构造函数
1 public class Demo { 2 private int x; 3 private String string; 4 public Demo(int x) { 5 this.x = x; 6 } 7 public Demo(int x,String string){ 8 this(x); //一个类的构造器调用这个类中的其他构造器 9 10 this.string=string; 11 } 12 }
1、构造函数void返回(构造函数可被重载,但不能被重写)
构造函数的返回类型不可指定,如果你在构造函数前面写上void ,那么构造函数就变成无效的了,但不会报错。因为构造函数的作用就是要生成一个类的对象,这个生成的对象的指针要返回给系统,如果写成void,那么构造函数就无任何返回。
eg:
1 class Scope { 2 3 String s="11"; 4 5 void Scope() { //注意此处构造函数添加了void,但不会编译错误,也不会运行错误 6 s = "constructor"; 7 } 8 public static void main(String[] args) { //注意此处main函数声明必须是public static void,否则运行出错! 9 Scope m = new Scope(); 10 m.go(); 11 } 12 13 void go() { 14 System.out.println(s); 15 } 16 }
结果是:
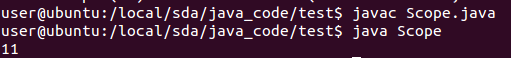
可以看出在构造函数前面写上void ,那么构造函数就变成无效。
2、构造函数void形参
public class Scope{ public static void main(String[] argv){ System.out.println("two"); Scope a=new Scope(); } Scope(void){ //构造函数参数void会导致编译报错 System.out.println("tq"); } Scope(){ System.out.println("tq1"); } }
this表示是当前类对象。类方法是指用static修饰的方法,普通方法叫对象方法。
构造方法每次都是构造出新的对象,不存在多个线程同时读写同一对象中的属性的问题,所以不需要同步 。
容器保存的是对象的引用
如果父类中的某个方法使用了
synchronized关键字,而子类中也覆盖了这个方法,默认情况下子类中的这个方法并不是同步的,必须显示的在子类的这个方法中加上
synchronized关键字才可。当然,也可以在子类中调用父类中相应的方法,这样虽然子类中的方法并不是同步的,但子类调用了父类中的同步方法,也就相当子类方法也同步了


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号