pytest测试框架(一)
一、pytest安装
pip install pytest
二、pytest的编写规则
1.测试文件以test_开头(以_test结尾也可以) 2.测试类以Test开头,并且不能带有 init 方法 3.测试函数以test_开头 4.断言使用基本的assert即可
三、pytest的运行方式--运行指定的case
1、主函数模式
if __name__ == '__main__': pytest.main(['s']) #s 表示输出调试信息,包括print打印的信息
2、命令行模式
示例代码如下:
import pytest class TestDemo_1(object): def test_01(self): x = 'hell' assert 'h' in x def test_02(self): sum = 4-2 assert 2 == sum class TestDemo_2(object): def test_add_01(self): print('add user 01') assert 1 == 2 def test_add_02(self): print('add user 02') assert 3 != 6
运行test_num.py文件中的全部用例:通过nodeld
命令窗口输入
pytest test_num.py
运行TestDemo_2类下的两个用例:
pytest test_num.py::TestDemo_2
运行TestDemo_1类下面的test_02用例
pytest test_num.py::TestDemo_1::test_02
3、通过读取pytest.ini配置文件运行(***企业自动化推荐使用)
pytest.ini是单元测试框架的核心配置文件(文件名必须是pytest.ini)
1、位置:一般放置于项目的根目录
2、编码:必须是ANSI
3、作用:改变pytest的默认行为
4、运行规则:不管是主函数的模式运行,命令行运行,都会去读取这个配置文件
pytest.ini配置文件范例:
1 [pytest] 2 # 命令行参数,多个参数用空格分隔 3 addopts = -vs --html ./report/report.html 4 5 # 测试用例文件夹,可自己配置(测试用例路径) 6 testpaths = ./testcase 7 8 # 配置测试搜索的模块文件名称 9 python_files = test_*.py 10 11 # 配置测试搜索的类名 12 python_classes = Test* 13 14 # 配置测试搜索的测试函数名 15 python_functions = test 16 17 #分组执行 18 markes = 19 smock:冒烟用例 20 productmanger:产品管理
命令行:pytest -vs ./testcase
参数详解:
1 -s 表示输出调试信息,包括print打印信息 2 -v 显示更详细的信息 3 -vs 两个参数一起使用 4 -n 支持多进程或多分布式运行测试用例,例:pytest -vs test_pro.py -n 5 5 --reruns NUM 失败用例重跑 6 -x 表示只要一个用例报错,那么测试停止 7 --maxfail=2 出现两个用例失败就停止 8 -k 指定运行测试用例(??) 9 --html 生成HTML的测试报告
四、多进程运行
在我们做接口自动化测试时,当测试用例很多时,就需要用到多进程运行
首先需要安装内置库
pip install -U pytest -xdist
运行
pytest test_num.py -n Num # Num表示要运行的进程数 pytest test_num.py -n 5
五、重试运行--失败用例重跑
当做接口自动化测试,遇到网络波动或503时导致case运行失败,这并不是测试失败,这时需要重试运行
首先也是需要安装内置库
pip install -U pytest-rerunfailures
运行
pytest test_se.py --reruns NUM # NUM表示重试的次数 pytest test_num.py --reruns 5
六、pytest的执行测试用例的顺序
unittest:通过ascll码的大小来绝对的执行顺序
pytest:1.从上到下
2.改变默认的执行顺序,通过装饰器方式来控制用例执行顺序,@pytest.mark.run(order=1)
1 import pytest 2 3 sum = 2 4 5 6 class TestOrder(object): 7 8 @pytest.mark.run(order=2) 9 def test_02(self): 10 print('我是02') 11 assert 'h' in 'hello' 12 13 @pytest.mark.run(order=1) 14 def test_01(self): 15 print('我是01') 16 assert 2 == sum 17 18 @pytest.mark.run(order=4) 19 def test_05(self): 20 print('我是05') 21 22 @pytest.mark.run(order=3) 23 def test_03(self): 24 print('我是03') 25 26 27 if __name__ == '__main__': 28 pytest.main(['vs'])
七、如何分组执行
smock:冒烟测试,测试用例分布在各个模块中
分模块执行:同样在pytest.ini配置文件配置markers即可,在分组执行的测试用例前加上@pytest.mark.smock(smock可以自定义)

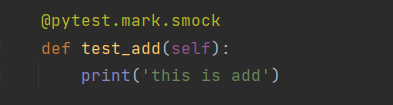
命令行执行:pytest -m "smock"
同时执行多个分组:pytest -m "smock or productmanager"
八、跳过测试用例
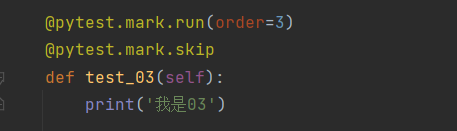
(1)无条件跳过
@pytest.mark.skip
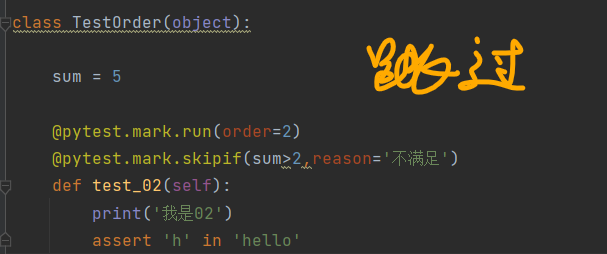
(2)有条件跳过
@pytest.mark.skipif(sum>2,reason='不满足')
九、生成HTML报告
安装pytest -html插件
pip install pytest-html
--html ./report/report.html
十、pytest框架实现前后置的处理(常用三种)
第一种:类似于unittest的前后置,setup/teardown/setup_class/teardown_class
class SetupDemo(object):
# 这个在所有的测试用例之前只运行一次
def setup_class(self):
print('在每个类执行前的初始化操作,如数据库的链接,创建日志对象')
# 每个测试用例执行前都会执行
def setup(self):
print('在每个测试用例执行之前运行,如打开网页')
def test_add(self):
print('this is add')
def test_delete(self):
print('this is delete')
def test_update(self):
print('this is update')
# 在每个类执行完后只执行一次
def teardown_class(self):
print('在每个类执行后的操作,如数据库的关闭,销毁日志对象')
# 每个测试用例执行后都会执行
def teardown(self):
print('在每个测试用例执行之后运行')
第二种(*****):pytest的核心,通过装饰器@pytest.fixtrue方式来实现部分用例的前后置和所有用例前后置。
格式和结构:
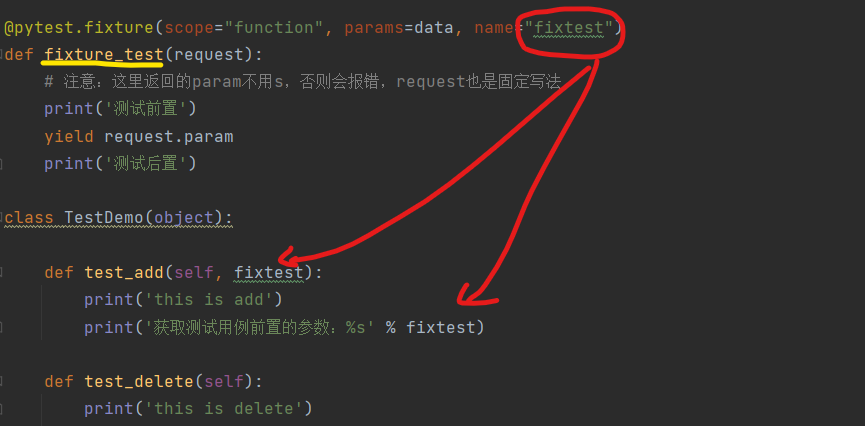
1 @pytest.fixture(scope="function", params="", autouse=False, ids="", name="") 2 def fixture_test(): 3 print('测试fixture处理用例的前后置')
1、scope(******):表示被@pytest.fixture标记的方法作用域,它有四个值--->function(默认)、class、module、package/session
2、params(****):参数化(支持的格式:list、tuple、字典列表[{},{},{}],字典元组({},{},{}) )
3、autouse(*****):自动使用,默认为False
4、ids(*):当使用params参数化时,给每一个值设置一个变量,意义不大
5、name(**):表示给@pytest.fixture标记的方法取一个别名
代码实践使用详细范例介绍:
一)、scope
1)scope="function"-->作用域函数,yield分隔,使用后置
1 import pytest 2 3 4 @pytest.fixture(scope="function") 5 def fixture_test(): 6 print('测试fixture处理用例的前置') 7 yield 8 print('测试fixture处理用例的后置') 9 10 11 class TestDemo(object): 12 13 def test_add(self,fixture_test): 14 print('this is add') 15 16 def test_delete(self): 17 print('this is delete')
如果类下面的两个方法都需要使用fixture_test前后置,可以直接加上autouse=True参数即可。--》@pytest.fixture(scope="function",autouse=True)
2)scope="class"-->作用域是类,类似于setup_class和teardown_class,只在类开始之前、结束之后执行一次
1 import pytest 2 3 @pytest.fixture(scope="class",autouse=True) 4 def fixture_test(): 5 print('测试fixture处理用例的前置') 6 yield 7 print('测试fixture处理用例的后置') 8 9 class TestDemo(object): 10 11 def test_add(self): 12 print('this is add')
3)scope="module"--->作用域是模块,一个文件中有多个类,也会只执行一次前置和后置
1 import pytest 2 3 4 @pytest.fixture(scope="module",autouse=True) 5 def fixture_test(): 6 print('测试fixture处理用例的前置') 7 yield 8 print('测试fixture处理用例的后置') 9 10 11 class TestDemo(object): 12 13 def test_add(self): 14 print('this is add') 15 16 def test_delete(self): 17 print('this is delete') 18 19 20 class TestDemo2: 21 22 def test_update(self): 23 print('this is update') 24 25 def test_query(self): 26 print('this is query')
二)、params-->参数化
1 import pytest 2 3 data = ['成都', '大理', '西安', '北京', '南昌'] 4 5 @pytest.fixture(scope="function", params=data) 6 def fixture_test(request): 7 # 注意:这里返回的param不用s,否则会报错,request也是固定写法 8 print('测试前置') 9 yield request.param 10 print('测试后置') 11 12 class TestDemo(object): 13 14 def test_add(self, fixture_test): 15 print('this is add') 16 print('获取测试用例前置的参数:%s' % fixture_test) 17 18 def test_delete(self): 19 print('this is delete')
三)、ids--->给参数化值设置变量
不设置的情况,执行结果显示的是Unicode值,如下:

设置以后,展示如下:
@pytest.fixture(scope="function", params=data, ids=['CD', 'DL', 'XA'])

四)、name-->给被fixture标记的方法修改别名



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号