实现,通常是与ACL结合。
abstract class SecurityExpressionRoot:上述 hasRole、hasAuthority等若干 expression 方法的具体实现者。开头中@PreAuthorize中的表达式最终解析为这里面的实现来判断是否成功。源码:

1 /* 2 * Copyright 2002-2016 the original author or authors. 3 * 4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at 7 * 8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 9 * 10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 14 * limitations under the License. 15 */ 16 package org.springframework.security.access.expression; 17 18 import java.io.Serializable; 19 import java.util.Collection; 20 import java.util.HashSet; 21 import java.util.Set; 22 23 import org.springframework.security.access.PermissionEvaluator; 24 import org.springframework.security.access.hierarchicalroles.RoleHierarchy; 25 import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationTrustResolver; 26 import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication; 27 import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority; 28 import org.springframework.security.core.authority.AuthorityUtils; 29 30 /** 31 * Base root object for use in Spring Security expression evaluations. 32 * 33 * @author Luke Taylor 34 * @since 3.0 35 */ 36 public abstract class SecurityExpressionRoot implements SecurityExpressionOperations { 37 protected final Authentication authentication; 38 private AuthenticationTrustResolver trustResolver; 39 private RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy; 40 private Set<String> roles; 41 private String defaultRolePrefix = "ROLE_"; 42 43 /** Allows "permitAll" expression */ 44 public final boolean permitAll = true; 45 46 /** Allows "denyAll" expression */ 47 public final boolean denyAll = false; 48 private PermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator; 49 public final String read = "read"; 50 public final String write = "write"; 51 public final String create = "create"; 52 public final String delete = "delete"; 53 public final String admin = "administration"; 54 55 /** 56 * Creates a new instance 57 * @param authentication the {@link Authentication} to use. Cannot be null. 58 */ 59 public SecurityExpressionRoot(Authentication authentication) { 60 if (authentication == null) { 61 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Authentication object cannot be null"); 62 } 63 this.authentication = authentication; 64 } 65 66 public final boolean hasAuthority(String authority) { 67 return hasAnyAuthority(authority); 68 } 69 70 public final boolean hasAnyAuthority(String... authorities) { 71 return hasAnyAuthorityName(null, authorities); 72 } 73 74 public final boolean hasRole(String role) { 75 return hasAnyRole(role); 76 } 77 78 public final boolean hasAnyRole(String... roles) { 79 return hasAnyAuthorityName(defaultRolePrefix, roles); 80 } 81 82 private boolean hasAnyAuthorityName(String prefix, String... roles) { 83 Set<String> roleSet = getAuthoritySet(); 84 85 for (String role : roles) { 86 String defaultedRole = getRoleWithDefaultPrefix(prefix, role); 87 if (roleSet.contains(defaultedRole)) { 88 return true; 89 } 90 } 91 92 return false; 93 } 94 95 public final Authentication getAuthentication() { 96 return authentication; 97 } 98 99 public final boolean permitAll() { 100 return true; 101 } 102 103 public final boolean denyAll() { 104 return false; 105 } 106 107 public final boolean isAnonymous() { 108 return trustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication); 109 } 110 111 public final boolean isAuthenticated() { 112 return !isAnonymous(); 113 } 114 115 public final boolean isRememberMe() { 116 return trustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication); 117 } 118 119 public final boolean isFullyAuthenticated() { 120 return !trustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) 121 && !trustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication); 122 } 123 124 /** 125 * Convenience method to access {@link Authentication#getPrincipal()} from 126 * {@link #getAuthentication()} 127 * @return 128 */ 129 public Object getPrincipal() { 130 return authentication.getPrincipal(); 131 } 132 133 public void setTrustResolver(AuthenticationTrustResolver trustResolver) { 134 this.trustResolver = trustResolver; 135 } 136 137 public void setRoleHierarchy(RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy) { 138 this.roleHierarchy = roleHierarchy; 139 } 140 141 /** 142 * <p> 143 * Sets the default prefix to be added to {@link #hasAnyRole(String...)} or 144 * {@link #hasRole(String)}. For example, if hasRole("ADMIN") or hasRole("ROLE_ADMIN") 145 * is passed in, then the role ROLE_ADMIN will be used when the defaultRolePrefix is 146 * "ROLE_" (default). 147 * </p> 148 * 149 * <p> 150 * If null or empty, then no default role prefix is used. 151 * </p> 152 * 153 * @param defaultRolePrefix the default prefix to add to roles. Default "ROLE_". 154 */ 155 public void setDefaultRolePrefix(String defaultRolePrefix) { 156 this.defaultRolePrefix = defaultRolePrefix; 157 } 158 159 private Set<String> getAuthoritySet() { 160 if (roles == null) { 161 roles = new HashSet<>(); 162 Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> userAuthorities = authentication 163 .getAuthorities(); 164 165 if (roleHierarchy != null) { 166 userAuthorities = roleHierarchy 167 .getReachableGrantedAuthorities(userAuthorities); 168 } 169 170 roles = AuthorityUtils.authorityListToSet(userAuthorities); 171 } 172 173 return roles; 174 } 175 176 public boolean hasPermission(Object target, Object permission) { 177 return permissionEvaluator.hasPermission(authentication, target, permission); 178 } 179 180 public boolean hasPermission(Object targetId, String targetType, Object permission) { 181 return permissionEvaluator.hasPermission(authentication, (Serializable) targetId, 182 targetType, permission); 183 } 184 185 public void setPermissionEvaluator(PermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator) { 186 this.permissionEvaluator = permissionEvaluator; 187 } 188 189 /** 190 * Prefixes role with defaultRolePrefix if defaultRolePrefix is non-null and if role 191 * does not already start with defaultRolePrefix. 192 * 193 * @param defaultRolePrefix 194 * @param role 195 * @return 196 */ 197 private static String getRoleWithDefaultPrefix(String defaultRolePrefix, String role) { 198 if (role == null) { 199 return role; 200 } 201 if (defaultRolePrefix == null || defaultRolePrefix.length() == 0) { 202 return role; 203 } 204 if (role.startsWith(defaultRolePrefix)) { 205 return role; 206 } 207 return defaultRolePrefix + role; 208 } 209 }
如前文所述,Authorize包括 who (Authentication)、where (MethodInvocation) 、what (SomeDomainObject) 三方面的内容,其中前两种用得最多且通常第二种为主第一种为辅,第三种较少用到。
下面的内容与这三方面的内容对应。
Web Security Expression
用于提供基于Web Request(即URL)的访问权限控制。
Sets up the filters and related service beans used to apply the framework authentication mechanisms, to secure URLs, render login and error pages and much more.
在 WebSecurityExpressionRoot 中继承了SecurityExpressionRoot中的方法,还定义了 hasIpAddress 方法;可以在表达式中引用IoC容器中的Bean;可以引用PathVariable。示例:

1 @Component 2 public class WebSecurity { 3 public boolean check(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request) { 4 ... 5 } 6 public boolean checkUserId(Authentication authentication, int id) { 7 ... 8 } 9 } 10 11 12 13 http 14 .authorizeRequests(authorize -> authorize 15 .antMatchers("/user/{userId}/**").access("hasIpAddress('192.168.1.0/24') and @webSecurity.check(authentication,request) and @webSecurity.checkUserId(authentication,#userId)") 16 ... 17 );
此方案的缺点是基于URL配置的权限规则通常很容易被绕过,例如对"/admin" 的限制可通过"/admin/"绕过,虽然可通配符或穷举可能的情况加以限制但比较冗余或麻烦,因此通常不仅在URL级别有限制,还结合下文所述的方案在handler方法级别进一步进行访问约束。
Method Security Expression
Securing the service layer.
From version 2.0 onwards Spring Security has improved support substantially for adding security to your service layer methods. It provides support for JSR-250 annotation security as well as the framework’s original
@Securedannotation. From 3.0 you can also make use of new expression-based annotations. You can apply security to a single bean, using theintercept-methodselement to decorate the bean declaration, or you can secure multiple beans across the entire service layer using the AspectJ style pointcuts.
这是最常用的authorize方式,SpringSecurity 3.0开始支持此方案。
需要先启用global-method-security:在主类或任何@Configuration类上加@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) 。
1 上述配置指定启用pre、post注解功能,有四个相应注解:
@PreAuthorize, @PreFilter, @PostAuthorize and @PostFilter
使用示例:
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('USER')") public void create(Contact contact);
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#contact, 'admin')") public void deletePermission(Contact contact, Sid recipient, Permission permission);
@PreAuthorize("#contact.name == authentication.name") public void doSomething(Contact contact);
import org.springframework.security.access.method.P; @PreAuthorize("#c.name == authentication.name") public void doSomething(@P("c") Contact contact);
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('USER')") @PostFilter("hasPermission(filterObject, 'read') or hasPermission(filterObject, 'admin')") public List<Contact> getAll();
2 也可通过 securedEnabled =true 指定启用@Secured注解功能。pre、post注解中的 @PreAuthorize("isAnonymous()") 、 @PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_TELLER')") 在此功能下的等价写法为:
@Secured("IS_AUTHENTICATED_ANONYMOUSLY") 、 @Secured("ROLE_TELLER")
3 还可通过 jsr250Enabled = true 指定支持 JSR-250 注解,包括:@PostConstruct、@PermitAll等。
Domain Object Security(ACL)
参阅:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.3.4.RELEASE/reference/html5/#domain-acls
https://www.jianshu.com/p/b971b4e6ec16
3.4 Protection Against Exploits
参阅:https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.3.4.RELEASE/reference/html5/#servlet-exploits
防御的措施包括如下几部分。
CSRF Protection
Security HTTP Response Headers
包括:(详细用途见:https://www.cnblogs.com/z-sm/p/7581495.html)
X-Content-Type-Options
X-Frame-Options
X-XSS-Protection
Strict-Transport-Security
Content-Security-Policy
Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only
Referrer-Policy
Feature-Policy
Clear-Site-Data
HttpFirewall
当允许请求的URL中包含 // /../ /* 等之类的字符串时,服务端所设置的URL匹配规则可能会被绕过,进而可能被恶意攻击。
SpringSecurity考虑了此情况,默认情况下当检测到了这些请求时会立即拒绝当前的请求。
其实现方式是定义了Firewall接口用来对request、response进行包装,内部会对URL进行检查;在FilterChainProxy#doInternal方法中会利用此Firewall来获取reques、response。默认采用的Firewall为StrictHttpFirewall,相关源码:

1 /* 2 * Copyright 2012-2017 the original author or authors. 3 * 4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at 7 * 8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 9 * 10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 14 * limitations under the License. 15 */ 16 17 package org.springframework.security.web.firewall; 18 19 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 20 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; 21 import java.util.Arrays; 22 import java.util.Collection; 23 import java.util.Collections; 24 import java.util.HashSet; 25 import java.util.List; 26 import java.util.Set; 27 28 /** 29 * <p> 30 * A strict implementation of {@link HttpFirewall} that rejects any suspicious requests 31 * with a {@link RequestRejectedException}. 32 * </p> 33 * <p> 34 * The following rules are applied to the firewall: 35 * </p> 36 * <ul> 37 * <li> 38 * Rejects URLs that are not normalized to avoid bypassing security constraints. There is 39 * no way to disable this as it is considered extremely risky to disable this constraint. 40 * A few options to allow this behavior is to normalize the request prior to the firewall 41 * or using {@link DefaultHttpFirewall} instead. Please keep in mind that normalizing the 42 * request is fragile and why requests are rejected rather than normalized. 43 * </li> 44 * <li> 45 * Rejects URLs that contain characters that are not printable ASCII characters. There is 46 * no way to disable this as it is considered extremely risky to disable this constraint. 47 * </li> 48 * <li> 49 * Rejects URLs that contain semicolons. See {@link #setAllowSemicolon(boolean)} 50 * </li> 51 * <li> 52 * Rejects URLs that contain a URL encoded slash. See 53 * {@link #setAllowUrlEncodedSlash(boolean)} 54 * </li> 55 * <li> 56 * Rejects URLs that contain a backslash. See {@link #setAllowBackSlash(boolean)} 57 * </li> 58 * <li> 59 * Rejects URLs that contain a URL encoded percent. See 60 * {@link #setAllowUrlEncodedPercent(boolean)} 61 * </li> 62 * </ul> 63 * 64 * @see DefaultHttpFirewall 65 * @author Rob Winch 66 * @since 5.0.1 67 */ 68 public class StrictHttpFirewall implements HttpFirewall { 69 private static final String ENCODED_PERCENT = "%25"; 70 71 private static final String PERCENT = "%"; 72 73 private static final List<String> FORBIDDEN_ENCODED_PERIOD = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList("%2e", "%2E")); 74 75 private static final List<String> FORBIDDEN_SEMICOLON = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(";", "%3b", "%3B")); 76 77 private static final List<String> FORBIDDEN_FORWARDSLASH = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList("%2f", "%2F")); 78 79 private static final List<String> FORBIDDEN_BACKSLASH = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList("\\", "%5c", "%5C")); 80 81 private Set<String> encodedUrlBlacklist = new HashSet<String>(); 82 83 private Set<String> decodedUrlBlacklist = new HashSet<String>(); 84 85 public StrictHttpFirewall() { 86 urlBlacklistsAddAll(FORBIDDEN_SEMICOLON); 87 urlBlacklistsAddAll(FORBIDDEN_FORWARDSLASH); 88 urlBlacklistsAddAll(FORBIDDEN_BACKSLASH); 89 90 this.encodedUrlBlacklist.add(ENCODED_PERCENT); 91 this.encodedUrlBlacklist.addAll(FORBIDDEN_ENCODED_PERIOD); 92 this.decodedUrlBlacklist.add(PERCENT); 93 } 94 95 /** 96 * <p> 97 * Determines if semicolon is allowed in the URL (i.e. matrix variables). The default 98 * is to disable this behavior because it is a common way of attempting to perform 99 * <a href="https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Reflected_File_Download">Reflected File Download Attacks</a>. 100 * It is also the source of many exploits which bypass URL based security. 101 * </p> 102 * <p>For example, the following CVEs are a subset of the issues related 103 * to ambiguities in the Servlet Specification on how to treat semicolons that 104 * led to CVEs: 105 * </p> 106 * <ul> 107 * <li><a href="https://pivotal.io/security/cve-2016-5007">cve-2016-5007</a></li> 108 * <li><a href="https://pivotal.io/security/cve-2016-9879">cve-2016-9879</a></li> 109 * <li><a href="https://pivotal.io/security/cve-2018-1199">cve-2018-1199</a></li> 110 * </ul> 111 * 112 * <p> 113 * If you are wanting to allow semicolons, please reconsider as it is a very common 114 * source of security bypasses. A few common reasons users want semicolons and 115 * alternatives are listed below: 116 * </p> 117 * <ul> 118 * <li>Including the JSESSIONID in the path - You should not include session id (or 119 * any sensitive information) in a URL as it can lead to leaking. Instead use Cookies. 120 * </li> 121 * <li>Matrix Variables - Users wanting to leverage Matrix Variables should consider 122 * using HTTP parameters instead. 123 * </li> 124 * </ul> 125 * 126 * @param allowSemicolon should semicolons be allowed in the URL. Default is false 127 */ 128 public void setAllowSemicolon(boolean allowSemicolon) { 129 if (allowSemicolon) { 130 urlBlacklistsRemoveAll(FORBIDDEN_SEMICOLON); 131 } else { 132 urlBlacklistsAddAll(FORBIDDEN_SEMICOLON); 133 } 134 } 135 136 /** 137 * <p> 138 * Determines if a slash "/" that is URL encoded "%2F" should be allowed in the path 139 * or not. The default is to not allow this behavior because it is a common way to 140 * bypass URL based security. 141 * </p> 142 * <p> 143 * For example, due to ambiguities in the servlet specification, the value is not 144 * parsed consistently which results in different values in {@code HttpServletRequest} 145 * path related values which allow bypassing certain security constraints. 146 * </p> 147 * 148 * @param allowUrlEncodedSlash should a slash "/" that is URL encoded "%2F" be allowed 149 * in the path or not. Default is false. 150 */ 151 public void setAllowUrlEncodedSlash(boolean allowUrlEncodedSlash) { 152 if (allowUrlEncodedSlash) { 153 urlBlacklistsRemoveAll(FORBIDDEN_FORWARDSLASH); 154 } else { 155 urlBlacklistsAddAll(FORBIDDEN_FORWARDSLASH); 156 } 157 } 158 159 /** 160 * <p> 161 * Determines if a period "." that is URL encoded "%2E" should be allowed in the path 162 * or not. The default is to not allow this behavior because it is a frequent source 163 * of security exploits. 164 * </p> 165 * <p> 166 * For example, due to ambiguities in the servlet specification a URL encoded period 167 * might lead to bypassing security constraints through a directory traversal attack. 168 * This is because the path is not parsed consistently which results in different 169 * values in {@code HttpServletRequest} path related values which allow bypassing 170 * certain security constraints. 171 * </p> 172 * 173 * @param allowUrlEncodedPeriod should a period "." that is URL encoded "%2E" be 174 * allowed in the path or not. Default is false. 175 */ 176 public void setAllowUrlEncodedPeriod(boolean allowUrlEncodedPeriod) { 177 if (allowUrlEncodedPeriod) { 178 this.encodedUrlBlacklist.removeAll(FORBIDDEN_ENCODED_PERIOD); 179 } else { 180 this.encodedUrlBlacklist.addAll(FORBIDDEN_ENCODED_PERIOD); 181 } 182 } 183 184 /** 185 * <p> 186 * Determines if a backslash "\" or a URL encoded backslash "%5C" should be allowed in 187 * the path or not. The default is not to allow this behavior because it is a frequent 188 * source of security exploits. 189 * </p> 190 * <p> 191 * For example, due to ambiguities in the servlet specification a URL encoded period 192 * might lead to bypassing security constraints through a directory traversal attack. 193 * This is because the path is not parsed consistently which results in different 194 * values in {@code HttpServletRequest} path related values which allow bypassing 195 * certain security constraints. 196 * </p> 197 * 198 * @param allowBackSlash a backslash "\" or a URL encoded backslash "%5C" be allowed 199 * in the path or not. Default is false 200 */ 201 public void setAllowBackSlash(boolean allowBackSlash) { 202 if (allowBackSlash) { 203 urlBlacklistsRemoveAll(FORBIDDEN_BACKSLASH); 204 } else { 205 urlBlacklistsAddAll(FORBIDDEN_BACKSLASH); 206 } 207 } 208 209 /** 210 * <p> 211 * Determines if a percent "%" that is URL encoded "%25" should be allowed in the path 212 * or not. The default is not to allow this behavior because it is a frequent source 213 * of security exploits. 214 * </p> 215 * <p> 216 * For example, this can lead to exploits that involve double URL encoding that lead 217 * to bypassing security constraints. 218 * </p> 219 * 220 * @param allowUrlEncodedPercent if a percent "%" that is URL encoded "%25" should be 221 * allowed in the path or not. Default is false 222 */ 223 public void setAllowUrlEncodedPercent(boolean allowUrlEncodedPercent) { 224 if (allowUrlEncodedPercent) { 225 this.encodedUrlBlacklist.remove(ENCODED_PERCENT); 226 this.decodedUrlBlacklist.remove(PERCENT); 227 } else { 228 this.encodedUrlBlacklist.add(ENCODED_PERCENT); 229 this.decodedUrlBlacklist.add(PERCENT); 230 } 231 } 232 233 private void urlBlacklistsAddAll(Collection<String> values) { 234 this.encodedUrlBlacklist.addAll(values); 235 this.decodedUrlBlacklist.addAll(values); 236 } 237 238 private void urlBlacklistsRemoveAll(Collection<String> values) { 239 this.encodedUrlBlacklist.removeAll(values); 240 this.decodedUrlBlacklist.removeAll(values); 241 } 242 243 @Override 244 public FirewalledRequest getFirewalledRequest(HttpServletRequest request) throws RequestRejectedException { 245 rejectedBlacklistedUrls(request); 246 247 if (!isNormalized(request)) { 248 throw new RequestRejectedException("The request was rejected because the URL was not normalized."); 249 } 250 251 String requestUri = request.getRequestURI(); 252 if (!containsOnlyPrintableAsciiCharacters(requestUri)) { 253 throw new RequestRejectedException("The requestURI was rejected because it can only contain printable ASCII characters."); 254 } 255 return new FirewalledRequest(request) { 256 @Override 257 public void reset() { 258 } 259 }; 260 } 261 262 private void rejectedBlacklistedUrls(HttpServletRequest request) { 263 for (String forbidden : this.encodedUrlBlacklist) { 264 if (encodedUrlContains(request, forbidden)) { 265 throw new RequestRejectedException("The request was rejected because the URL contained a potentially malicious String \"" + forbidden + "\""); 266 } 267 } 268 for (String forbidden : this.decodedUrlBlacklist) { 269 if (decodedUrlContains(request, forbidden)) { 270 throw new RequestRejectedException("The request was rejected because the URL contained a potentially malicious String \"" + forbidden + "\""); 271 } 272 } 273 } 274 275 @Override 276 public HttpServletResponse getFirewalledResponse(HttpServletResponse response) { 277 return new FirewalledResponse(response); 278 } 279 280 private static boolean isNormalized(HttpServletRequest request) { 281 if (!isNormalized(request.getRequestURI())) { 282 return false; 283 } 284 if (!isNormalized(request.getContextPath())) { 285 return false; 286 } 287 if (!isNormalized(request.getServletPath())) { 288 return false; 289 } 290 if (!isNormalized(request.getPathInfo())) { 291 return false; 292 } 293 return true; 294 } 295 296 private static boolean encodedUrlContains(HttpServletRequest request, String value) { 297 if (valueContains(request.getContextPath(), value)) { 298 return true; 299 } 300 return valueContains(request.getRequestURI(), value); 301 } 302 303 private static boolean decodedUrlContains(HttpServletRequest request, String value) { 304 if (valueContains(request.getServletPath(), value)) { 305 return true; 306 } 307 if (valueContains(request.getPathInfo(), value)) { 308 return true; 309 } 310 return false; 311 } 312 313 private static boolean containsOnlyPrintableAsciiCharacters(String uri) { 314 int length = uri.length(); 315 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { 316 char c = uri.charAt(i); 317 if (c < '\u0020' || c > '\u007e') { 318 return false; 319 } 320 } 321 322 return true; 323 } 324 325 private static boolean valueContains(String value, String contains) { 326 return value != null && value.contains(contains); 327 } 328 329 /** 330 * Checks whether a path is normalized (doesn't contain path traversal 331 * sequences like "./", "/../" or "/.") 332 * 333 * @param path 334 * the path to test 335 * @return true if the path doesn't contain any path-traversal character 336 * sequences. 337 */ 338 private static boolean isNormalized(String path) { 339 if (path == null) { 340 return true; 341 } 342 343 if (path.indexOf("//") > -1) { 344 return false; 345 } 346 347 for (int j = path.length(); j > 0;) { 348 int i = path.lastIndexOf('/', j - 1); 349 int gap = j - i; 350 351 if (gap == 2 && path.charAt(i + 1) == '.') { 352 // ".", "/./" or "/." 353 return false; 354 } else if (gap == 3 && path.charAt(i + 1) == '.' && path.charAt(i + 2) == '.') { 355 return false; 356 } 357 358 j = i; 359 } 360 361 return true; 362 } 363 364 }
该类默认不允许URL中出现 Semicolon(分号)、Period(句号)、Percent(百分号)、Slash(斜杠)、 BackSlash(反斜杠)及其相应的经URL编码的字符。




