此方法用于三角形栅格化,需要传入的点有A,B,C三点的整数坐标。
本文主要考虑了以下四种情况对三角形进行栅格化遍历。
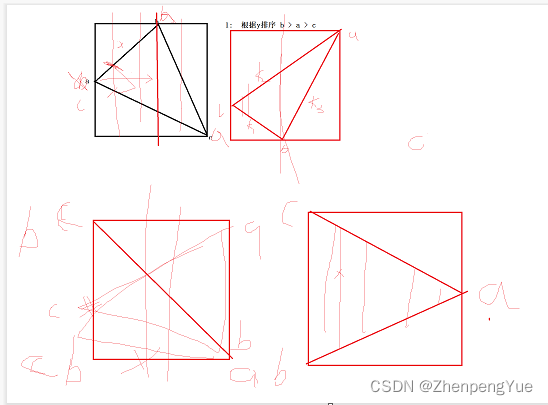
相对于传统逐像素扫描算法大概提高一倍的效率。
步骤如下:
- 根据X坐标对A,B,C进行排序交换,使得C.X<= B.X <=A.X
- 计算BC,AC,AB的斜率为k1,k2,k3,截距为b1,b2,b3
- 讨论是否有任意一个斜率不存在(趋于无穷大)
- 如果斜率存在,则以B.X作为分界线,用在逐X遍历通过解析式之差计算逐Y遍历范围
- 如果斜率不存在,则以矩形边界为范围逐X遍历,以斜率存在两线进行做差得到逐Y遍历范围
- 根据逐像素范围调用坐标回调传出结果
注意:该算法可能在矩形外的1像素范围内扩展,如果假定栅格化范围是10个格子,则11格内均可能有位置被回调。
using System;
/// <summary>
/// 整形向量
/// </summary>
public struct IntVector2 : IEquatable<IntVector2>, IFormattable
{
public int x;
public int y;
public IntVector2(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public static IntVector2 operator +(IntVector2 a, IntVector2 b)
{
return new IntVector2(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y);
}
public static IntVector2 operator -(IntVector2 a, IntVector2 b)
{
return new IntVector2(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y);
}
public bool Equals(IntVector2 other)
{
return x == other.x && y == other.y;
}
public string ToString(string? format, IFormatProvider? formatProvider)
{
return $"({x},{y})";
}
public static bool operator ==(IntVector2 left, IntVector2 right)
{
return left.x == right.x && left.y == right.y;
}
public static bool operator !=(IntVector2 left, IntVector2 right)
{
return left.x != right.x && left.y != right.y;
}
}
public static class TriSteper
{
static void Swap<T>(ref T a, ref T b)
{
T temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
static float GetK(ref IntVector2 a, ref IntVector2 b)
{
if (a.x == b.x) return float.MaxValue;
return ((float)a.y - (float)b.y) / ((float)a.x - (float)b.x);
}
static float GetB(ref float k, ref IntVector2 a)
{
return a.y - k * a.x;
}
public static void ForeachTri(IntVector2 a, IntVector2 b, IntVector2 c, Action<int, int> callback)
{
//排序 a> b > c
if (b.x > a.x) Swap(ref a, ref b);
if (c.x > b.x) Swap(ref b, ref c);
if (b.x > a.x) Swap(ref a, ref b);
//斜率
float k1 = GetK(ref c, ref b);
float k2 = GetK(ref a, ref c);
float k3 = GetK(ref a, ref b);
//截距
float b1 = GetB(ref k1, ref c);
float b2 = GetB(ref k2, ref a);
float b3 = GetB(ref k3, ref b);
//解析式
//c -b
Func<int, int> anal1 = (x) => (int)Math.Round(k1 * x + b1);
//a - c
Func<int, int> anal2 = (x) => (int)Math.Round(k2 * x + b2);
// a b
Func<int, int> anal3 = (x) => (int)Math.Round(k3 * x + b3);
//非极端三角形
if (k1 != float.MaxValue && k2 != float.MaxValue && k3 != float.MaxValue)
{
//斜率分区遍历
if (k1 > k2)
{
//从c到b的遍历
for (int i = c.x; i <= b.x; ++i)
{
int end = anal1(i);
int start = anal2(i);
for (int j = start; j <= end; ++j) callback(i, j);
}
//从b到a的遍历
for (int i = b.x + 1; i <= a.x; ++i)
{
int end = anal3(i);
int start = anal2(i);
for (int j = start; j <= end; ++j) callback(i, j);
}
}
else
{
//从c到b的遍历
for (int i = c.x; i <= b.x; ++i)
{
int start = anal1(i);
int end = anal2(i);
for (int j = start; j <= end; ++j) callback(i, j);
}
//从b到a的遍历
for (int i = b.x + 1; i <= a.x; ++i)
{
int end = anal2(i);
int start = anal3(i);
for (int j = start; j <= end; ++j) callback(i, j);
}
}
}
//极端三角型
else
{
//cb 斜率极限
if (k1 == float.MaxValue)
{
for (int i = c.x; i <= a.x; ++i)
{
int end = anal2(i);
int start = anal3(i);
if (end < start) Swap<int>(ref start, ref end);
for (int j = start; j <= end; ++j) callback(i, j);
}
}
//ab斜率极限
else if (k3 == float.MaxValue)
{
for (int i = c.x; i <= a.x; ++i)
{
int end = anal2(i);
int start = anal1(i);
if (end < start) Swap<int>(ref start, ref end);
for (int j = start; j <= end; ++j) callback(i, j);
}
}
}
}
}
例程如下,此程序实现了简单的三角形栅格化,生成bitmap并保存
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
class Pro
{
//例程
public static void Main()
{
IntVector2 a = new IntVector2(0, 5);
IntVector2 b = new IntVector2(10, 0);
IntVector2 c = new IntVector2(5, 10);
Bitmap bitMap = new(11, 11);
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) for (int j = 0; j < 11; j++) bitMap.SetPixel(i, j, Color.White);
TriSteper.ForeachTri(a, b, c, (x, y) =>
{
bitMap.SetPixel(x, y, Color.Red);
Console.WriteLine($"{new IntVector2(x, y)}");
});
Stream writer = new FileStream("haha.bmp", FileMode.OpenOrCreate);
bitMap.Save(writer, ImageFormat.Bmp);
writer.Close();
}
}
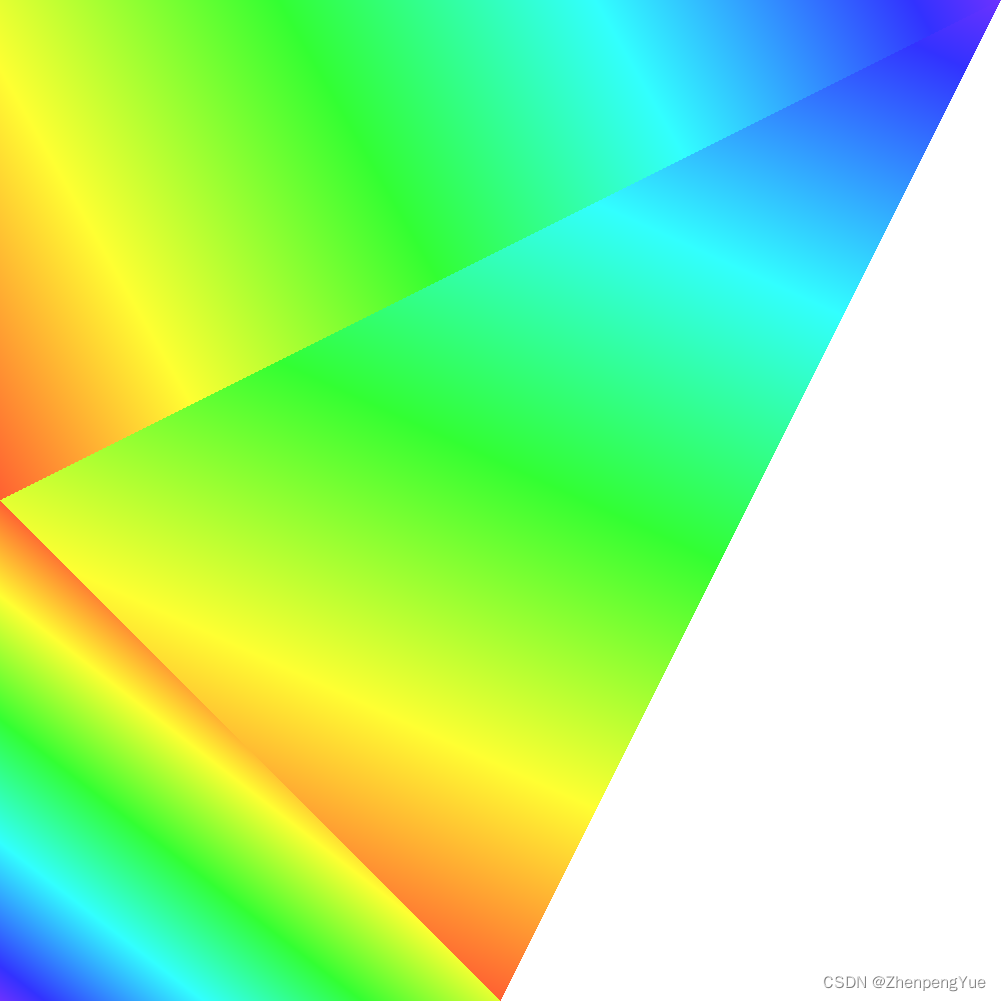
注:图是使用例程指出方法绘制三次所得



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号