poj 3744 Scout (Another) YYF I - 概率与期望 - 动态规划 - 矩阵快速幂
(Another) YYF is a couragous scout. Now he is on a dangerous mission which is to penetrate into the enemy's base. After overcoming a series difficulties, (Another) YYF is now at the start of enemy's famous "mine road". This is a very long road, on which there are numbers of mines. At first, (Another) YYF is at step one. For each step after that, (Another) YYF will walk one step with a probability of p, or jump two step with a probality of 1- p. Here is the task, given the place of each mine, please calculate the probality that (Another) YYF can go through the "mine road" safely.
Input
The input contains many test cases ended with EOF.
Each test case contains two lines.
The First line of each test case is N (1 ≤ N ≤ 10) and p (0.25 ≤ p ≤ 0.75) seperated by a single blank, standing for the number of mines and the probability to walk one step.
The Second line of each test case is N integer standing for the place of N mines. Each integer is in the range of [1, 100000000].
Each test case contains two lines.
The First line of each test case is N (1 ≤ N ≤ 10) and p (0.25 ≤ p ≤ 0.75) seperated by a single blank, standing for the number of mines and the probability to walk one step.
The Second line of each test case is N integer standing for the place of N mines. Each integer is in the range of [1, 100000000].
Output
For each test case, output the probabilty in a single line with the precision to 7 digits after the decimal point.
Sample Input
1 0.5 2 2 0.5 2 4
Sample Output
0.5000000 0.2500000
题目大意 另一个叫做yyf的人在一个数轴上,他在位置1,每次他有p的概率向右跳1格,有(1 - p)的概率向右跳2格,如果踩到地雷就死了,问生还的概率。
显然动态规划。当位置i没有地雷的时候,显然有
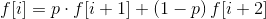
如果位置i有地雷,那么有

由于值域很大,所以按照递推式动态规划的通用套路:构建转移矩阵加快动态规划。
由于n很小,所以可以分段,段内用矩阵快速幂处理,然后特殊处理一下f[i],继续往前。
现在来构建转移矩阵:
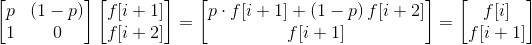
Code
1 /** 2 * poj 3 * Problem#3744 4 * Accepted 5 * Time: 0ms 6 * Memory: 232k 7 */ 8 #include <iostream> 9 #include <fstream> 10 #include <sstream> 11 #include <cstdio> 12 #include <cstdlib> 13 #include <cstring> 14 #include <cmath> 15 #include <ctime> 16 #include <cctype> 17 #include <algorithm> 18 #include <set> 19 #include <map> 20 #include <vector> 21 #include <queue> 22 #include <stack> 23 #include <bitset> 24 #include <cassert> 25 #ifndef WIN32 26 #define Auto "%lld" 27 #else 28 #define Auto "%I64d" 29 #endif 30 using namespace std; 31 typedef bool boolean; 32 #define clra(a) memset(a, false, sizeof(a)) 33 const signed int inf = ((~0u) >> 1); 34 #define smin(a, b) a = min(a, b) 35 #define smax(a, b) a = max(a, b) 36 37 template <typename T> 38 class Matrix { 39 public: 40 T a[2][2]; 41 int row; 42 int col; 43 44 Matrix() { } 45 Matrix(int row, int col):row(row), col(col) { } 46 47 Matrix<T> operator * (Matrix<T> b) { 48 Matrix<T> rt(row, b.col); 49 assert(col == b.row); 50 for(int i = 0; i < row; i++) 51 for(int j = 0; j < b.col; j++) { 52 rt[i][j] = 0; 53 for(int k = 0; k < col; k++) 54 rt[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j]; 55 } 56 return rt; 57 } 58 59 T* operator [] (int pos) { 60 return &a[pos][0]; 61 } 62 }; 63 64 int n; 65 double p; 66 Matrix<double> unit(2, 2); 67 Matrix<double> trans(2, 2); 68 int boom[15]; 69 70 template <typename T> 71 Matrix<T> matpow(Matrix<T>& a, int pos) { 72 if(pos == 0) return unit; 73 if(pos == 1) return a; 74 Matrix<T> temp = matpow(a, pos >> 1); 75 temp = temp * temp; 76 if(pos & 1) temp = temp * a; 77 return temp; 78 } 79 80 inline void prepare() { 81 unit[0][0] = unit[1][1] = 1; 82 unit[0][1] = unit[1][0] = 0; 83 } 84 85 inline void init() { 86 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 87 scanf("%d", boom + i); 88 sort(boom, boom + n); 89 trans[0][0] = p, trans[0][1] = 1 - p; 90 trans[1][0] = 1, trans[1][1] = 0; 91 } 92 93 inline void solve() { 94 int last = boom[n - 1]; 95 Matrix<double> f(2, 1); 96 f[0][0] = 0, f[1][0] = 1; 97 for(int i = n - 2; ~i; f[0][0] = 0, last = boom[i], i--) 98 f = matpow(trans, last - boom[i]) * f; 99 f = matpow(trans, last - 1) * f; 100 printf("%.7lf\n", f[0][0]); 101 } 102 103 int main() { 104 prepare(); 105 while(~scanf("%d%lf", &n, &p)) { //坑啊,scanf交G++ WA了,交C++过了 106 init(); 107 solve(); 108 } 109 return 0; 110 }

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号