Spring Batch Example – XML File To CSV File(六)
In this tutorial, we will show you how to configure a Spring Batch job to read XML file (JAXB2 library)
into a csv file, and filter out the record before writing with ItemProcessor.
Tools and libraries used
- Maven 3
- Eclipse 4.2
- JDK 1.6
- Spring Core 3.2.2.RELEASE
- Spring Batch 2.2.0.RELEASE
- Spring OXM 3.2.2.RELEASE
P.S This example – XML file (reader) – filtering (itemProcessor) – CSV (writer).
1. Simple Java Project
1. Create a quick start Java Project with Maven, converts and imports into Eclipse IDE.
$ mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.mkyong -DartifactId=SpringBatchExample3
-DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart -DinteractiveMode=false
$ cd SpringBatchExample3/
$ mvn eclipse:eclipse
2. Project Dependencies
Declares all project dependencies in the pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.mkyong</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBatchExample</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>SpringBatchExample</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<jdk.version>1.6</jdk.version>
<spring.version>3.2.2.RELEASE</spring.version>
<spring.batch.version>2.2.0.RELEASE</spring.batch.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring XML to/back object -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-oxm</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Batch dependencies -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.batch</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-batch-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.batch.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.batch</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-batch-infrastructure</artifactId>
<version>${spring.batch.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>spring-batch</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-eclipse-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.9</version>
<configuration>
<downloadSources>true</downloadSources>
<downloadJavadocs>false</downloadJavadocs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>${jdk.version}</source>
<target>${jdk.version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
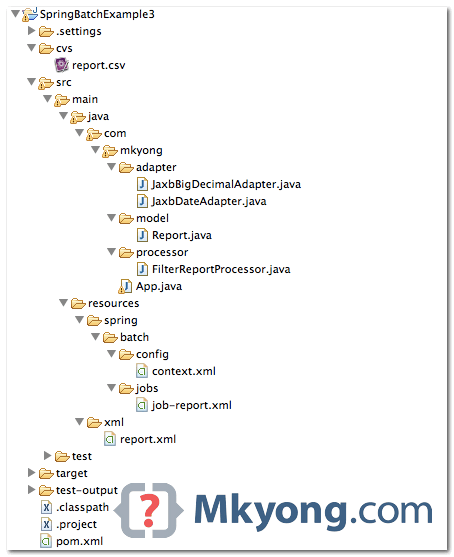
3. Project Directory Structure
Review the final project structure, get an overview what will going on next.
4. XML File
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<company>
<record refId="1001">
<name>mkyong</name>
<age>31</age>
<dob>31/8/1982</dob>
<income>200,000</income>
</record>
<record refId="1002">
<name>kkwong</name>
<age>30</age>
<dob>26/7/1983</dob>
<income>100,999</income>
</record>
<record refId="1003">
<name>joel</name>
<age>29</age>
<dob>21/8/1984</dob>
<income>1,000,000</income>
</record>
<record refId="1004">
<name>leeyy</name>
<age>29</age>
<dob>21/3/1984</dob>
<income>80,000.89</income>
</record>
</company>
5. Read XML File
In this example, we use Jaxb2Marshaller to map XML values and attributes
to an object.
<!-- ...... -->
<bean id="xmlItemReader"
class="org.springframework.batch.item.xml.StaxEventItemReader">
<property name="fragmentRootElementName" value="record" />
<property name="resource" value="classpath:xml/report.xml" />
<property name="unmarshaller" ref="reportUnmarshaller" />
</bean>
<!-- Read and map values to object, via jaxb2 -->
<bean id="reportUnmarshaller"
class="org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Jaxb2Marshaller">
<property name="classesToBeBound">
<list>
<value>com.mkyong.model.Report</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
Annotate the Report to tell which XML value maps to which field.
package com.mkyong.model;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAttribute;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.adapters.XmlJavaTypeAdapter;
import com.mkyong.adapter.JaxbBigDecimalAdapter;
import com.mkyong.adapter.JaxbDateAdapter;
@XmlRootElement(name = "record")
public class Report {
private int refId;
private String name;
private int age;
private Date dob;
private BigDecimal income;
@XmlAttribute(name = "refId")
public int getRefId() {
return refId;
}
public void setRefId(int refId) {
this.refId = refId;
}
@XmlElement(name = "age")
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@XmlElement
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@XmlJavaTypeAdapter(JaxbDateAdapter.class)
@XmlElement
public Date getDob() {
return dob;
}
public void setDob(Date dob) {
this.dob = dob;
}
@XmlJavaTypeAdapter(JaxbBigDecimalAdapter.class)
@XmlElement
public BigDecimal getIncome() {
return income;
}
public void setIncome(BigDecimal income) {
this.income = income;
}
// for csv file only
public String getCsvDob() {
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy");
return dateFormat.format(getDob());
}
}
In JAXB2, those “complex” data type like Date and BigDecimal,
will not map to the field automatically, even it’s annotated.
To make JAXB2 supports Date conversion, you need to create a custom Adapter
to handle the Date formatmanually, then attaches the adapter via @XmlJavaTypeAdapter.
package com.mkyong.adapter;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.adapters.XmlAdapter;
public class JaxbDateAdapter extends XmlAdapter<String, Date> {
private SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy");
@Override
public String marshal(Date date) throws Exception {
return dateFormat.format(date);
}
@Override
public Date unmarshal(String date) throws Exception {
return dateFormat.parse(date);
}
}
Same to BigDecimal, the commas “,” in the XML’s income element is causing
the conversion problem, you need a custom adapter to handle it also.
package com.mkyong.adapter;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.adapters.XmlAdapter;
public class JaxbBigDecimalAdapter extends XmlAdapter<String, BigDecimal> {
@Override
public String marshal(BigDecimal obj) throws Exception {
return obj.toString();
}
@Override
public BigDecimal unmarshal(String obj) throws Exception {
return new BigDecimal(obj.replaceAll(",", ""));
}
}
6. Spring Batch Core Setting
Define jobRepository and jobLauncher.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd">
<!-- stored job-meta in memory -->
<bean id="jobRepository"
class="org.springframework.batch.core.repository.support.MapJobRepositoryFactoryBean">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" />
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.batch.support.transaction.ResourcelessTransactionManager" />
<bean id="jobLauncher"
class="org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.SimpleJobLauncher">
<property name="jobRepository" ref="jobRepository" />
</bean>
</beans>
7. Spring Batch Jobs
A Spring batch job, read the report.xml file, map it to Report object,
and write it into a csv file. Read the comments, it should be self-explanatory.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:batch="http://www.springframework.org/schema/batch"
xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/batch
http://www.springframework.org/schema/batch/spring-batch-2.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd">
<batch:job id="reportJob">
<batch:step id="step1">
<batch:tasklet>
<batch:chunk reader="xmlItemReader"
writer="cvsFileItemWriter" processor="filterReportProcessor"
commit-interval="1">
</batch:chunk>
</batch:tasklet>
</batch:step>
</batch:job>
<!-- Filtering process -->
<bean id="filterReportProcessor" class="com.mkyong.processor.FilterReportProcessor" />
<bean id="xmlItemReader"
class="org.springframework.batch.item.xml.StaxEventItemReader">
<property name="fragmentRootElementName" value="record" />
<property name="resource" value="classpath:xml/report.xml" />
<property name="unmarshaller" ref="reportUnmarshaller" />
</bean>
<!-- Read and map values to object, via jaxb2 -->
<bean id="reportUnmarshaller" class="org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Jaxb2Marshaller">
<property name="classesToBeBound">
<list>
<value>com.mkyong.model.Report</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="cvsFileItemWriter" class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.FlatFileItemWriter">
<!-- write to this csv file -->
<property name="resource" value="file:cvs/report.csv" />
<property name="shouldDeleteIfExists" value="true" />
<property name="lineAggregator">
<bean
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.transform.DelimitedLineAggregator">
<property name="delimiter" value="," />
<property name="fieldExtractor">
<bean
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.transform.BeanWrapperFieldExtractor">
<property name="names" value="refId, name, age, csvDob, income" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
8. Spring Batch – ItemProcessor
In Spring batch, the wired Processor will be fired before writing to any
resources, so, this is the best place to handle any conversion, filtering and business logic. In this example, the Report object
will be ignored (not write to csv file) if its’ age is equal to 30.
package com.mkyong.processor;
import org.springframework.batch.item.ItemProcessor;
import com.mkyong.model.Report;
//run before writing
public class FilterReportProcessor implements ItemProcessor<Report, Report> {
@Override
public Report process(Report item) throws Exception {
//filter object which age = 30
if(item.getAge()==30){
return null; // null = ignore this object
}
return item;
}
}
9. Run It
The most simplest way to run a batch job.
package com.mkyong;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Job;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobExecution;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobParameters;
import org.springframework.batch.core.launch.JobLauncher;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] springConfig =
{
"spring/batch/config/context.xml",
"spring/batch/jobs/job-report.xml"
};
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(springConfig);
JobLauncher jobLauncher = (JobLauncher) context.getBean("jobLauncher");
Job job = (Job) context.getBean("reportJob");
try {
JobExecution execution = jobLauncher.run(job, new JobParameters());
System.out.println("Exit Status : " + execution.getStatus());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Done");
}
}
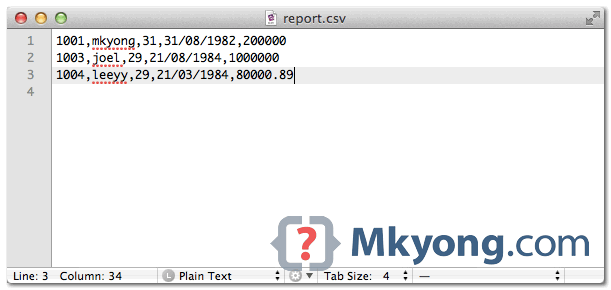
Output. The XML values are inserted into a csv file.
1001,mkyong,31,31/08/1982,200000
1003,joel,29,21/08/1984,1000000
1004,leeyy,29,21/03/1984,80000.89