LCT
如果是学习的话,可以看一下这篇博客
LCT有一点类似于树链剖分,只不过是实链和虚链,然后可以不断变化。每一条实链用一个splay(深度为关键字)维护,splay还原出来就应该是一条由浅到深的链。
Splay的根的father是原树中链顶的父节点。特别的,原树根所在的Splay根节点的father为空。
而且splay的根的父亲是原树中链顶的父节点,但父亲却没有存儿子。这就是“儿子认父亲,父亲不认儿子”(也是和splay的不同之处)
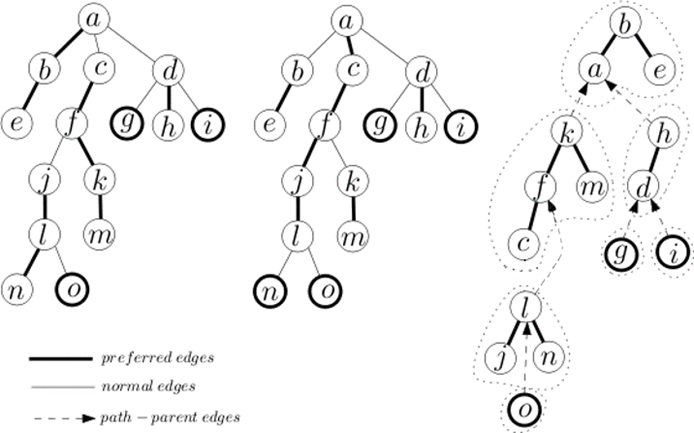
下面说一下LCT的基础操作(以下摘自WYS学长的PPT)
access
access(x) 是将点 x 到原树根的路径设为实链。此操作后,x所在的 Splay 仅包含 x 到根路径上的点, x 是该链中深度最大的节点,x与其儿子的边都将变为虚边


void access(int x) { int y=0; while(x) { splay(x); ch[x][1]=y; pushup(x); y=x;x=f[x]; } }
findroot
findroot()的作用是找整棵树的根


int findroot(int x) { access(x);splay(x); while(ch[x][0])x=ch[x][0]; return x; }
makeroot
makeroot(x)的作用是将点x设为整棵树的根
考虑换根对原树形态带来的影响
x到root链上的点的深度翻转,父子关系改变
其余父子关系维持原状
正确性
执行access(x)后,x是其所在链中深度最大的点。Splay翻转后,x变成了深度最小的点(即根),root变成了深度最大的点,中序遍历发生变化,这条链的父子关系随即改变其他父子关系没有改变
使用makeroot和access可以很方便的提取出两点间的路径

void makeroot(int x) { access(x);splay(x); pushreverse(x); }
split
就是提取出一条链

void split(int x,int y) { makeroot(x);access(y);splay(y); }
link
link( x , y )的作用是,添加一条连接x和y的边
我们可以先添加虚边,在后续操作中如有需要,再改成实边

void link(int x,int y)//f[x]=y { if(findroot(x)==findroot(y)) return ; makeroot(x); if(findroot(y)!=x)f[x]=y; }
cut
cut( x , y )的作用是,断掉一条连接x和y的边
必须有边才能断
如果不知道有没有,可以这样判断
1.x和y连通
2.x到y路径上没有其他节点

void cut(int x,int y) { if(findroot(x)!=findroot(y)) return ; split(x,y); if(ch[y][0]==x) f[x]=ch[y][0]=0; pushup(y); }
然后我们会发现LCT中的splay有一些不同
它是这样的

void rotate(int x) { int old=f[x],oldf=f[old]; int which=get(x); if(!isroot(old)) ch[oldf][ch[oldf][1]==old]=x;//特殊判断 ch[old][which]=ch[x][which^1]; f[ch[old][which]]=old; ch[x][which^1]=old;f[old]=x; f[x]=oldf; pushup(old);pushup(x); } void splay(int x) { int y=x,z=0; stackk[++z]=y; while(!isroot(y))stackk[++z]=y=f[y]; while(z)pushdown(stackk[z--]); while(!isroot(x)) { int fa=f[x]; if(!isroot(fa)) rotate((get(fa)==get(x))?fa:x); rotate(x); } pushup(x); }
我们用一个栈暂存当前点到根的整条路径,pushdown时一定要从上往下放标记
rotate的时候有一个特殊判断if(!isroot(old)) ch[oldf][ch[oldf][1]==old]=x; 保证这棵splay的根的父亲不会连向它
记得最后3操作的时候,要把x splay到根再修改,还有就是cut的打法,因为题目不保证x,y间是有边的

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define N 300003 using namespace std; int read() { int x=0,f=1;char s=getchar(); while(s<'0'||s>'9'){if(s=='-')f=-1;s=getchar();} while(s>='0'&&s<='9'){x=x*10+s-'0';s=getchar();} return x*f; } int ch[N][3],rev[N],f[N],a[N],s[N],stackk[N]; bool isroot(int x){return (ch[f[x]][0]!=x&&ch[f[x]][1]!=x);} int get(int x){return ch[f[x]][1]==x;} void pushup(int x){s[x]=s[ch[x][0]]^s[ch[x][1]]^a[x];} void pushreverse(int x){swap(ch[x][0],ch[x][1]); rev[x]^=1;} void pushdown(int x) { if(rev[x]) { if(ch[x][0])pushreverse(ch[x][0]); if(ch[x][1])pushreverse(ch[x][1]); rev[x]=0; } } void rotate(int x) { int old=f[x],oldf=f[old]; int which=get(x); if(!isroot(old)) ch[oldf][ch[oldf][1]==old]=x;//特殊判断 ch[old][which]=ch[x][which^1]; f[ch[old][which]]=old; ch[x][which^1]=old;f[old]=x; f[x]=oldf; pushup(old);pushup(x); } void splay(int x) { int y=x,z=0; stackk[++z]=y; while(!isroot(y))stackk[++z]=y=f[y]; while(z)pushdown(stackk[z--]); while(!isroot(x)) { int fa=f[x]; if(!isroot(fa)) rotate((get(fa)==get(x))?fa:x); rotate(x); } pushup(x); } void access(int x) { int y=0; while(x) { splay(x); ch[x][1]=y; pushup(x); y=x;x=f[x]; } } int findroot(int x) { access(x);splay(x); while(ch[x][0])x=ch[x][0]; return x; } void makeroot(int x) { access(x);splay(x); pushreverse(x); } void split(int x,int y) { makeroot(x);access(y);splay(y); } void link(int x,int y)//f[x]=y { makeroot(x); if(findroot(y)!=x)f[x]=y; } void cut(int x,int y) { makeroot(x); if(findroot(y)==x&&f[x]==y&&ch[y][0]==x) f[x]=ch[y][0]=0; pushup(y); //如果要先判x,y的联通,可用findroot看是不是同一个,再看x,y的splay大小是不是2 } int main() { int n=read(),m=read(); for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)a[i]=read(),s[i]=a[i]; for(int i=1;i<=m;++i) { int op=read(),x=read(),y=read(); if(op==0){split(x,y);printf("%d\n",s[y]);} if(op==1)link(x,y); if(op==2)cut(x,y); if(op==3){access(x);splay(x);a[x]=y;pushup(x);} } }
特别想说的是关于pushup
access和cut更新了儿子关系,所以需要pushup





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号