5.1 Lua执行过程概述
脚本语言处理代码生成字节码,让虚拟机执行。硬件平台的差异由虚拟机解决,因此相同的代码可以运行在不同的操作系统、硬件平台上。
Lua是基于寄存器虚拟机的编程语言,这里的寄存器并不是物理意义上的寄存器,而是某个物理内存地址。
相比于基于栈的虚拟机,Lua只需一条指令即可执行加减乘除等操作,不需要PUSH和POP操作,因此更加高效,但缺点是程序需要关注操作数的位置。
// lauxlib.c:111 // lual_loadfile 函数用于进行词法和语法分析以生成字节码, // lua_pcall 字节码放到虚拟机中执行 #define luaL_dofile(L, fn) \ (luaL_loadfile(L, fn) || lua_pcall(L, 0, LUA_MULTRET, 0)) // ldo.c:490 // luaL_loadfile -> lua_load -> luaD_protectedparser -> f_parser // f_parser : 生成 Proto 并将其压入栈中 static void f_parser (lua_State *L, void *ud) { struct SParser *p = cast(struct SParser *, ud); int c = luaZ_lookahead(p->z); luaC_checkGC(L); Proto *tf = ((c == LUA_SIGNATURE[0]) ? luaU_undump : luaY_parser) (L, p->z,&p->buff, p->name); Closure * cl = luaF_newLclosure(L, tf->nups, hvalue(gt(L))); cl->l.p = tf; // 将生成的 Proto (含有字节码等相关数据) 绑定到 Closure 上 for (int i = 0; i < tf->nups; i++) /* initialize eventual upvalues */ cl->l.upvals[i] = luaF_newupval(L); setclvalue(L, L->top, cl); //压入栈中 incr_top(L); } // lapi.c:805 // lua_pcall -> luaD_pcall -> luaD_rawrunprotected -> f_call -> luaD_call -> luaV_execute LUA_API int lua_pcall (lua_State *L, int nargs, int nresults, int errfunc) { // struct CallS c; ...... c.func = L->top - (nargs+1); /* function to be called:由 f_parser 最后两行得到 */ c.nresults = nresults; int status = luaD_pcall(L, f_call, &c, savestack(L, c.func), func); adjustresults(L, nresults); lua_unlock(L); return status; } // ldo.c:455 // lua_pcall -> luaD_pcall -> luaD_rawrunprotected -> f_call -> luaD_call -> luaV_execute int luaD_pcall (lua_State *L, Pfunc func, void *u, ptrdiff_t old_top, ptrdiff_t ef) { // ...... int status = luaD_rawrunprotected(L, func, u); // ...... } // ldo.c:111 // lua_pcall -> luaD_pcall -> luaD_rawrunprotected -> f_call -> luaD_call -> luaV_execute int luaD_rawrunprotected (lua_State *L, Pfunc f, void *ud) { struct lua_longjmp lj; lj.status = 0; lj.previous = L->errorJmp; /* chain new error handler */ L->errorJmp = &lj; LUAI_TRY(L, &lj, (*f)(L, ud); // f: f_call ); L->errorJmp = lj.previous; /* restore old error handler */ return lj.status; } // lapi.c:798 // lua_pcall -> luaD_pcall -> luaD_rawrunprotected -> f_call -> luaD_call -> luaV_execute static void f_call (lua_State *L, void *ud) { struct CallS *c = cast(struct CallS *, ud); luaD_call(L, c->func, c->nresults); } /* ** Call a function (C or Lua). The function to be called is at *func. ** The arguments are on the stack, right after the function. ** When returns, all the results are on the stack, starting at the original ** function position. */ // ldo.c:369 // lua_pcall -> luaD_pcall -> luaD_rawrunprotected -> f_call -> luaD_call -> luaV_execute void luaD_call (lua_State *L, StkId func, int nResults) { // ...... if (luaD_precall(L, func, nResults) == PCRLUA) /* is a Lua function? */ luaV_execute(L, 1); /* call it */ L->nCcalls--; luaC_checkGC(L); } // ldo.c:264 // lua_pcall -> luaD_pcall -> luaD_rawrunprotected -> f_call -> luaD_call -> luaV_execute // luaD_precall 为 luaV_execute 做准备工作 // 从 lua_State 的 CallInfo 数组中得到一个新的 CallInfo 结构体,设置它的 func、base、top 指针 int luaD_precall (lua_State *L, StkId func, int nresults) { // ...... LClosure *cl = &clvalue(func)->l; L->ci->savedpc = L->savedpc; if (!cl->isC) { /* Lua function? prepare its call */ StkId base; Proto *p = cl->p; // ...... CallInfo *ci = inc_ci(L); /* now 'enter' new function */ ci->func = func; L->base = ci->base = base; ci->top = L->base + p->maxstacksize; lua_assert(ci->top <= L->stack_last); L->savedpc = p->code; /* starting point, code 即为字节码 */ ci->tailcalls = 0; ci->nresults = nresults; for (StkId st = L->top; st < ci->top; st++) // 多余的未传入的参数置为 nil setnilvalue(st); L->top = ci->top; // ...... return PCRLUA; } else { /* if is a C function, call it */ // ...... } } // lvm.c:373 // lua_pcall -> luaD_pcall -> luaD_rawrunprotected -> f_call -> luaD_call -> luaV_execute void luaV_execute (lua_State *L, int nexeccalls) { LClosure *cl; StkId base; TValue *k; const Instruction *pc; reentry: /* entry point */ lua_assert(isLua(L->ci)); pc = L->savedpc; cl = &clvalue(L->ci->func)->l; base = L->base; k = cl->p->k; /* main loop of interpreter */ for (;;) { const Instruction i = *pc++; StkId ra; if ((L->hookmask & (LUA_MASKLINE | LUA_MASKCOUNT)) && (--L->hookcount == 0 || L->hookmask & LUA_MASKLINE)) { traceexec(L, pc); if (L->status == LUA_YIELD) { /* did hook yield? */ L->savedpc = pc - 1; return; } base = L->base; } /* warning!! several calls may realloc the stack and invalidate `ra' */ ra = RA(i); lua_assert(base == L->base && L->base == L->ci->base); lua_assert(base <= L->top && L->top <= L->stack + L->stacksize); lua_assert(L->top == L->ci->top || luaG_checkopenop(i)); //这里是各种字节码处理流程 switch (GET_OPCODE(i)) { case OP_MOVE: { setobjs2s(L, ra, RB(i)); continue; } // ...... // ldo.c:342 // 最后,执行完毕后, 还会调用 luaD_poscall 函数恢复到上一次函数调用的环境: int luaD_poscall (lua_State *L, StkId firstResult) { if (L->hookmask & LUA_MASKRET) firstResult = callrethooks(L, firstResult); CallInfo *ci = L->ci--; StkId res = ci->func; /* res == final position of 1st result */ int wanted = ci->nresults; L->base = (ci - 1)->base; /* restore base */ L->savedpc = (ci - 1)->savedpc; /* restore savedpc */ /* move results to correct place */ for (int i = wanted; i != 0 && firstResult < L->top; i--) setobjs2s(L, res++, firstResult++); while (i-- > 0) setnilvalue(res++); L->top = res; return (wanted - LUA_MULTRET); /* 0 iff wanted == LUA_MULTRET */ }
Proto是分析阶段的产物,会有许多数据结构辅助生成Proto。luaY_parser -> Proto -> luaV_execute
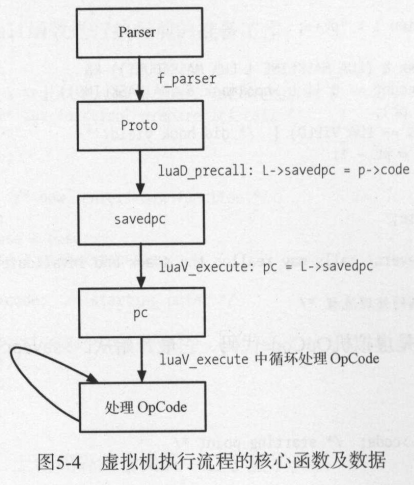
5.2 数据结构与栈
每个虚拟机对应一个lua_State结构体,它使用TValue数组来模拟栈。
lua_State中有CallInfo base_ci[](大小是有限的),ci 则指向当前函数的CallInfo指针。
在调用函数之前,一般会调用 luaD_precall 函数,它主要完成如下几个操作 。
(1) 保存当前虚拟机执行的指令 savedpc 到ci->savedpc中 。 此处保存下来是为了后面调用完毕之后恢复执行。
(2) 分别计算出待调用函数的 base 、 top值,这些值的计算依赖于函数的参数数量。
(3) 从 lua_State 的 base_ci 数组中分配一个新的CallInfo指针,指向ci并切换到这个函数中准备调用。
lua_State结构体中的top和 base指针始终指向当前执行函数的对应位置。
5.3 指令的解析
--fsl local function a() -- fsa local function b() -- fsb end end


5.4 指令格式
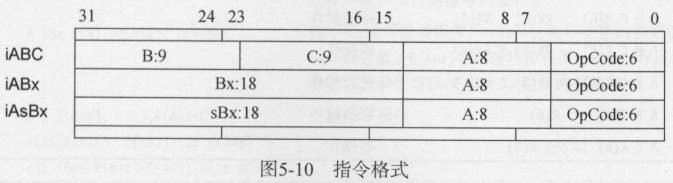
lopcodes.h定义了指令格式和读写的宏
/* ** size and position of opcode arguments. */ #define SIZE_C 9 #define SIZE_B 9 #define SIZE_Bx (SIZE_C + SIZE_B) #define SIZE_A 8 #define SIZE_OP 6 #define POS_OP 0 #define POS_A (POS_OP + SIZE_OP) #define POS_C (POS_A + SIZE_A) #define POS_B (POS_C + SIZE_C) #define POS_Bx POS_C #define GET_OPCODE(i) (cast(OpCode, ((i)>>POS_OP) & MASK1(SIZE_OP,0))) #define SET_OPCODE(i,o) ((i) = (((i)&MASK0(SIZE_OP,POS_OP)) | \ ((cast(Instruction, o)<<POS_OP)&MASK1(SIZE_OP,POS_OP)))) #define GETARG_A(i) (cast(int, ((i)>>POS_A) & MASK1(SIZE_A,0))) #define SETARG_A(i,u) ((i) = (((i)&MASK0(SIZE_A,POS_A)) | \ ((cast(Instruction, u)<<POS_A)&MASK1(SIZE_A,POS_A)))) #define GETARG_B(i) (cast(int, ((i)>>POS_B) & MASK1(SIZE_B,0))) #define SETARG_B(i,b) ((i) = (((i)&MASK0(SIZE_B,POS_B)) | \ ((cast(Instruction, b)<<POS_B)&MASK1(SIZE_B,POS_B)))) #define GETARG_C(i) (cast(int, ((i)>>POS_C) & MASK1(SIZE_C,0))) #define SETARG_C(i,b) ((i) = (((i)&MASK0(SIZE_C,POS_C)) | \ ((cast(Instruction, b)<<POS_C)&MASK1(SIZE_C,POS_C)))) #define GETARG_Bx(i) (cast(int, ((i)>>POS_Bx) & MASK1(SIZE_Bx,0))) #define SETARG_Bx(i,b) ((i) = (((i)&MASK0(SIZE_Bx,POS_Bx)) | \ ((cast(Instruction, b)<<POS_Bx)&MASK1(SIZE_Bx,POS_Bx)))) #define GETARG_sBx(i) (GETARG_Bx(i)-MAXARG_sBx) #define SETARG_sBx(i,b) SETARG_Bx((i),cast(unsigned int, (b)+MAXARG_sBx))
lopcodes.c定义了指令格式和读写的宏
const lu_byte luaP_opmodes[NUM_OPCODES] = { /* T A B C mode opcode */ opmode(0, 1, OpArgR, OpArgN, iABC) /* OP_MOVE */ ,opmode(0, 1, OpArgK, OpArgN, iABx) /* OP_LOADK */ ,opmode(0, 1, OpArgU, OpArgU, iABC) /* OP_LOADBOOL */ ,opmode(0, 1, OpArgR, OpArgN, iABC) /* OP_LOADNIL */
T: 是否是逻辑测试相关的指令,可能将pc指针自增1
A: 是否赋值给R(A)
B/C: B、C参数格式。
OpArgN:参数未使用。OpArgU:已使用参数。OpArgR:参数是寄存器或跳转偏移。OpArgK:参数是常量
mode: 这个OpCode的格式。
指令获取数据的宏(lvm.c)
/*** some macros for common tasks in `luaV_execute'*/ #define runtime_check(L, c) { if (!(c)) break; } #define RA(i) (base+GETARG_A(i)) /* to be used after possible stack reallocation */ #define RB(i) check_exp(getBMode(GET_OPCODE(i)) == OpArgR, base+GETARG_B(i)) #define RC(i) check_exp(getCMode(GET_OPCODE(i)) == OpArgR, base+GETARG_C(i)) #define RKB(i) check_exp(getBMode(GET_OPCODE(i)) == OpArgK, \ ISK(GETARG_B(i)) ? k+INDEXK(GETARG_B(i)) : base+GETARG_B(i)) #define RKC(i) check_exp(getCMode(GET_OPCODE(i)) == OpArgK, \ ISK(GETARG_C(i)) ? k+INDEXK(GETARG_C(i)) : base+GETARG_C(i)) #define KBx(i) check_exp(getBMode(GET_OPCODE(i)) == OpArgK, k+GETARG_Bx(i))
循环执行指令(lvm.c)
void luaV_execute (lua_State *L, int nexeccalls) { LClosure *cl; StkId base; TValue *k; const Instruction *pc; reentry: /* entry point */ lua_assert(isLua(L->ci)); pc = L->savedpc; //保存当前指令的执行位置(即Proto的code成员变量) cl = &clvalue(L->ci->func)->l; //当前所在的函数环境 base = L->base; //当前函数环境的栈base地址 k = cl->p->k; //当前函数环境的常量数组 /* main loop of interpreter */ for (;;) {
5.6 调试工具
gdb断点关键函数:指令的生成luaK_code,指令的执行 luaV_execute
使用ChunkSpy(http://files.luaforge.net/releases/chunkspy/chunkspy/ChunkSpy-0.9.8)
直接使用会报错:
ChunkSpy.lua:1120: mismatch in size_t size (needs 4 but read 8)
需要将size_size_t = 4改为size_size_t = 8
[yoyu@localhost api]$ lua -v Lua 5.1.4 Copyright (C) 1994-2008 Lua.org, PUC-Rio [yoyu@localhost api]$ lua ChunkSpy.lua --source c_call_lua/a.lua --brief ; source chunk: c_call_lua/a.lua ; x86 standard (32-bit, little endian, doubles) ; function [0] definition (level 1) ; 0 upvalues, 0 params, 2 stacks .function 0 0 2 2 .local "a" ; 0 .const 1 ; 0 [1] loadk 0 0 ; 1 [2] return 0 1 ; end of function [yoyu@localhost api]$ cat c_call_lua/a.lua local a = 1 [yoyu@localhost api]$
; 注释
. 数据类型的定义
[数字] OpCode

