Python 基础系列一:初识python(二)基本数据类型
上节拾遗
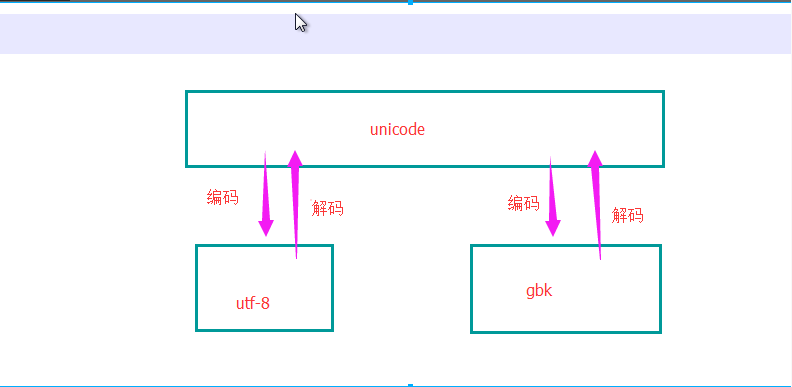
1、编码转换过程,utf-8转换gbk 过程 经过解码(py27):
x.decode('utf-8')-->unicode-->编码x.encode('gbk')
ps:py3 默认的字符编码为UTF-8
运算符
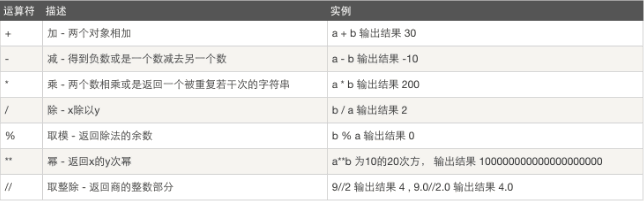
1、算数运算:
实例:

>>> 5 + 4 # 加法 9 >>> 4.3 - 2 # 减法 2.3 >>> 3 * 7 # 乘法 21 >>> 2 / 4 # 除法,得到一个浮点数 0.5 >>> 2 // 4 # 除法,得到一个整数 0 >>> 17 % 3 # 取余 2 >>> 2 ** 5 # 乘方 32
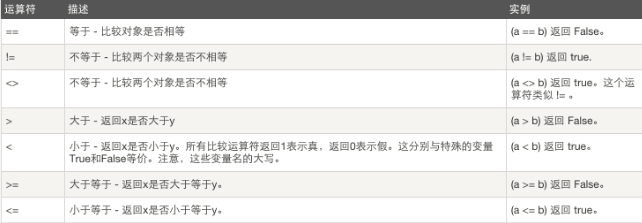
2、比较运算:
实例:

#!/usr/bin/python a = 21 b = 10 c = 0 if ( a == b ): print "Line 1 - a is equal to b" else: print "Line 1 - a is not equal to b" if ( a != b ): print "Line 2 - a is not equal to b" else: print "Line 2 - a is equal to b" if ( a <> b ): print "Line 3 - a is not equal to b" else: print "Line 3 - a is equal to b" if ( a < b ): print "Line 4 - a is less than b" else: print "Line 4 - a is not less than b" if ( a > b ): print "Line 5 - a is greater than b" else: print "Line 5 - a is not greater than b" a = 5; b = 20; if ( a <= b ): print "Line 6 - a is either less than or equal to b" else: print "Line 6 - a is neither less than nor equal to b" if ( b >= a ): print "Line 7 - b is either greater than or equal to b" else: print "Line 7 - b is neither greater than nor equal to b"
3、赋值运算:

实例:

#!/usr/bin/python a = 21 b = 10 c = 0 c = a + b print "Line 1 - Value of c is ", c c += a print "Line 2 - Value of c is ", c c *= a print "Line 3 - Value of c is ", c c /= a print "Line 4 - Value of c is ", c c = 2 c %= a print "Line 5 - Value of c is ", c c **= a print "Line 6 - Value of c is ", c c //= a print "Line 7 - Value of c is ", c
4、逻辑运算:

实例:

#!/usr/bin/python a = 10 b = 20 c = 0 if ( a and b ): print "Line 1 - a and b are true" else: print "Line 1 - Either a is not true or b is not true" if ( a or b ): print "Line 2 - Either a is true or b is true or both are true" else: print "Line 2 - Neither a is true nor b is true" a = 0 if ( a and b ): print "Line 3 - a and b are true" else: print "Line 3 - Either a is not true or b is not true" if ( a or b ): print "Line 4 - Either a is true or b is true or both are true" else: print "Line 4 - Neither a is true nor b is true" if not( a and b ): print "Line 5 - Either a is not true or b is not true" else: print "Line 5 - a and b are true"
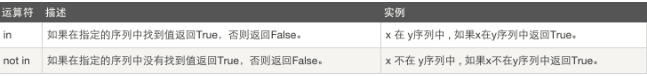
5、成员运算:
实例:

#!/usr/bin/python a = 10 b = 20 list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]; if ( a in list ): print "Line 1 - a is available in the given list" else: print "Line 1 - a is not available in the given list" if ( b not in list ): print "Line 2 - b is not available in the given list" else: print "Line 2 - b is available in the given list" a = 2 if ( a in list ): print "Line 3 - a is available in the given list" else: print "Line 3 - a is not available in the given list"
基本数据类型
1、数字类型(int)
在32位机器上,整数的位数为32位,取值范围为-2**31~2**31-1,即-2147483648~2147483647 在64位系统上,整数的位数为64位,取值范围为-2**63~2**63-1,即-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807
int内部优化

n1,n2 共享同一块内存,
- Python中的int对象就是c语言中long类型数值的扩展
- 小整数对象[-5, 257]在python中是共享的
- 整数对象都是从缓冲池中获取的。
方法:
bit_length()#返回表示该数字的时占用的最少位数 conjugate()#返回该复数的共轭复数
实例:

n1=5 print (n1.bit_length()) print (3+2j.conjugate())
2、布尔值(bool)
-->真或假 -->1 或 0
3、字符串(str)
创建字符串:
al = 'Hello,world'
字符串(str)类型和bytes类型转换py3版本

str(bytes_or_buffer[, encoding[, errors]]) -> str name ="博客园" for i in name: print(i) bytes_list = bytes(i, encoding='utf-8') print(bytes_list) # 默认每一个字节都是16进制表示 for x in bytes_list: print(x,bin(x)) # 默认每一个字节都是10进制表示
由于utf-8--》3个字节
gbk --》 2字节
输出结果:

博 b'\xe5\x8d\x9a' 229 0b11100101 141 0b10001101 154 0b10011010 客 b'\xe5\xae\xa2' 229 0b11100101 174 0b10101110 162 0b10100010 园 b'\xe5\x9b\xad' 229 0b11100101 155 0b10011011 173 0b10101101
- 进制的转换如下图:

方法:
str.capitalize() #首字母变大写 str.center(self, width, fillchar=None) #内容居中,width:总长度;fillchar:空白处填充内容,默认无 str.count(self, sub, start=None, end=None) #子序列个数 str.decode(self, encoding=None, errors=None) #解码 str.encode(self, encoding=None, errors=None) #编码,针对unicode str.endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None) #是否以 xxx 结尾 str.expandtabs(self,tabsize=None) #将tab转换成空格,默认一个tab转换成8个空格 str.find(self,sub,start=None,end=None) #寻找子序列位置,如果没找到,返回 -1 str.format(*args, **kwargs) #字符串格式化 str.index(self,sub,start=None,end=None)#子序列位置,如果没找到,报错 str.isalnum() #检查是否是字母和数字 str.isalpha() #检查是否是字母 str.isdigit() #检查是否是数字 str.islower() #检查是否小写 str.isspace() #检查是否有空格 str.istitle() #检查所有单词首字母大写且其他字母为小写返回True str.isupper() #检查是否为大写 str.join() #连接 str.ljust() #内容左对齐,右侧填充 str.lower() #变小写 str.lstrip()# 左侧去除空格 str.rstrip()#右侧去除空格 str.strip()#去除两侧空格 str.partition()#指定分割成3部分,从左往右 str.replace()#替换 str.rfind()#返回字符串最后一次出现的位置,如果没有匹配项则返回-1。 str.rindex()#返回子字符串 str 在字符串中最后出现的位置,如果没有匹配的字符串会报异常,你可以指定可选参数[beg:end]设置查找的区间。 str.rjust()#右侧对齐,左侧填充 str.rpartiton()#指定分割成3部分,从右往左 str.split()#分割, maxsplit最多分割几次 str.splitlines() #根据换行分割 str.startswith() #是否起始 str.swapcase()# 反转,大小变小写,小写变大写 str.upper()#小写转换成大写 str.zfill()#方法返回指定长度的字符串,原字符串右对齐,前面填充0。
字符串常用功能分别为:移除空格、分割、长度、索引、切片等。
4、列表(list)
创建列表:
name_list = ['Hello', 'cnblogs'] 或 name_list = list(['Hello', 'Hello'])
方法:
list.append(obj)#在列表末尾添加新的对象 list.count(obj)#统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数 list.extend(seq)#在列表末尾一次性追加另一个序列中的多个值(用新列表扩展原来的列表) list.index(obj)#从列表中找出某个值第一个匹配项的索引位置 list.insert(index, obj)#将对象插入列表 list.pop(obj=list[-1])#移除列表中的一个元素(默认最后一个元素),并且返回该元素的值 list.remove(obj)#移除列表中某个值的第一个匹配项 list.reverse()#反向列表中元素 list.sort([func])#对原列表进行排序
列表常用基本操作为:索引、切片、追加、删除、长度、循环、包含等。
5、元组(tuple)
创建元组:
ages = (11, 22, 33, 44, 55) 或 ages = tuple((11, 22, 33, 44, 55))
方法:
tuple.count()#统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数 tuple.index()#找出某个值第一个匹配项的索引位置
元祖常用基本操作为:索引、切片、删除、长度、包含等。
6、字典(dict)
创建字典:
person = {"name": "mr.wu", 'age': 18}
或
person = dict({"name": "mr.wu", 'age': 18})
- 小案例,取出字典里的123:
li = [ "alex" , 123, {"k1":"v1", "k2": {"vv": (11,22,123), "ii": 456}}]print(li[2]['k2']['vv'][2])
- dict.fromkeys的用法了解:
a1= dict.fromkeys(['k1','k2','k3'],[]) print(a1) a1['k1'].append('1') print(a1)
方法:
dict.clear()#删除字典内所有元素 dict.copy()#返回一个字典的浅复制 dict.fromkeys()#创建一个新字典,以序列seq中元素做字典的键,val为字典所有键对应的初始值 dict.get(key, default=None)#返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回default值 dict.has_key(key)#如果键在字典dict里返回true,否则返回false dict.items()#以列表返回可遍历的(键, 值) 元组数组 dict.keys()#以列表返回一个字典所有的键 dict.setdefault(key, default=None)#和get()类似, 但如果键不存在于字典中,将会添加键并将值设为default dict.update(dict2)#把字典dict2的键/值对更新到dict里 dict.values()#以列表返回字典中的所有值
字典常用基本操作为:索引、新增、删除、键值对、循环、长度等。
优雅的用法
1、for循环
用户按照顺序循环可迭代对象中的内容
li = [11,22,33,44]
for item in li:
print item
2、enumrate
为可迭代的对象添加序号
li = [11,22,33]
for k,v in enumerate(li, 1):
print(k,v)
3、range和xrange
print range(1, 10) # 结果:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] print range(1, 10, 2) # 结果:[1, 3, 5, 7, 9] print range(30, 0, -2) # 结果:[30, 28, 26, 24, 22, 20, 18, 16, 14, 12, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2]
ps:py3没有xrange只有range,但是range为xrange的功能
练习题
1、元素分类
有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中。
即: {'k1': 大于66的所有值, 'k2': 小于66的所有值}
dict_list = {
'k1':[],
'k2':[]
}
li =[11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90]
for i in li:
if i <=66:
dict_list['k1'].append(i)
else:
dict_list['k2'].append(i)
print (dict_list)
2、查找
查找列表中元素,移动空格,并查找以 a或A开头 并且以 c 结尾的所有元素。
li = ["alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain"]
li = ["alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain"]
for i in li:
a = i.lstrip()
if (a.startswith('a') or a.startswith('A')) and a.endswith('c'):
print (a)
tu = ("alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain")
for i in tu:
if i.strip().capitalize().startswith('A') and i.strip().endswith('c'):
print (i)
dic = {'k1': "alex", 'k2': ' aric', "k3": "Alex", "k4": "Tony"}
for i in dic.values():
a = i.strip()
if (a.startswith('a') or a.startswith('A')) and a.endswith('c'):
print (a)
3、输出商品列表,用户输入序号,显示用户选中的商品
商品 li = ["手机", "电脑", '鼠标垫', '游艇']
li = ["手机", "电脑", '鼠标垫', '游艇']
for i,k in enumerate(li,1):
print (i,k)
inp = int(input('请输入要购买的商品编号:'))
print (li[inp - 1])
4 、购物车
功能需求:
- 要求用户输入总资产,例如:2000
- 显示商品列表,让用户根据序号选择商品,加入购物车
- 购买,如果商品总额大于总资产,提示账户余额不足,否则,购买成功。
- 附加:可充值、某商品移除购物车
import time
goods = [
{"name": "电脑", "price": 1999},
{"name": "鼠标", "price": 10},
{"name": "游艇", "price": 20},
{"name": "美女", "price": 998},
]
other = ['继续购物','充值','查看购物车','删除商品','离开商城']
shop_list = []
chose = int(input('请输入您的工资:'))
while True:
print('序列','商品','价格')
for k,v in enumerate(goods,1):
print(k,('%s:%s元'%(v['name'],v['price'])))
inp_list =int(input('请输入您要购买的商品序列号:'))
a,b = goods[inp_list -1]['name'],goods[inp_list -1]['price']
if b < chose:
chose-=b
shop_list.append(a)
print('您够买的商品为:\033[32m[%s]\033[0m已经加入购物车,帐号剩余:\033[32m%s\033[0m元'%(a,chose))
for i,k in enumerate(other,1):
print(i,k)
choose = int(input('请输入您的选择:'))
if choose == 1:
continue
elif choose == 2:
up = int(input('请输入您充值多少钱:'))
chose +=up
for i,k in enumerate(other,1):
print(i,k)
choose = int(input('请输入您的选择:'))
elif choose == 3:
for i,k in enumerate(shop_list,1):
print('\033[34m%s.%s\033[0m'%(i,k))
print('2秒后返回商城'.center(50,'-'))
time.sleep(2)
elif choose == 4:
for i,k in enumerate(shop_list,1):
print('\033[34m%s.%s\033[0m'%(i,k))
sp = int(input('请输入您要删除的商品编号:'))
sp-=1
shop_list.remove(shop_list[sp])
print ('您已经删除商品:\033[32m[%s]\033[0m'%(k))
chose+=b
print('钱已经返回账户,余额为:\033[35m[%s元]\033[0m'%(chose))
print('2秒后返回商城')
time.sleep(2)
elif choose ==5:
print('您购买的商品如下:\033[35m%s\n\033[0m还剩人民币:\033[35m%s元\033[0m'%(shop_list,chose))
break
else:
print('\033[31m 您的余额不足请充值 \033[0m')
print('充值请输入1,退出请按2:')
choose = int(input('请输入您的选择:'))
if choose ==1:
up = int(input('请输入您充值多少钱:'))
chose +=up
elif choose ==2:
print('您购买的商品如下:\033[35m%s\033[0m还剩人民币:\033[35m%s元\033[0m'%(shop_list,chose))
break
5、用户交互,显示省市县三级联动的选择
dic = {
"河北": {
"石家庄": ["鹿泉", "藁城", "元氏"],
"邯郸": ["永年", "涉县", "磁县"],
},
"河南": {
"郑州市":["中原区", "二七区", "管城区", "金水区", "上街区", "惠济区", "巩义市"],
"开封市":["鼓楼区", "龙亭区", "顺河区", "禹王台", "金明区", "杞 县", "通许县", "尉氏县"],
},
"山西": {
"大同市":["城区","矿区","南郊区","新荣区"],
"晋中市":["榆次区","左权县","太谷县"],
}
}
法一:
#/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
flag = True
while flag:
Provinces = []
city = []
counties = []
while flag:
for k,v in enumerate(dic,1):
print(k,v)
Provinces.append(v)
Pro_inp = int(input('请输入省份的编号:'))
print('您当前所在的位置为:%s'%(Provinces[Pro_inp -1]))
#-----------------------------------------------------
while flag:
for a,b in enumerate(dic[Provinces[Pro_inp -1]],1):
print(a,b)
city.append(b)
city_inp = int(input('请输入城市的编号:'))
if city_inp > a or city_inp == 0:
continue
print('您当前所在的位置为:%s'%(city[city_inp - 1]))
#---------------------------------------------------
while flag:
inp = input("b 返回上一级\nn 继续\nq 退出\n请输入你的选择:")
if inp == "q" or inp == "b" or inp == "n":
break
else:
print("输入错误,请重新输入!")
continue
if inp == 'b':
continue
elif inp =='q':
flag=False
continue
while flag:
for c ,d in enumerate(dic[Provinces[Pro_inp -1]][city[city_inp -1]],1):
print(c,d)
counties.append(d)
coun_inp = int(input('请输入城市的编号:'))
if city_inp > a or city_inp == 0:
continue
print('您当前所在的位置为:%s'%(counties[coun_inp - 1]))
while flag:
inp = input("b 返回上一级\nq 退出\n请输入你的选择:")
if inp == "q" or inp == "b" :
break
else:
print("输入错误,请重新输入!")
continue
if inp =='q':
flag=False
break
elif inp =='b':
continue
法二:
print('欢迎进入行政区划查询系统:')
for i in dic.keys():
print (i)
flag = True
while flag:
inp = input('请输入省份:')
for x in dic.keys():
if x ==inp:
for a in dic[inp]:
print(a)
inp_c = input('请输入市:')
for b in dic[inp][inp_c]:
print(b)
inp_d = input('请输入县:')
for d in dic[inp][inp_c]:
if inp_d ==d:
print('您当前所在的位置:\033[31m%s(省)-->%s(市)-->%s(县)\033[0m'%(inp,inp_c,inp_d))
print('退出请按:1')
int_inp = int(input('请选择:'))
if int_inp =='1':
continue
flag =False



