LLFormer
LLFormer
1、rearrange:重塑形状
大佬链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/594012790
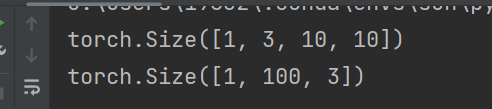
import torch import torch.nn.functional as F from einops import rearrange input = torch.randn(1,3,10,10) print(input.shape) x = rearrange(input, 'b c h w -> b (h w) c') print(x.shape)
2、.var 返回给定维度 dim 中 input 张量的每一行的方差
torch.var(input, dim, unbiased=True, keepdim=False, *, out=None) → Tensor
大佬链接:PyTorch - torch.var 返回输入张量中所有元素的方差。 (runebook.dev)
3、pytorch 中 torch.optim.Adam 方法的使用和参数的解释

大佬链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Ibelievesunshine/article/details/99624645
4、normalize
大佬链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41356707/article/details/121809012
# normalize将某一个维度除以那个维度对应的范数 q = F.normalize(q, dim=-1)
import torch.nn.functional as F F.normalize(input: Tensor, p: float = 2.0, dim: int = 1) -> Tensor input: 是一个任意维度的Tensor类型的数据 p:默认为2,表示2范数;同理,p=1表示1范数 dim:(后面我会总结,先这样解释,方便大家理解,看完例子再看我总结的,会很清楚) 默认 dim=1,在输入数据input的shape是二维的且p=2情况下,表示对行进行操作,即所有元素除以第一行元素的根号下平方和; dim=0 时,在输入数据input的shape是二维的且p=2情况下,表示对列进行操作,即所有元素除以第一列元素的根号下平方和; dim=2 时,我们通过例子分析... normalize的参数不止这三个,其他的可以参考官方文档。
5、unsqueeze在dim= * 的地方升一个维度,squeeze降维(只降维度为1的维度)
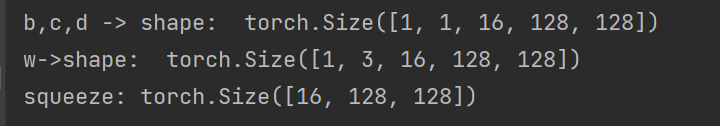
import torch import torch.nn.functional as F import einops a = torch.randn(1,16,128,128) # unsqueeze 扩展维度 b = a.unsqueeze(1) c = a.unsqueeze(1) d = a.unsqueeze(1) print('b,c,d -> shape: ',b.shape) w = torch.cat([b,c,d],dim=1) print('w->shape: ',w.shape) input = torch.randn(1,1,16,128,128) output = torch.squeeze(input) print('squeeze:', output.shape)
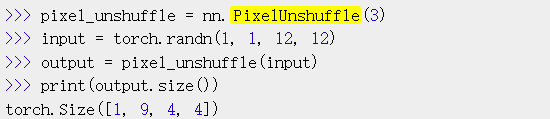
6、class torch.nn.PixelUnshuffle(downscale_factor)

对应的PixelShuffle
import torch import torch.nn.functional as F import einops import torch.nn as nn a = torch.randn(1,16,128,128) class Downsample(nn.Module): def __init__(self, n_feat): super(Downsample, self).__init__() self.con1 = nn.Conv2d(n_feat, n_feat // 2, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False) self.pi = nn.PixelShuffle(2) # self.body = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(n_feat, n_feat // 2, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False), nn.PixelUnshuffle(2)) def forward(self, x): print(x.shape) x = self.con1(x) print(x.shape) y = self.pi(x) print(y.shape) # return self.body(x) down = Downsample(16) b = down(a)
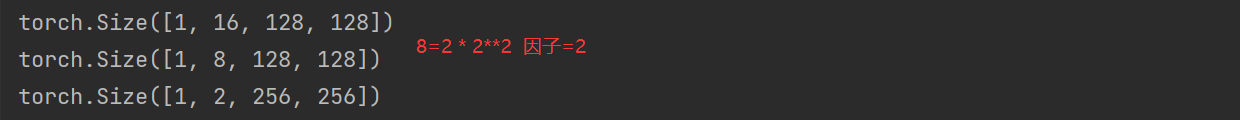
7、torch.cat
import torch # 随机产生一个两行三列的tensor a = torch.randn(2,3) b = torch.randn(2,3) print(a) print(b) # dim = 0 按照列拼接a,b dim=1按照行拼接a,b c = torch.cat((a, b),dim=0) print(c)
dim = 0
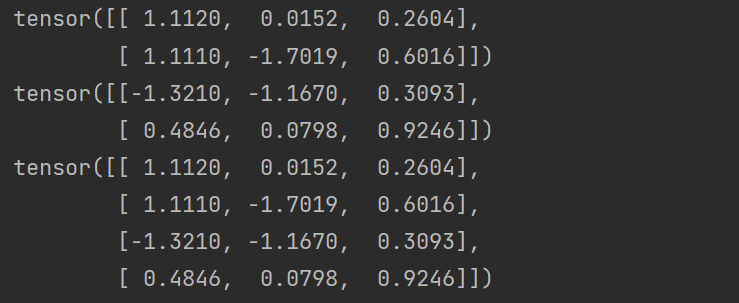
dim = 1

8、F.interpolate插值
大佬链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_50001789/article/details/120297401
torch.nn.functional.interpolate(input, size=None, scale_factor=None, mode='nearest', align_corners=None, recompute_scale_factor=None)


import torch.nn.functional as F import torch a=torch.arange(1*2*2*3,dtype=torch.float32).reshape(1,2,2,3) b=F.interpolate(a,scale_factor=2,mode='nearest') c=F.interpolate(a,scale_factor=2,mode='bilinear') print('原数组:',a) print('mode=nearest',b) print('mode=bilinear:',c)
结果:
原数组尺寸: tensor([[[[ 0., 1., 2.], [ 3., 4., 5.]], [[ 6., 7., 8.], [ 9., 10., 11.]]]]) size采样尺寸: tensor([[[[ 0., 0., 1., 1., 2., 2.], [ 0., 0., 1., 1., 2., 2.], [ 3., 3., 4., 4., 5., 5.], [ 3., 3., 4., 4., 5., 5.]], [[ 6., 6., 7., 7., 8., 8.], [ 6., 6., 7., 7., 8., 8.], [ 9., 9., 10., 10., 11., 11.], [ 9., 9., 10., 10., 11., 11.]]]]) scale_factor采样尺寸: tensor([[[[ 0.0000, 0.2500, 0.7500, 1.2500, 1.7500, 2.0000], [ 0.7500, 1.0000, 1.5000, 2.0000, 2.5000, 2.7500], [ 2.2500, 2.5000, 3.0000, 3.5000, 4.0000, 4.2500], [ 3.0000, 3.2500, 3.7500, 4.2500, 4.7500, 5.0000]], [[ 6.0000, 6.2500, 6.7500, 7.2500, 7.7500, 8.0000], [ 6.7500, 7.0000, 7.5000, 8.0000, 8.5000, 8.7500], [ 8.2500, 8.5000, 9.0000, 9.5000, 10.0000, 10.2500], [ 9.0000, 9.2500, 9.7500, 10.2500, 10.7500, 11.0000]]]])
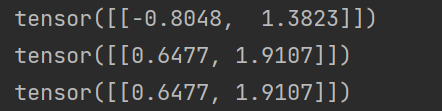
9、torch.pow(x, y) 返回x的y次方:对输入的每分量求幂次运算
大佬链接:https://blog.csdn.net/March_A/article/details/128717443
import torch x = torch.randn(1,2) print(x) y = torch.pow(x,2) print(y) z = x.pow_(2) print(z)





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号