Round #429 (Div.2)
---恢复内容开始---
One day Kefa found n baloons. For convenience, we denote color of i-th baloon as si — lowercase letter of the Latin alphabet. Also Kefa has k friends. Friend will be upset, If he get two baloons of the same color. Kefa want to give out all baloons to his friends. Help Kefa to find out, can he give out all his baloons, such that no one of his friens will be upset — print «YES», if he can, and «NO», otherwise. Note, that Kefa's friend will not upset, if he doesn't get baloons at all.
The first line contains two integers n and k (1 ≤ n, k ≤ 100) — the number of baloons and friends.
Next line contains string s — colors of baloons.
Answer to the task — «YES» or «NO» in a single line.
You can choose the case (lower or upper) for each letter arbitrary.
4 2
aabb
YES
6 3
aacaab
NO
In the first sample Kefa can give 1-st and 3-rd baloon to the first friend, and 2-nd and 4-th to the second.
In the second sample Kefa needs to give to all his friends baloons of color a, but one baloon will stay, thats why answer is «NO».
题意:Kefa有n个气球,26个小写字母表示颜色,k个朋友,他要把气球分给k个朋友,但是朋友要得到不同的颜色,否则就是NO
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 int a[26]; 6 int n,k,m; 7 bool cmp(int x,int y){ 8 return x>y; 9 } 10 int main(){ 11 cin>>n>>k; 12 m=k; 13 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 14 char x; 15 scanf(" %c",&x); 16 a[x-'a']++; //标记每种颜色气球的数量 17 18 sort(a,a+26,cmp); //从大到小排序,例2:a[0]=4 19 a[0]>k?printf("NO\n"):printf("YES\n"); //4>3 NO 20 return 0; 21 }
Leha somehow found an array consisting of n integers. Looking at it, he came up with a task. Two players play the game on the array. Players move one by one. The first player can choose for his move a subsegment of non-zero length with an odd sum of numbers and remove it from the array, after that the remaining parts are glued together into one array and the game continues. The second player can choose a subsegment of non-zero length with an even sum and remove it. Loses the one who can not make a move. Who will win if both play optimally?
First line of input data contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 106) — length of the array.
Next line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 109).
Output answer in single line. "First", if first player wins, and "Second" otherwise (without quotes).
4
1 3 2 3
First
2
2 2
Second
In first sample first player remove whole array in one move and win.
In second sample first player can't make a move and lose
n个数和为偶要分情况讨论,为奇first胜,
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main(){ 5 int n,m,sum=0,t; 6 scanf("%d",&n); 7 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 8 scanf("%d",&m); 9 if(m&1) t++; //奇数 10 sum+=m; 11 } 12 if(sum&1) printf("First\n"); //为奇 13 else { 14 if(t==0) printf("Second\n"); 15 else printf("First\n"); 16 } 17 return 0; 18 }
or................................................................................or..............................................................................or
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main(){ 5 int n,m,s=0; 6 scanf("%d",&n); 7 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 8 scanf("%d",&m); 9 if(m&1) s=1; 10 } 11 if(s) printf("First\n"); 12 else printf("Second\n"); 13 return 0; 14 }
Leha like all kinds of strange things. Recently he liked the function F(n, k). Consider all possible k-element subsets of the set [1, 2, ..., n]. For subset find minimal element in it. F(n, k) — mathematical expectation of the minimal element among all k-element subsets.
But only function does not interest him. He wants to do interesting things with it. Mom brought him two arrays A and B, each consists of m integers. For all i, j such that 1 ≤ i, j ≤ m the condition Ai ≥ Bj holds. Help Leha rearrange the numbers in the array A so that the sum 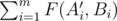 is maximally possible, where A' is already rearranged array.
is maximally possible, where A' is already rearranged array.
First line of input data contains single integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 2·105) — length of arrays A and B.
Next line contains m integers a1, a2, ..., am (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — array A.
Next line contains m integers b1, b2, ..., bm (1 ≤ bi ≤ 109) — array B.
Output m integers a'1, a'2, ..., a'm — array A' which is permutation of the array A.
5
7 3 5 3 4
2 1 3 2 3
4 7 3 5 3
7
4 6 5 8 8 2 6
2 1 2 2 1 1 2
2 6 4 5 8 8 6
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 5 #define maxn 200001 6 using namespace std; 7 int a[maxn],n; 8 pair<int ,int>b[maxn]; 9 bool cmp(int a,int b){ 10 return a>b; 11 } 12 bool cmp2(pair<int,int>a,pair<int,int>b){ 13 return a.first<b.first; 14 } 15 bool cmp3(pair<int,int>a,pair<int,int>b){ 16 return a.second<b.second; 17 } 18 int main(){ 19 cin>>n; 20 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 21 cin>>a[i]; 22 sort(a+1,a+1+n,cmp); 23 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 24 cin>>b[i].first; 25 b[i].second=i; 26 } 27 sort(b+1,b+n+1,cmp2); 28 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 29 b[i].first=a[i]; 30 sort(b+1,b+1+n,cmp3); 31 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 32 cout<<b[i].first<<' '; 33 return 0; 34 }
---恢复内容结束---




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 智能桌面机器人:用.NET IoT库控制舵机并多方法播放表情
· Linux glibc自带哈希表的用例及性能测试
· 深入理解 Mybatis 分库分表执行原理
· 如何打造一个高并发系统?
· .NET Core GC压缩(compact_phase)底层原理浅谈
· 手把手教你在本地部署DeepSeek R1,搭建web-ui ,建议收藏!
· 新年开篇:在本地部署DeepSeek大模型实现联网增强的AI应用
· 程序员常用高效实用工具推荐,办公效率提升利器!
· Janus Pro:DeepSeek 开源革新,多模态 AI 的未来
· 【译】WinForms:分析一下(我用 Visual Basic 写的)