Deep learning:十四(Softmax Regression练习)
Deep learning:十四(Softmax Regression练习)
前言:
这篇文章主要是用来练习softmax regression在多分类器中的应用,关于该部分的理论知识已经在前面的博文中Deep learning:十三(Softmax Regression)有所介绍。本次的实验内容是参考网页:http://deeplearning.stanford.edu/wiki/index.php/Exercise:Softmax_Regression。主要完成的是手写数字识别,采用的是MNIST手写数字数据库,其中训练样本有6万个,测试样本有1万个,且数字是0~9这10个。每个样本是一张小图片,大小为28*28的。
实验环境:matlab2012a
实验基础:
这次实验只用了softmax模型,也就是说没有隐含层,而只有输入层和输出层,因为实验中并没有提取出MINST样本的特征,而是直接用的原始像素特征。实验中主要是计算系统的损失函数和其偏导数,其计算公式如下所示:

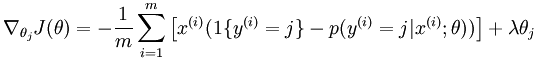
一些matlab函数:
sparse:
生成一个稀疏矩阵,比如说sparse(A, B, k),,其中A和B是个向量,k是个常量。这里生成的稀疏矩阵的值都为参数k,稀疏矩阵位置值坐标点有A和B相应的位置点值构成。
full:
生成一个正常矩阵,一般都是利用稀疏矩阵来还原的。
实验错误:
按照作者给的starter code,结果连数据都加载不下来,出现如下错误提示:Error using permute Out of memory. Type HELP MEMORY for your options. 结果跟踪定位到loadMNISTImages.m文件中的images = permute(images,[2 1 3])这句代码,究其原因就是说images矩阵过大,在有限内存下不能够将其进行维度旋转变换。可是这个数据已经很小了,才几十兆而已,参考了很多out of memory的方法都不管用,后面直接把改句的前面一句代码images = reshape(images, numCols, numRows, numImages);改成images = reshape(images, numRows, numCols, numImages);反正实现的效果都是一样的。因为原因是内存问题,所以要么用64bit的matlab,要买自己对该函数去优化下,节省运行过程中的内存。
实验结果:
Accuracy: 92.640%
和网页教程中给的结果非常相近了。
实验主要部分代码:
softmaxExercise.m:
%% CS294A/CS294W Softmax Exercise
% Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the
% softmax exercise. You will need to write the softmax cost function
% in softmaxCost.m and the softmax prediction function in softmaxPred.m.
% For this exercise, you will not need to change any code in this file,
% or any other files other than those mentioned above.
% (However, you may be required to do so in later exercises)
%%======================================================================
%% STEP 0: Initialise constants and parameters
%
% Here we define and initialise some constants which allow your code
% to be used more generally on any arbitrary input.
% We also initialise some parameters used for tuning the model.
inputSize = 28 * 28; % Size of input vector (MNIST images are 28x28)
numClasses = 10; % Number of classes (MNIST images fall into 10 classes)
lambda = 1e-4; % Weight decay parameter
%%======================================================================
%% STEP 1: Load data
%
% In this section, we load the input and output data.
% For softmax regression on MNIST pixels,
% the input data is the images, and
% the output data is the labels.
%
% Change the filenames if you've saved the files under different names
% On some platforms, the files might be saved as
% train-images.idx3-ubyte / train-labels.idx1-ubyte
images = loadMNISTImages('train-images.idx3-ubyte');
labels = loadMNISTLabels('train-labels.idx1-ubyte');
labels(labels==0) = 10; % Remap 0 to 10
inputData = images;
% For debugging purposes, you may wish to reduce the size of the input data
% in order to speed up gradient checking.
% Here, we create synthetic dataset using random data for testing
% DEBUG = true; % Set DEBUG to true when debugging.
DEBUG = false;
if DEBUG
inputSize = 8;
inputData = randn(8, 100);
labels = randi(10, 100, 1);
end
% Randomly initialise theta
theta = 0.005 * randn(numClasses * inputSize, 1);%输入的是一个列向量
%%======================================================================
%% STEP 2: Implement softmaxCost
%
% Implement softmaxCost in softmaxCost.m.
[cost, grad] = softmaxCost(theta, numClasses, inputSize, lambda, inputData, labels);
%%======================================================================
%% STEP 3: Gradient checking
%
% As with any learning algorithm, you should always check that your
% gradients are correct before learning the parameters.
%
if DEBUG
numGrad = computeNumericalGradient( @(x) softmaxCost(x, numClasses, ...
inputSize, lambda, inputData, labels), theta);
% Use this to visually compare the gradients side by side
disp([numGrad grad]);
% Compare numerically computed gradients with those computed analytically
diff = norm(numGrad-grad)/norm(numGrad+grad);
disp(diff);
% The difference should be small.
% In our implementation, these values are usually less than 1e-7.
% When your gradients are correct, congratulations!
end
%%======================================================================
%% STEP 4: Learning parameters
%
% Once you have verified that your gradients are correct,
% you can start training your softmax regression code using softmaxTrain
% (which uses minFunc).
options.maxIter = 100;
%softmaxModel其实只是一个结构体,里面包含了学习到的最优参数以及输入尺寸大小和类别个数信息
softmaxModel = softmaxTrain(inputSize, numClasses, lambda, ...
inputData, labels, options);
% Although we only use 100 iterations here to train a classifier for the
% MNIST data set, in practice, training for more iterations is usually
% beneficial.
%%======================================================================
%% STEP 5: Testing
%
% You should now test your model against the test images.
% To do this, you will first need to write softmaxPredict
% (in softmaxPredict.m), which should return predictions
% given a softmax model and the input data.
images = loadMNISTImages('t10k-images.idx3-ubyte');
labels = loadMNISTLabels('t10k-labels.idx1-ubyte');
labels(labels==0) = 10; % Remap 0 to 10
inputData = images;
size(softmaxModel.optTheta)
size(inputData)
% You will have to implement softmaxPredict in softmaxPredict.m
[pred] = softmaxPredict(softmaxModel, inputData);
acc = mean(labels(:) == pred(:));
fprintf('Accuracy: %0.3f%%\n', acc * 100);
% Accuracy is the proportion of correctly classified images
% After 100 iterations, the results for our implementation were:
%
% Accuracy: 92.200%
%
% If your values are too low (accuracy less than 0.91), you should check
% your code for errors, and make sure you are training on the
% entire data set of 60000 28x28 training images
% (unless you modified the loading code, this should be the case)
softmaxCost.m
function [cost, grad] = softmaxCost(theta, numClasses, inputSize, lambda, data, labels)
% numClasses - the number of classes
% inputSize - the size N of the input vector
% lambda - weight decay parameter
% data - the N x M input matrix, where each column data(:, i) corresponds to
% a single test set
% labels - an M x 1 matrix containing the labels corresponding for the input data
%
% Unroll the parameters from theta
theta = reshape(theta, numClasses, inputSize);%将输入的参数列向量变成一个矩阵
numCases = size(data, 2);%输入样本的个数
groundTruth = full(sparse(labels, 1:numCases, 1));%这里sparse是生成一个稀疏矩阵,该矩阵中的值都是第三个值1
%稀疏矩阵的小标由labels和1:numCases对应值构成
cost = 0;
thetagrad = zeros(numClasses, inputSize);
%% ---------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------------------------
% Instructions: Compute the cost and gradient for softmax regression.
% You need to compute thetagrad and cost.
% The groundTruth matrix might come in handy.
M = bsxfun(@minus,theta*data,max(theta*data, [], 1));
M = exp(M);
p = bsxfun(@rdivide, M, sum(M));
cost = -1/numCases * groundTruth(:)' * log(p(:)) + lambda/2 * sum(theta(:) .^ 2);
thetagrad = -1/numCases * (groundTruth - p) * data' + lambda * theta;
% ------------------------------------------------------------------
% Unroll the gradient matrices into a vector for minFunc
grad = [thetagrad(:)];
end
softmaxTrain.m:
function [softmaxModel] = softmaxTrain(inputSize, numClasses, lambda, inputData, labels, options)
%softmaxTrain Train a softmax model with the given parameters on the given
% data. Returns softmaxOptTheta, a vector containing the trained parameters
% for the model.
%
% inputSize: the size of an input vector x^(i)
% numClasses: the number of classes
% lambda: weight decay parameter
% inputData: an N by M matrix containing the input data, such that
% inputData(:, c) is the cth input
% labels: M by 1 matrix containing the class labels for the
% corresponding inputs. labels(c) is the class label for
% the cth input
% options (optional): options
% options.maxIter: number of iterations to train for
if ~exist('options', 'var')
options = struct;
end
if ~isfield(options, 'maxIter')
options.maxIter = 400;
end
% initialize parameters
theta = 0.005 * randn(numClasses * inputSize, 1);
% Use minFunc to minimize the function
addpath minFunc/
options.Method = 'lbfgs'; % Here, we use L-BFGS to optimize our cost
% function. Generally, for minFunc to work, you
% need a function pointer with two outputs: the
% function value and the gradient. In our problem,
% softmaxCost.m satisfies this.
minFuncOptions.display = 'on';
[softmaxOptTheta, cost] = minFunc( @(p) softmaxCost(p, ...
numClasses, inputSize, lambda, ...
inputData, labels), ...
theta, options);
% Fold softmaxOptTheta into a nicer format
softmaxModel.optTheta = reshape(softmaxOptTheta, numClasses, inputSize);
softmaxModel.inputSize = inputSize;
softmaxModel.numClasses = numClasses;
end
softmaxPredict.m:
function [pred] = softmaxPredict(softmaxModel, data) % softmaxModel - model trained using softmaxTrain % data - the N x M input matrix, where each column data(:, i) corresponds to % a single test set % % Your code should produce the prediction matrix % pred, where pred(i) is argmax_c P(y(c) | x(i)). % Unroll the parameters from theta theta = softmaxModel.optTheta; % this provides a numClasses x inputSize matrix pred = zeros(1, size(data, 2)); %% ---------- YOUR CODE HERE -------------------------------------- % Instructions: Compute pred using theta assuming that the labels start % from 1. [nop, pred] = max(theta * data); % pred= max(peed_temp); % --------------------------------------------------------------------- end
参考资料:
Deep learning:十三(Softmax Regression)
http://deeplearning.stanford.edu/wiki/index.php/Exercise:Softmax_Regression






