对数据库表的操作
1.创建表:
create table +表名称(
列名称 字段长度(int/char/varchar) (not Null/default '男'/primary key),
列名称 字段长度(int/char/varchar) (not Null/default '男'/primary key)
)
2.删除表:drop table+表名称
3.增加一条或者多条新数据:insert 表名(字段)values(对应字段的值);
4.根据条件删除一条数据:delete 字段名 from 表名 where+条件句
5.更改数据:
Oracle:update 表名 set 字段名称='字段值'(,字段名称='字段值');
MySQL:update 表名 set 字段名称="字段值"(,字段名称="字段值");
注意:Oracle数据库只能支持单引号包起字符串,MySQL数据库可以支持双引号包起字符串
6.查询表所有字段:select * from 表名
7.查询表中某个字段 select 字段名 from 表名
8.根据条件查询表中的某个字段 select 字段名 from 表名 where 条件(如:userName='杨林')
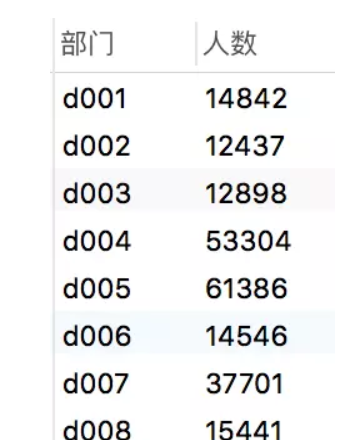
9. 使用group by去除重复的字段 例如:
SELECT
dept_no as 部门,
count( emp_no) as 人数
FROM
dept_emp
WHERE
to_date = '9999-01-01'
GROUP BY
dept_no
选择某个部门目前的在职员工数;
效果:
![]()
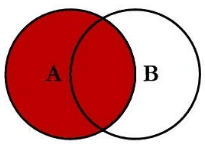
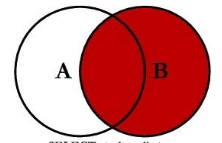
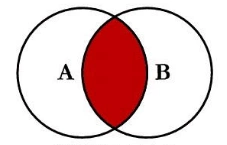
10.使用left join、right join和inner join查询实现跨表查询:
left join:
right join :
inner join:
11.分页查询
MySQL: select * from table limt 0,10; 查询第一页数据第一条到第十条数据即:select * from table limt (1-1)*10,10;
Oracle:select * from (select A.* ROWNUM rm from (select * from table where userName='杨林') A where ROWNUM<100) where rm>80;
12.使用去除笛卡尔积的方式查询多个表
select userName from table1 t1,table2 t2 where t1.age=t2.age 查询出t1和t2所有的userName并使用where条件去除笛卡尔积;
13.分组函数
MySQL:select name count(money) from emp;
Oracle:select name count(money) from emp group by (empDate);



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号