什么是链表?
struct Node
{
//next是下一个Node的地址
struct Node* next;
//val是这个节点记录的值
int val;
}
这就是一个链表节点,里面存储了下一个节点的地址和节点值,链表是一个这样的结构
由n个这样的节点关联而成,就像一条锁链
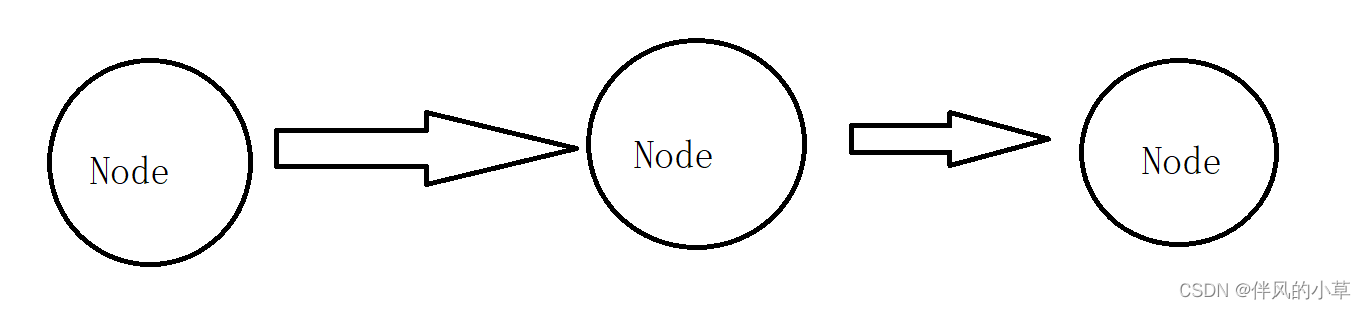
所以从图形来看,链表是内存不连续(CPU 缓存不友好)的,但是也不会像顺序表(点击传送)那样增加或者删除元素会移动后面的所有元素。
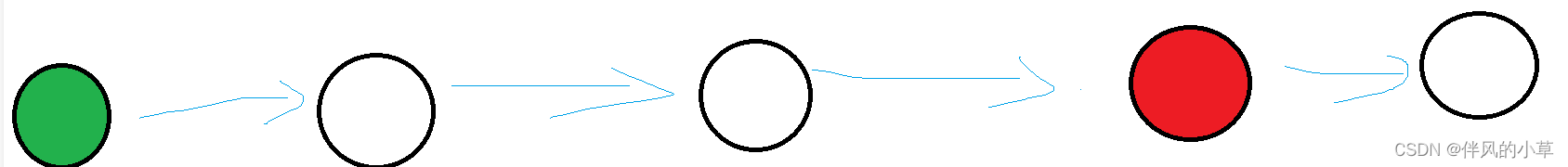
1.单(向)链表
如上图,它就是一条单向链表,我们如果已经拿到了第一个节点,那么我们就可以访问接下来的每个节点,但是我们如果拿到第二个节点,我们就不能去回溯第一个节点,因为next记录的是下一个节点的地址,而没有记录上一个节点的地址,我们并不清楚上一个节点位于内存的何处。
// 遍历链表的函数
void traverseLinkedList(struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* current = head;
// 从头节点开始遍历链表
while (current != NULL)
{
// 访问当前节点的值
printf("%d ", current->val);
// 将指针移动到下一个节点
current = current->next;
}
}
2.双向链表

我们期望实现这样的链表,让我们可以去访问一个节点之前的,和之后的节点
struct Node
{
//next是下一个Node的地址
struct Node* next;
//last是上一个节点的地址
struct Node* last;
//val是这个节点记录的值
int val;
}
我们需要记录上一个和下一个节点的地址,才能向前后回溯。
3.(单向)循环链表
如果单向链表和双向链表可以比作一条锁链的话,那我们只需把首尾接起来,就是一条循环链表
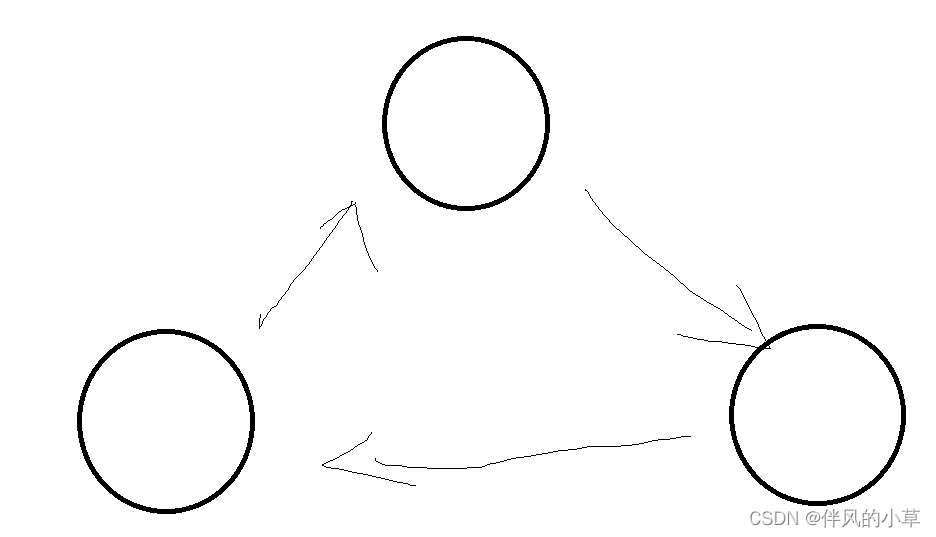
// 遍历循环链表的函数
void traverseCircularLinkedList(struct Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("Empty circular linked list.\n");
return;
}
struct Node* current = head;
do
{
// 访问当前节点的值
printf("%d ", current->val);
// 将指针移动到下一个节点
current = current->next;
} while (current != head); // 当回到起始节点时停止遍历
}
链表的优缺点
1.元素数量变更容易
如果我们想要增加一个节点,那么我们只需要把这个链条切断,然后把新的节点接进去
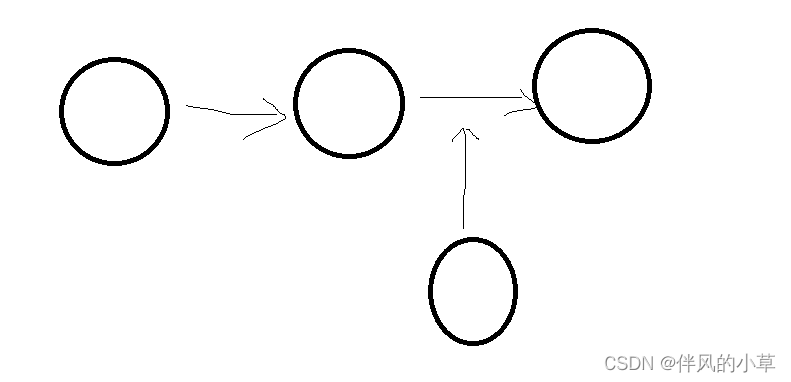
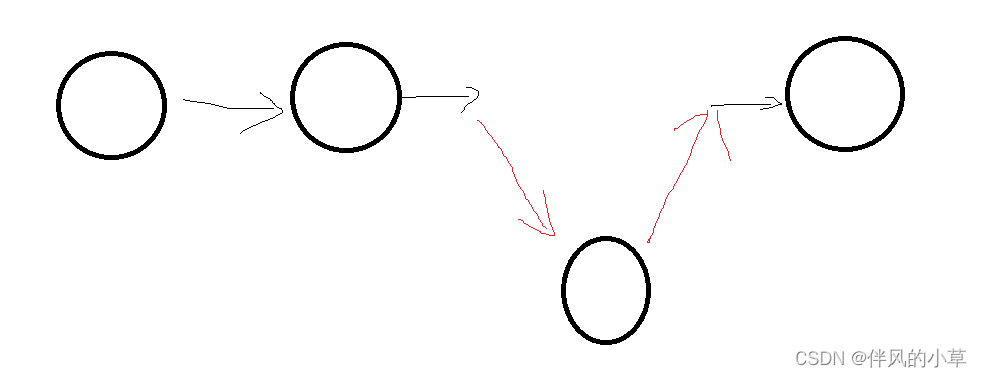
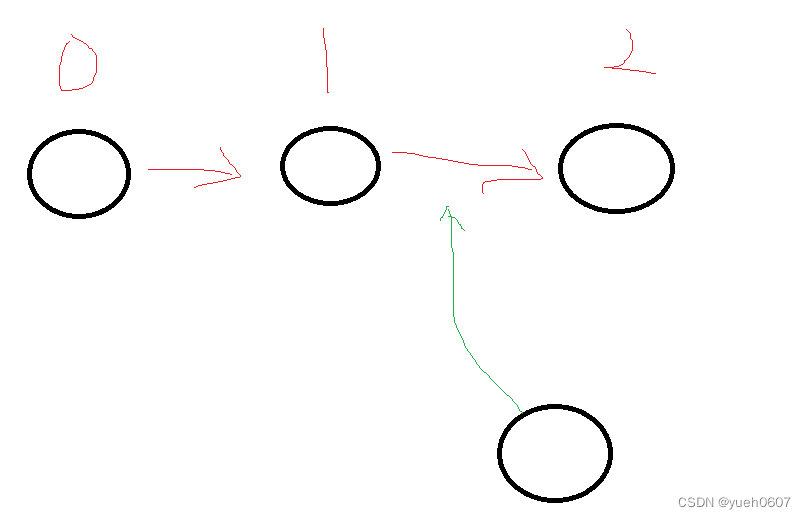
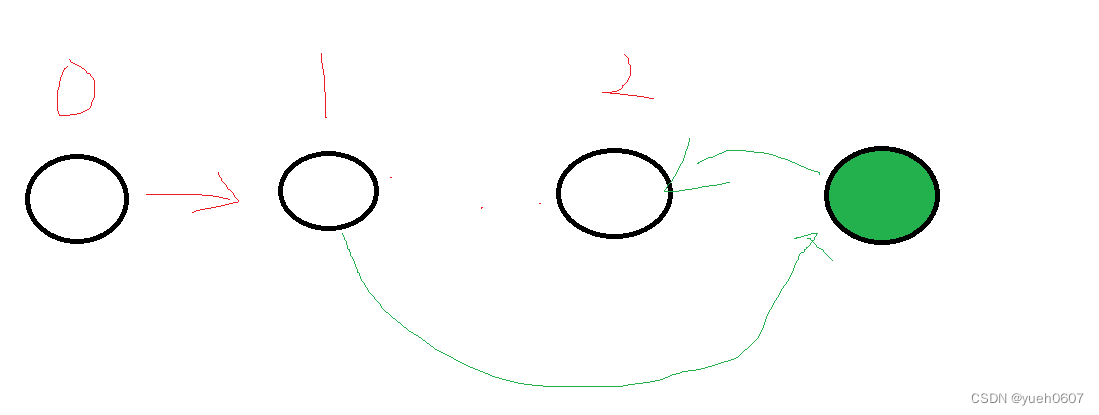
2.查找困难
如果我们现在需要找到某个节点,哪怕我们知道它在哪个位置,我们也只能迫不得已的逐个遍历,例如当前持有节点位置为0(绿色的),要取得往后的第三个节点(红色的),那么就需要一步一步的向后移动。如果我们不知道红色在哪,就要挨个比较,直到找到红色,
也就是说,需要通过遍历来查找。
如果我们(绿色)是在中间的位置,且为双向链表,查找红色甚至还需要两个方向分别交替的查找。
为了克服这个问题,我们引入一种新的链表
4.静态链表
- 创建一个大小是n的数组,类型为链表节点,不需要处理顺序
- 链表节点存储下一个节点的数组下标或者上一个节点的数组下标
这样做有非常大的好处
- 能根据一个节点直接找到上或者下一个节点
- 能根据数组轻松遍历或者无序访问一个链表
- 在n元素数量内保留了链表轻松变得节点关系,插入,删除比较高效
缺点是:
4. 多用了一个数组的空间
5. 超过n的扩容受到数组容量的限制,速度和空间应用顺序表的性质。
// 定义静态链表节点
struct StaticNode
{
int data; // 存储节点的数据
int next; // 存储下一个节点的索引
};
// 静态链表的最大容量
#define MAX_SIZE 100
int main()
{
// 创建静态链表数组
struct StaticNode staticList[MAX_SIZE];
// 向静态链表中插入数据
staticList[0].data = 1;
staticList[0].next = 1;
staticList[1].data = 2;
staticList[1].next = 2;
staticList[2].data = 3;
staticList[2].next = -1; // 最后一个节点的下一个节点索引为-1
return 0;
}
链表插入
struct Node
{
//next是下一个Node的地址
struct Node* next = NULL;
//val是这个节点记录的值
int val = 0;
}
//在一个节点后面插入节点
void InsertNode(Node* node,Node* nNode)
{
Node* next = node->next;
if(next==NULL)
{
node->next = nNode;
return;
}
node->next = nNode;
nNode->next = next;
}
链表移除
struct Node
{
//next是下一个Node的地址
struct Node* next = NULL;
struct Node* last = NULL;
//val是这个节点记录的值
int val = 0;
}
//移除这个节点,返回下一个位置的节点,如果在末尾返回NULL
Node* DeleteNode(Node* node)
{
Node* last = node->last;
Node* next = node->next;
last->next = next;
next->last = last;
//释放内存
delete node;
return next;
}
合并链表
struct Node
{
//next是下一个Node的地址
struct Node* next = NULL;
//val是这个节点记录的值
int val = 0;
}
//给出两个链表的头节点
//另一种实现可以是给尾节点,就没法返回头了
Node* MergeLinkedList(Node* node1,Node* node2)
{
Node* current = node1;
while(current->next != NULL)
{
current = node1->next;
}
current->next = node2;
return node1;
}
交叉合并
在上文的InsertNode的基础上
void CrossMerge(struct Node* list1, struct Node* list2)
{
if (list1 == NULL || list2 == NULL)
{
return; // 如果其中一个链表为空,无法合并
}
struct Node* current1 = list1;
struct Node* current2 = list2;
while (current1 != NULL && current2 != NULL)
{
struct Node* temp1 = current1->next;
struct Node* temp2 = current2->next;
current1->next = current2;
current2->next = temp1;
current1 = temp1;
current2 = temp2;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号